Covid-19 and facemasks.
According to WHO:
If you are healthy, you only need to wear a mask if you are taking care of a person with suspected 2019-nCoV infection.
Wear a mask if you are coughing or sneezing.
Covid-19 and facemasks.
According to WHO:
If you are healthy, you only need to wear a mask if you are taking care of a person with suspected 2019-nCoV infection.
Wear a mask if you are coughing or sneezing.
California-based biotech company Cepheid Inc reports that it has been granted FDA approval for a new rapid diagnostic test, able to detect the COVID-19 virus in just 45 minutes.
Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) have used Summit, the world’s fastest and most powerful supercomputer, to identify 77 small-molecule drug compounds that might warrant further study in the fight against the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus.
The team performed simulations of more than 8,000 compounds to screen for those that are most likely to bind to the main “spike” protein of the coronavirus, rendering it unable to infect host cells. They ranked compounds of interest that could have value in experimental studies of the virus.
Earlier this year, when Chinese researchers sequenced the virus, they discovered that it infects the body by one of the same mechanisms as Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), which spread to 26 countries during an epidemic in 2003. The similarity between the two virus structures and their entry point into a host cell facilitated this latest new study at ORNL.
MIT’s Open Source ventilator design submitted for fast-track FDA approval. #COVID19
In many parts of the world the COVID-19 pandemic is causing shortages in hospital space, staff, medical supplies, and equipment. Severe cases may require breathing support, but there are only so many ventilators available. With that in mind, MIT is working on FDA approval of an emergency ventilator system (E-Vent). They have submitted the design to the FDA for fast track review. The project is open source, so once they have approval the team will release all the data needed to replicate it.
The design is actually made simple by using something that is very common: a manual resuscitator. You have doubtlessly seen these on your favorite medical show. It is the bag someone squeezes while the main character struggles valiantly to save their patient. Of course, having someone sit and squeeze the bag for days on end for thousands of people isn’t very practical and that’s where they’ve included an Arduino-controlled motor to automate the process.

This movement towards a more automated society has some positives: it will help us stay healthy during times like the present, it will drive down the cost of goods and services, and it will grow our GDP in the long run. But by leaning into automation, will we be enabling a future that keeps us more physically, psychologically, and emotionally distant from each other?
We’re in a crisis, and desperate times call for desperate measures. We’re sheltering in place, practicing social distancing, and trying not to touch each other. And for most of us, this is really unpleasant and difficult. We can’t wait for it to be over.
For better or worse, this pandemic will likely make us pick up the pace on our path to automation, across many sectors and processes. The solutions people implement during this crisis won’t disappear when things go back to normal (and, depending who you talk to, they may never really do so).

As the COVID-19 cases continue to rise globally, the National Medical Products Administration of China has approved the first-ever antiviral medicine called Favilavir. This medicine is said to possibly treat the now-declared pandemic illness.
Over the weekend, Taizhou’s city government announced that Favilavir, which was initially formulated by a Chinese-owned pharmaceutical firm, is the first medicine authorized to stop the widespread of this fatal illness. At present, this drug is being promoted with the label, Avigan.
According to the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, the Favilavir of Hisun Pharmaceutical is among the three drugs that have presented results for hindering COVID-19 (in initial trials) from spreading and further damaging the health of the people worldwide.
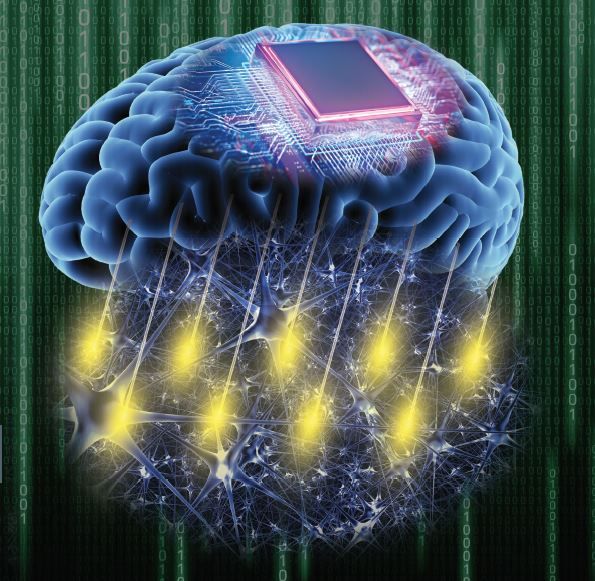
A new method to accurately record brain activity at scale has been developed by researchers at the Crick, Stanford University and UCL. The technique could lead to new medical devices to help amputees, people with paralysis or people with neurological conditions such as motor neurone disease.
The research in mice, published in Science Advances, developed an accurate and scalable method to record brain activity across large areas, including on the surface and in deeper regions simultaneously.


The genetic information of an organism is stored within DNA. It contains the code for making other molecules that make all cells and organs of the body functional. Interestingly, only 1% of DNA makes up genes, of which proteins are produced via RNA intermediaries. There is much debate on the role of the remaining DNA, but different types of RNA are thought to be produced from it and direct the fate of the cell. Even though each cell of the body contains the same DNA, how they read and process DNA to make RNA can differ quite dramatically between single cells. This has especially been known for the transcriptome, which includes all RNA that are produced from genes, but not so much for other RNA.
“Genes have been the main focus of biological research for a long time,” says lead author of the study Haruka Ozaki. “We wanted to focus on what we call read coverage of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data, which also includes RNA that are not products of genes. Although we can measure the amount of different RNA a single cell produces by scRNA-seq technologies, we wanted to come up with a new method that also visualizes specifically read coverage, because only then we can get a full picture of RNA biology and how it contributes to cell biology at the single-cell level.”
To achieve their goal, the researchers developed a new computational tool that they called Millefy uses existing scRNA-seq data to visualize read coverage of single cells as a heat map, illustrating differences between individual cells on a relative scale. The researchers first demonstrated the utility of Millefy in a well-established mouse embryonic stem cell model by showing heterogeneity of read coverage between developing cells. They then applied Millefy to cancer cells from patients with triple-negative breast cancer, a particularly aggressive type of breast cancer. Not only did Millefy show heterogeneity between cancer cells in general, but it revealed heterogeneity in a specific aspect of RNA biology that had previously been unknown.
“Our approach simplifies the investigation of cellular heterogeneity in RNA biology using scRNA-seq data,” says Ozaki. ” Our findings could help identify what makes single cells individual, which would help us understand why patients with the same disease are often treated with varying success. Additionally, to enable rapid progress in field, we made Millefy publicly available to the scientific community.”