Looking to clone your cat? At Viagen Pets, we offer pet cloning and genetic preservation services to cat owners across the world. Learn about cloned cats today!
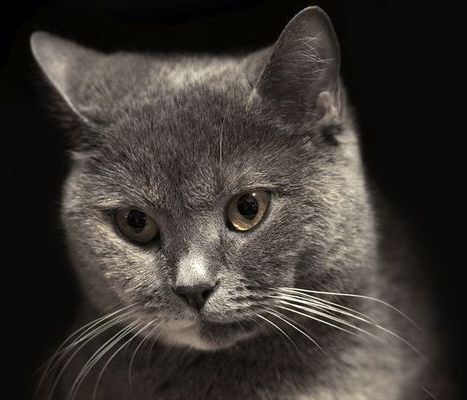


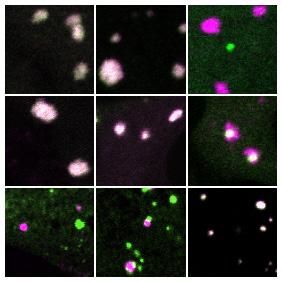
Networks are at the heart of everything from communications systems to pandemics. Now researchers have found that a unique type of network also underlies the structures of critical cellular compartments known as membraneless organelles. These findings may provide key insights into the role of these structures in both disease and cellular operations.
“Prior to this study, we knew the basic physical principle by which these protein-rich compartments form — they condense from the cytoplasm into liquid droplets like dew on a blade of grass,” said David Sanders, a post-doctoral researcher in Chemical and Biological Engineering at Princeton University. “But unlike dew drops, which are composed of a single component (water), cellular droplets are intimidatingly complex. Our work uncovers surprisingly simple principles that we think are universal to the assembly of liquid organelles, and opens new frontiers into studying their role in health and disease.”
Sanders is the lead author in an article in the journal Cell describing a blueprint for the assembly of these liquid structures, also called condensates. The researchers looked closely at two types of condensates, stress granules and processing bodies (“P-bodies”). In the Cell paper, researchers directed by Clifford Brangwynne, a professor of Chemical and Biological Engineering at Princeton and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, combined genetic engineering and live cell microscopy approaches to reveal the rules underlying the assembly and structure of stress granules, and why they remain distinct from their close relatives, P-bodies.

Google plans to add a Zoom-like gallery view to its business- and education-focused Meet videoconferencing service and let users start calls and join meetings right from Gmail, Google’s GM and VP of G Suite Javier Soltero told Reuters in an interview. The additions come amid huge growth for Meet as families, students, and workers use the service while at home due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The upcoming gallery view will let users display up to 16 meeting participants in one frame, according to Reuters. That functionality is coming later this month, said Soltero. Zoom’s gallery view, by contrast, lets you see the thumbnails of up to 49 people in one screen, if you have a powerful enough CPU to display them all.

Human clones have long been a topic of science fiction, but how far off are they in reality? Let’s take a look at current advances and see when and where we might see the first human clone.

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration, NASA, aims to send human missions to Mars in the 2030s. But scientists are still trying to learn more about the potential cancer risks for astronauts due to radiation exposure. Cancer risk from galactic cosmic radiation exposure is considered a potential “showstopper” for a manned mission to Mars.
A team led by researchers at Colorado State University used a novel approach to test assumptions in a model used by NASA to predict these health risks. The NASA model predicts that astronauts will have more than a three percent risk of dying of cancer from the radiation exposures they will receive on a Mars mission. That level of risk exceeds what is considered acceptable.
The study, “Genomic mapping in outbred mice reveals overlap in genetic susceptibility for HZE ion- and gamma-ray-induced tumors,” was published April 15 in Science Advances.
👽 Facial recognition and Covid 19 in Moscow, Russia.
Fyodor R.
MOSCOW – The Russian capital is home to a network of 178,000 surveillance cameras. Thousands of these cameras are already connected to facial recognition software under a program called “Safe City.” Police claim the technology has helped arrest more than 300 people.
Now, as part of the response to COVID-19, authorities are trying to bring every surveillance camera into the facial recognition network. This Orwelian step is supposedly to catch people breaking quarantine.
At the end of January, before Moscow had any confirmed cases of coronavirus, the city purchased the latest version of NTechLab’s facial recognition software.
A version of this story was first published by COVID-19 Waterblog. Read the original.
There has been quite some talk about SARS-CoV-2 shedding in faeces and what that might mean for the water industry. Here, Susan Petterson provides a snapshot of the current data.
As I see it, there are two aspects to this conversation: the first is a concern that sewage may contain infectious SARS-CoV-2 viruses; and the second relates to the more theoretical potential of using SARS-CoV-2 RNA concentration in sewage as a public health surveillance tool.