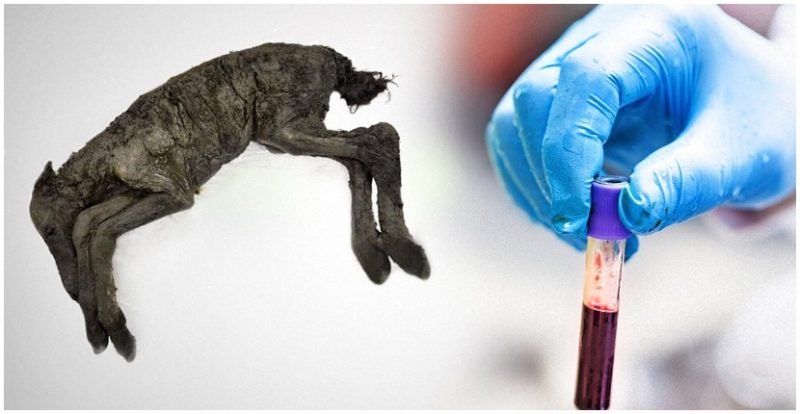
Liquid blood and urine were found inside the 42,000-yr-old foal. The oldest blood ever found by 10,000 years!
It made headlines in 2018 when researchers discovered the frozen remains of a foal that died 42,000 years ago in the Verkhoyansk region of Siberia, miraculously preserved in permafrost. But now an even more startling announcement has been made: Liquid blood and urine were found inside of the foal.
In an interview given to the Siberian Times, Semyon Grigoryev, head of the Mammoth Museum in Yakutsk, said, “The autopsy shows beautifully preserved internal organs. Samples of liquid blood were taken from heart vessels — it was preserved in the liquid state for 42,000 years thanks to favorable burial conditions and permafrost. The muscle tissues preserved their natural reddish color.”
Grigorvev then made the statement which is reverberating throughout the scientific community: “We can now claim that this is the best-preserved Ice Age animal ever found in the world.”