Artificial intelligence researchers are building tools to quickly and accurately turn data into diagnoses. But practical limitations and ethical concerns mean humans should remain in charge.


In the world of things we already know.
MooDFOOD, the largest randomized clinical trial to study the effects of nutritional strategies on the prevention of major depressive disorder concludes that daily intake of nutritional supplements cannot prevent depression.
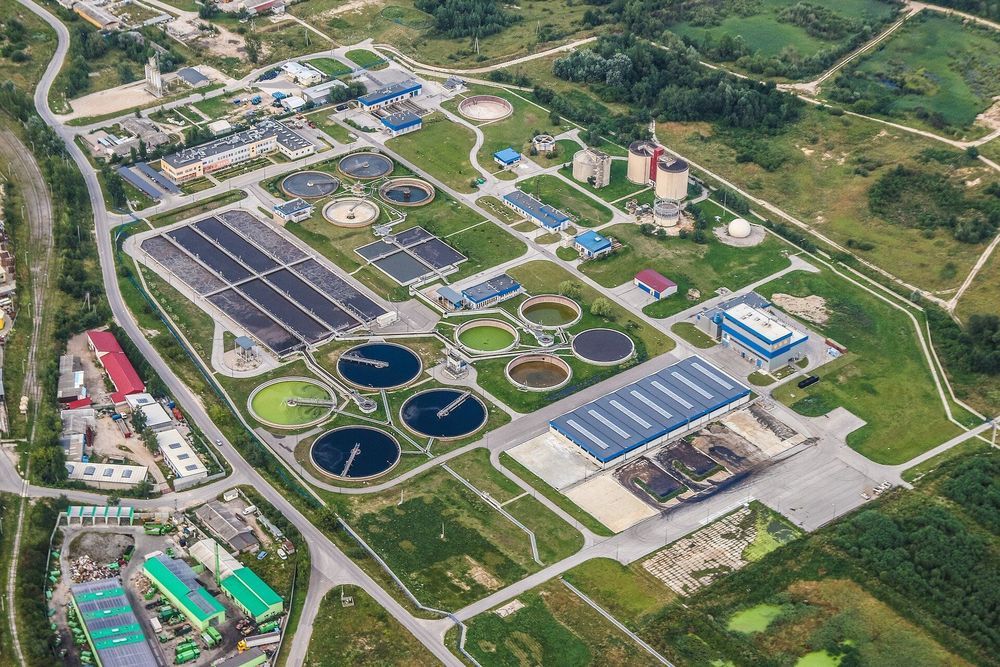

The products of wastewater treatment have been found to contain trace amounts of antibiotic resistant DNA. These products are often reintroduced to the environment and water supply, potentially resulting in the spread of antibiotic resistance. As such, researchers at the University of Southern California Viterbi School of Engineering have been studying the development of these potentially harmful and dangerous genes in wastewater treatment processes. Their findings, published in Environmental Science & Technology, indicate that even low concentrations of just a single type of antibiotic leads to resistance to multiple classes of antibiotics.
“We’re quickly getting to a scary place that’s called a “post-antibiotic world,” where we can no longer fight infections with antibiotics anymore because microbes have adapted to be resilient against those antibiotics,” said Adam Smith, assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering at USC and lead investigator of the study. “Unfortunately, engineered water treatment systems end up being sort of a hot-bed for antibiotic resistance.”
The majority of the antibiotics we consume are metabolized in our bodies. However, small amounts pass through us in our waste, which are then carried to wastewater treatment plants. At these plants, one of the common ways in which the wastewater is treated is with a membrane bioreactor, which uses both a filtration system and a biological process where microscopic bacteria consume waste products.
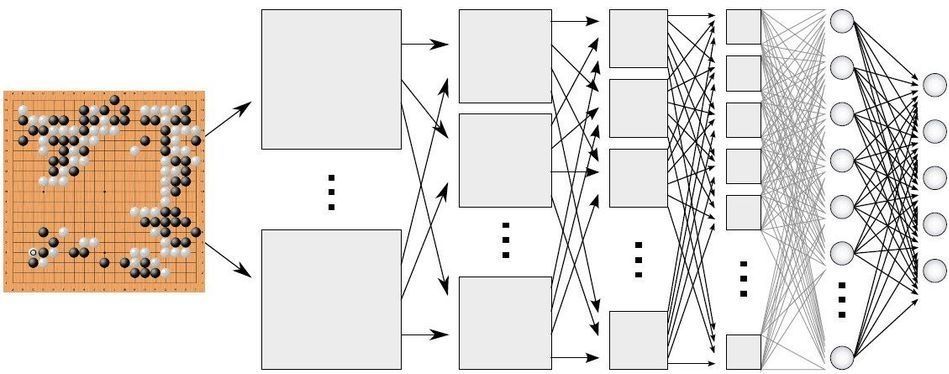
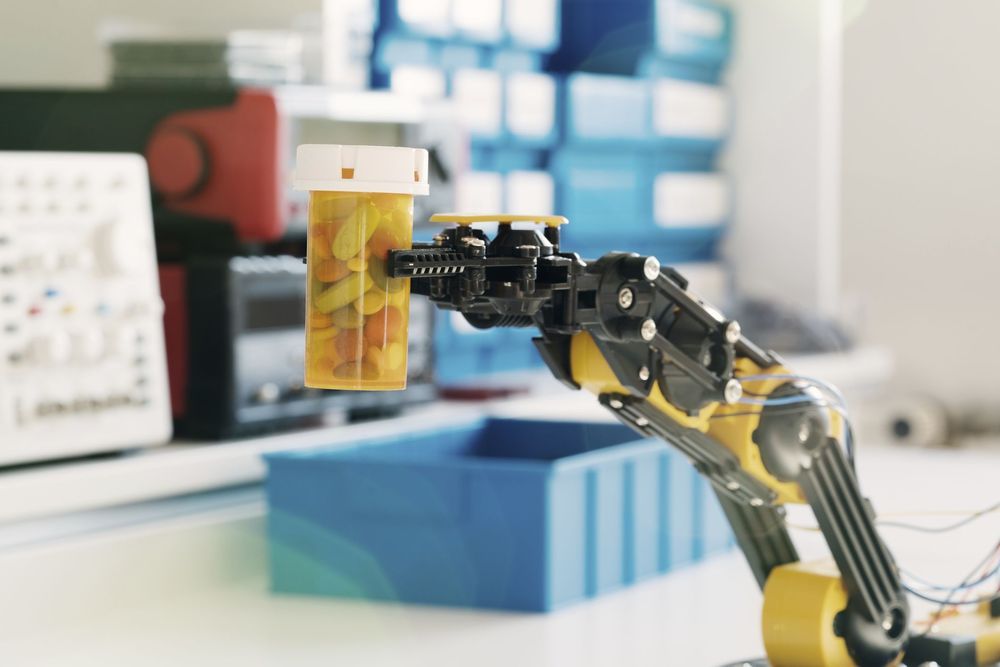
A startup called CogitAI has developed a platform that lets companies use reinforcement learning, the technique that gave AlphaGo mastery of the board game Go.
Gaining experience: AlphaGo, an AI program developed by DeepMind, taught itself to play Go by practicing. It’s practically impossible for a programmer to manually code in the best strategies for winning. Instead, reinforcement learning let the program figure out how to defeat the world’s best human players on its own.
Drug delivery: Reinforcement learning is still an experimental technology, but it is gaining a foothold in industry. DeepMind has talked of using it to optimize the performance of data centers and wind turbines. Amazon recently launched a reinforcement-learning platform, but it is aimed more at researchers and academics. CogitAI’s first commercial customers include those working in robotics for drug manufacturing. Its platform lets the robot figure out the optimal way to process drug orders.


(3D-printed heart scaffold)
As the head of the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign’s innovative Cancer Center, Bhargava has been plugging away at injecting more advanced engineering solutions into medical problems. The freeform 3D printer is one of the first futuristic achievements of that effort.
But Bhargava’s project is just one of a wave of technologies that stand to transform medicine and healthcare as we know it; to make them faster, more accurate, and hopefully, drastically more affordable. Microneedle patches, handheld diagnostic machines, and better sensing capabilities, as well as 3D bioprinting, are just a few of the technologies coming to a doctor’s office near you—or maybe even into your home—in the next decade.
Intel is creating blockchain-controlled robots with other members of the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance.

Samsara Therapeutics has completed a seed financing round in collaboration with Apollo Ventures, a venture capital company and biotech incubator that supports longevity research and treatments for age-related diseases.
Samsara Therapeutics, Inc. (“Samsara,”) a platform biotechnology startup engaged in the discovery and development of compounds that address the primary molecular causes of aging, announced today the closing of a seed financing round. The financing was led by Apollo Ventures, a life sciences venture capital firm and company builder working across Europe and North America.
Additionally, on February 19th, 2019 Nature Communications published a peer-reviewed paper, “The flavonoid 4,4′-dimethoxychalcone promotes autophagy-dependent longevity across species” authored by Samsara’s scientific team [1]. The paper demonstrates the capability of the Samsara platform to identify novel MoA geroprotective small molecules that extend healthy lifespan across species and which are protective in mammalian models of disease.
