If you are interested in age reversal, and you haven’t read Dr David Sinclair (Harvard Medical School) yet, then I’d recommend this research paper.
“Excitingly, new studies show that age-related epigenetic changes can be reversed with interventions such as cyclic expression of the Yamanaka reprogramming factors. This review presents a summary of epigenetic changes that occur in aging, highlights studies indicating that epigenetic changes may contribute to the aging process and outlines the current state of research into interventions to reprogram age-related epigenetic changes.”
The aging process results in significant epigenetic changes at all levels of chromatin and DNA organization. These include reduced global heterochromatin, nucleosome remodeling and loss, changes in histone marks, global DNA hypomethylation with CpG island hypermethylation, and the relocalization of chromatin modifying factors. Exactly how and why these changes occur is not fully understood, but evidence that these epigenetic changes affect longevity and may cause aging, is growing. Excitingly, new studies show that age-related epigenetic changes can be reversed with interventions such as cyclic expression of the Yamanaka reprogramming factors. This review presents a summary of epigenetic changes that occur in aging, highlights studies indicating that epigenetic changes may contribute to the aging process and outlines the current state of research into interventions to reprogram age-related epigenetic changes.
The term “epigenetics” is thrown around a lot. Originally, it was coined to describe heritable changes that were non-mendelian, but use of the term has evolved. These days, “epigenetics” more generally refers to all non-genomic information storage in cells including gene networks, chromatin structure and post-translational modifications to histones. With aging, there are distinct changes across the epigenome from DNA modifications to alterations in global chromatin organization. But key questions remain unanswered: How and why do these changes occur? Do these changes drive disease and aging? Are they reversible?
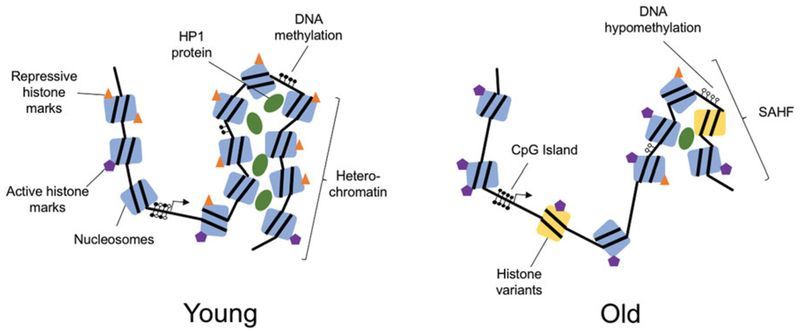
Genomic organization is determined by the complex structure of chromatin ( Figure 1 ). The basic unit of chromatin is the nucleosome, which is made up of 147 DNA base pairs wrapped around an octamer of histone proteins. This octamer usually comprises two copies each of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 (Luger et al. 1997; Hansen 2002). Within nucleosomes, both histones and the DNA itself are subject to a range of chemical modifications that affect the chromatin structure and ultimately the expression of genes. Chromatin falls into one of two major subtypes: euchromatin, in which the chromatin is open and transcriptionally active and heterochromatin, in which the chromatin is tightly closed and transcriptionally silent (Wallrath 1998; Grewal and Moazed 2003). Regulating the epigenetic network are factors that modify chromatin including DNA- and histone-modifying enzymes, transcription factors, and the more recently identified noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs).