Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery, in which a surgeon uses tools and a tiny camera inserted into small incisions to perform operations, has made surgical procedures safer for both patients and doctors over the last half-century. Recently, surgical robots have started to appear in operating rooms to further assist surgeons by allowing them to manipulate multiple tools at once with greater precision, flexibility, and control than is possible with traditional techniques. However, these robotic systems are extremely large, often taking up an entire room, and their tools can be much larger than the delicate tissues and structures on which they operate.
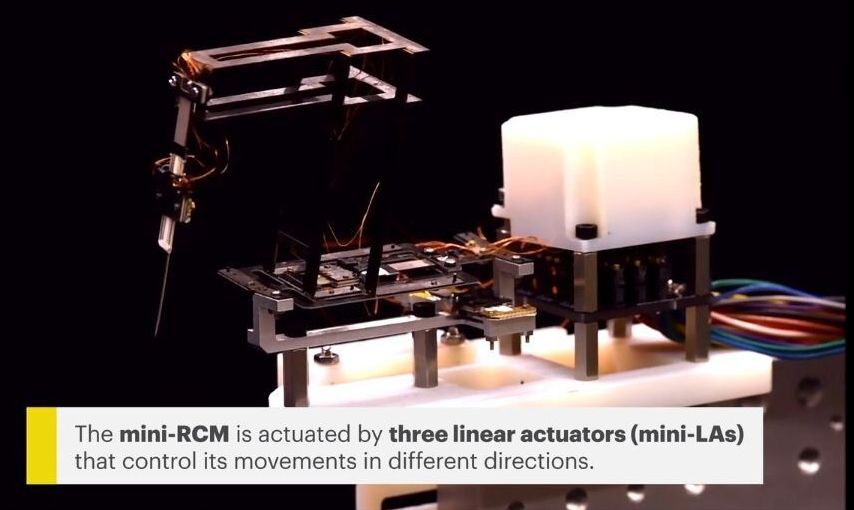
A collaboration between Wyss Associate Faculty member Robert Wood, Ph.D. and Robotics Engineer Hiroyuki Suzuki of Sony Corporation has brought surgical robotics down to the microscale by creating a new, origami-inspired miniature remote center of motion manipulator (the “mini-RCM”). The robot is the size of a tennis ball, weighs about as much as a penny, and successfully performed a difficult mock surgical task, as described in a recent issue of Nature Machine Intelligence.
“The Wood lab’s unique technical capabilities for making micro-robots have led to a number of impressive inventions over the last few years, and I was convinced that it also had the potential to make a breakthrough in the field of medical manipulators as well,” said Suzuki, who began working with Wood on the mini-RCM in 2018 as part of a Harvard-Sony collaboration. “This project has been a great success.”