New immunology research has discovered the cure to cancer was possibly within us all along.


Researchers at the Montpellier Cancer Research Institute (IRCM) have discovered a new component in blood that has never been detected there before. Mitochondria are normally found inside cells, but the team has now discovered them floating around on their own in the bloodstream.
Often referred to as the power houses of cells, mitochondria are organelles that play a key role in metabolizing energy and cell signaling. Occasionally they are found outside of cells, but usually only as fragments within platelets.
But after a seven-year study, an IRCM team has now found complete and fully-functioning mitochondria in blood plasma, contained inside highly-stable structures. Using electron microscopy, the researchers analyzed plasma samples from about 100 people, and found up to 3.7 million of these mitochondria-containing structures per milliliter of plasma.

CHICAGO/LONDON (Reuters) — When a newly organized vaccine research group at the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) met for the first time this week, its members had expected to be able to ease into their work. But their mandate is to conduct human trials for emerging health threats — and their first assignment came at shocking speed.
Corpses of coronavirus victims are being left unattended in a corridor of a hospital flooded with patients in Wuhan as the Chinese city is ravaged by the deadly infection, it has been revealed.
The chilling scene, captured by a woman who claims to be a nurse, was posted on the country’s social media network today but quickly censored.
Dozens of videos posted online appear show people lying in the street after collapsing where they stood as they walked through the streets of Wuhan.
Circa 2019 Event 201, hosted by the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, envisions a fast-spreading coronavirus with a devastating impact.
Back in 2001, it was a smallpox outbreak, set off by terrorists in U.S. shopping malls. This fall, it was a SARS-like virus, germinating quietly among pig farms in Brazil before spreading to every country in the world. With each fictional pandemic Johns Hopkins experts have designed, the takeaway lesson is the same: We are nowhere near prepared.
Event 201 simulation hosted by university’s Center for Health Security envisions a fast-spreading coronavirus with a devastating impact.

A new study has demonstrated that increasing the expression of a single gene was enough to reverse age-related visual decline in the eyes of old mice.
Introducing ELOVL2
Elongation of Very Long Chain Fatty Acids Protein 2 (ELOVL2) is both a bit of a tongue twister and a known aging biomarker. The results of a new study from researchers at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine suggest that the ELOVL2 gene plays a pivotal role in both the functional and anatomical aging of the retinas of mice and may also have relevance to human age-related eye conditions.

In a 24–10 vote, the House Judiciary Committee approved a bill that would effectively end marijuana prohibition on Wednesday. The Marijuana Opportunity Reinvestment and Expungement (MORE) Act of 2019, or H.R. 3884, was introduced by House Judiciary Committee Chairman Jerrold Nadler (D-NY) and currently has 55 co-sponsors. This is the first time that a congressional committee has approved a bill to make cannabis legal. The MORE Act would federally decriminalize cannabis by removing it from the Controlled Substances Act, and would require the expungement of past federal cannabis convictions.
The bill would also establish a Cannabis Justice Office to administer a program to reinvest resources in the communities that have been most detrimentally impacted by prohibition, funded by a 5% tax on state-legal cannabis commerce.
Moreover, it will allow the Small Business Administration to provide loans and grants to cannabis-related businesses and support state and local equity licensing programs, and would permit doctors within the Veterans Affairs system to recommend medical cannabis to patients in accordance with applicable state laws.
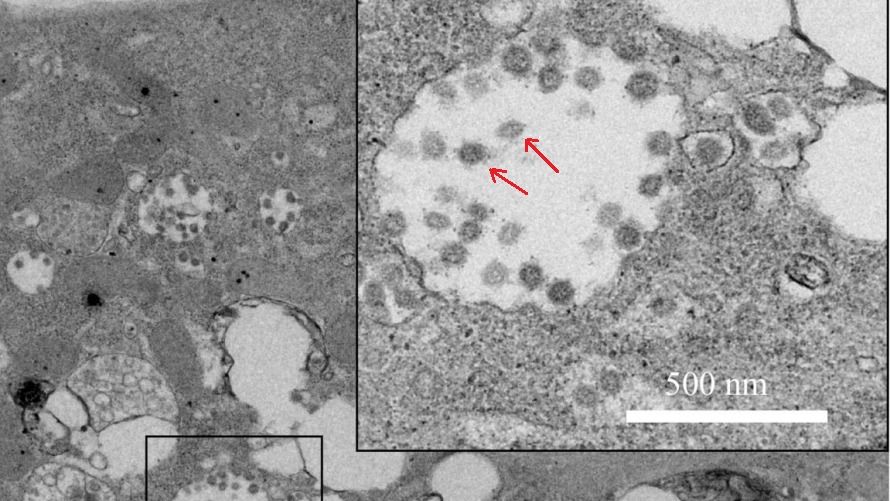
Researchers say the virus spreading through China is in the same family as SARS and closest to one found in bats. Discovery: Today, researchers led by Zheng-Li Shi at the Wuhan Institute for Virology posted a paper describing the virus in detail for the first time, including a picture of the virus infecting cells. The new virus, dubbed nCoV-2019, is in the same family as SARS—a coronavirus that caused global mayhem starting in 2003—and even uses the same receptor to hack into a person’s lung cells, Li’s team found.
Discovery: Today, researchers led by Zheng-Li Shi at the Wuhan Institute for Virology posted a paper describing the virus in detail for the first time, including a picture of the virus infecting cells.
Genomics and BioPharma Pioneer!! — On this ideaXme (http://radioideaxme.com/) episode, I had the honor of being joined by Dr. William Haseltine — biologist, entrepreneur and philanthropist, known for his groundbreaking work on HIV/AIDS and the human genome, now focusing on the issues of healthcare costs, dementia care, and aging — #Ideaxme #Genomics #RegenerativeMedicine #BillHaseltine #Dementia #Biotechnology #Harvard #JamesWatson #WalterGilbert #DavidBaltimore #MIT #CraigVenter #Health #Wellness #Regeneration #Longevity #Aging #IraPastor #Bioquark #Regenerage
Ira Pastor, ideaXme exponential health ambassador, interviews Dr. William Haseltine, American biologist, entrepreneur and philanthropist, known for his groundbreaking work on HIV/AIDS and the human genome.
Ira Pastor Comments:
On today’s show we have a thought leader who sits amongst a rare group of people who have been responsible for creating many aspects of the modern biopharma / genomics / regenerative medicine system as we know it today.
Probiotics are live microorganisms, usually bacteria, that can be consumed to offer health benefits.
The ability of certain microbes to confer health benefits on their host was recognized more than 100 years ago. In 1904, Elie Metchnikoff, a scientist at the Pasteur Institute, claimed that Bulgarian peasants lived longer by eating yogurt made from bacteria that served to ferment the milk. Parisians rushed out to buy yogurt in response.
However, the huge variety of bacteria living on the planet was not appreciated back then. More recently, the development of technology that identifies organisms from their DNA has allowed scientists to show that plants, animals, insects and humans can be hosts for many different types of microorganisms.