Subtle patterns can be seen in people’s reaction times as their memories are recalled, and boosting these brainwaves could help treat Alzheimer’s disease.
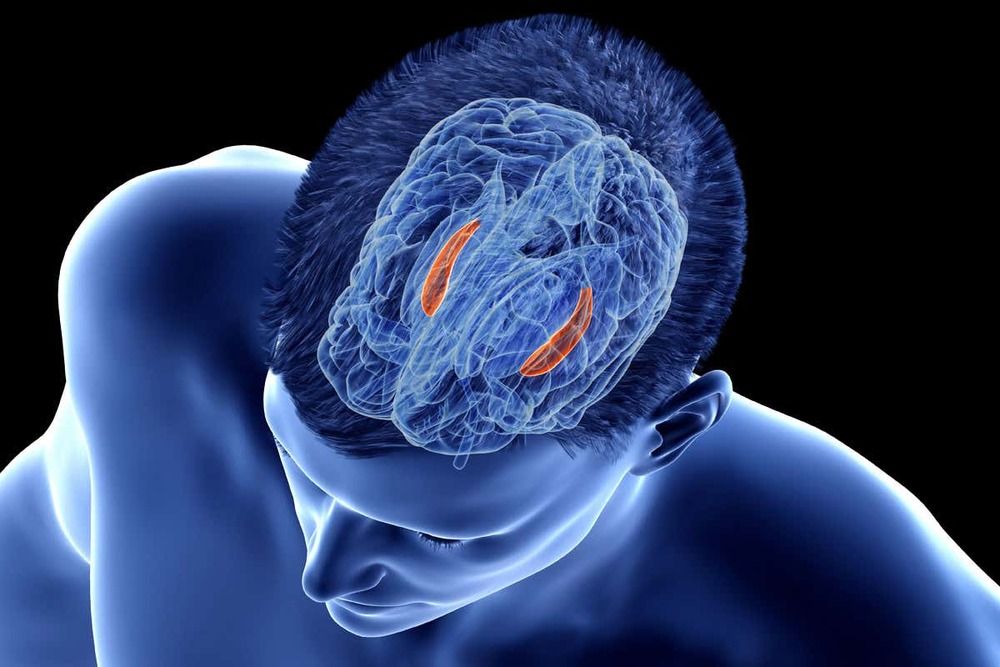


Although we often think of knowledge as “knowing that” (for example, knowing that Paris is the capital of France), each of us also knows many procedures consisting of “knowing how,” such as knowing how to tie a knot or start a car. Now, a new study has found the brain programs that code the sequence of steps in performing a complex procedure.
In a just published paper in Psychological Science, researchers at Carnegie Mellon University have found a way to find decode the procedural information required to tie various knots with enough precision to identify which knot is being planned or performed. To reach this conclusion, Drs. Robert Mason and Marcel Just first trained a group of participants to tie seven types of knots, and then scanned their brains while they imagined tying, or actually tied the knots while they were in an MRI scanner. The main findings were that each knot had a distinctive neural signature, so the researchers could tell which knot was being tied from the sequence of brain images collected. Furthermore, the neural signatures were very similar for imagining tying a particular knot and planning to tie it.
Dr. Just said, “Tying a knot is an ancient and frequently performed human action that is the epitome of everyday procedural knowledge, making it an excellent target for investigation.”

A machine-learning algorithm has been developed by scientists in Japan to breathe new life into old molecules. Called BoundLess Objective-free eXploration, or Blox, it allows researchers to search chemical databases for molecules with the right properties to see them repurposed. The team demonstrated the power of their technique by finding molecules that could work in solar cells from a database designed for drug discovery.
Chemical repurposing involves taking a molecule or material and finding an entirely new use for it. Suitable molecules for chemical repurposing tend to stand apart from the larger group when considering one property against another. These materials are said to be out-of-trend and can display previously undiscovered yet exceptional characteristics.
‘In public databases there are a lot of molecules, but each molecule’s properties are mostly unknown. These molecules have been synthesised for a particular purpose, for example drug development, so unrelated properties were not measured,’ explains Koji Tsuda of the Riken Centre for Advanced Intelligence and who led the development of Blox. ‘There are a lot of hidden treasures in databases.’

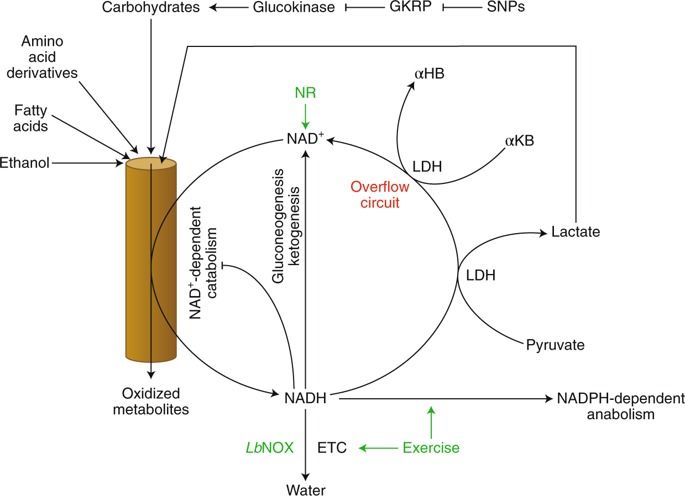
Whereas textbooks depict metabolism in perfect homeostasis, disturbances occur in real life. One particularly relevant disturbance, caused by excess food and alcohol consumption and exacerbated by genetics, is reductive stress. New work by Goodman et al. identifies a biomarker of reductive stress and uses a gene therapy solution in mice. This work suggests how exercise and an accessible nutritional technology can synergistically increase catabolism and relieve reductive stress.
Sirtuins, telomeres, A.I. experiment with vitamin A and personalized medicine, a bit of everything here.
https://facebook.com/LongevityFB https://instagram.com/longevityyy https://twitter.com/Longevityyyyy https://linkedin.com/company/longevityy
- Please also subscribe and hit the notification bell and click “all” on these YouTube channels:
https://youtube.com/Transhumania
https://youtube.com/BrentNally
https://youtube.com/EternalLifeFan
https://youtube.com/MaxEternalLife
https://youtube.com/LifespanIO
https://youtube.com/LifeXTenShow
https://youtube.com/BitcoinComOfficialChannel
https://youtube.com/RogerVer
https://youtube.com/RichardHeart
https://youtube.com/sciVive
Brian Kennedy’s Lab Website:

Not all viruses set out to cause widespread death and sickness — some have the potential to fight cancer, according to new research.
Researchers from Hokkaido University in Japan have genetically engineered adenoviruses, which is a family of viruses that cause mild symptoms, to replicate inside cancer cells and kill them, according to a new paper in the journal Cancers.
To do this, Fumihiro Higashino, a molecular oncologist, and his team inserted adenylate-uridylate-rich elements (AREs) from two human genes — a stabilizing element found in a type of macromolecule present in all biological cells — into two strains of the virus to help specifically attack cancer cells.