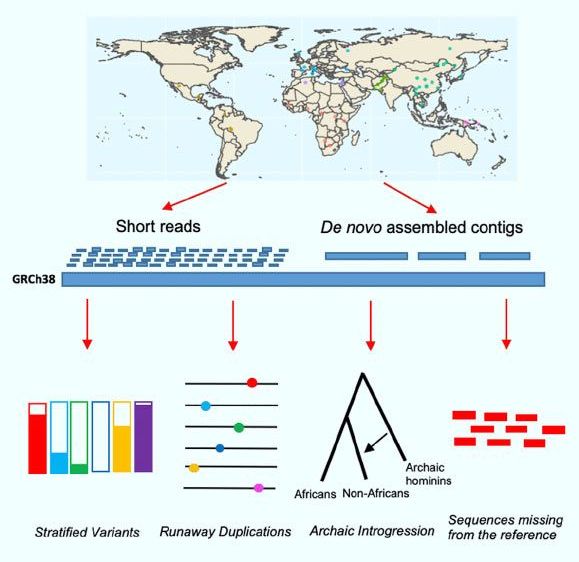
This is really old news:
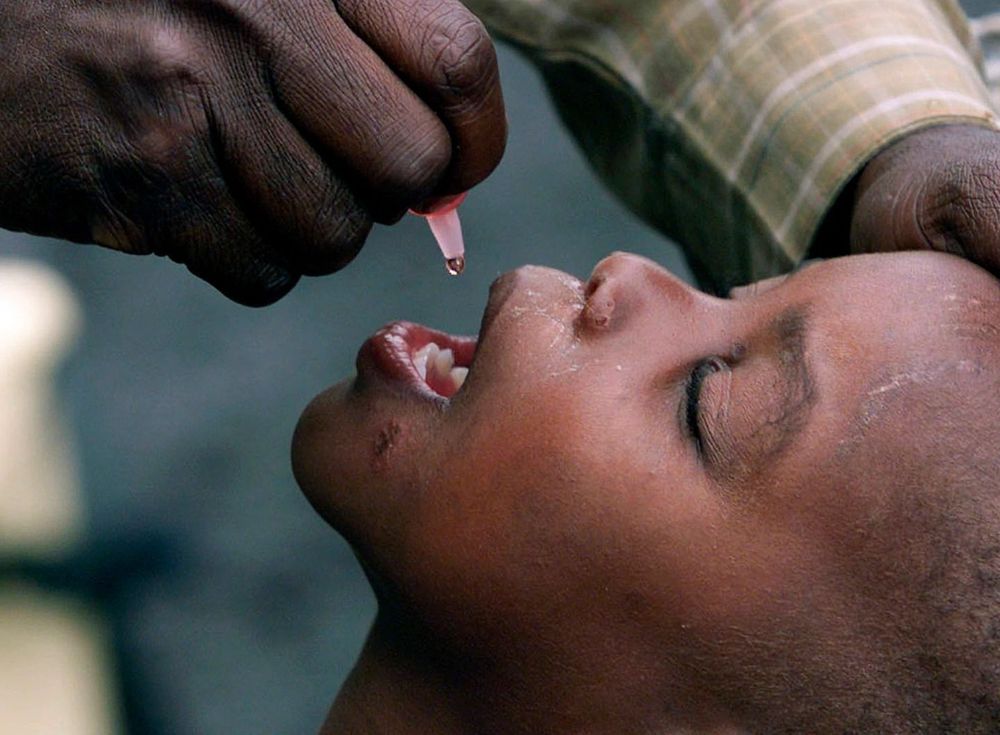
Two tried-and-true vaccines — a century-old inoculation against tuberculosis and a decades-old polio vaccine once given as a sugar cube — are being evaluated to see if they can offer limited protection against the coronavirus.
The old vaccines are oddities among the cutting-edge and targeted technologies being developed to combat the novel coronavirus. New vaccines aim to teach the body’s immune system to recognize and destroy the coronavirus, but scientists are only now beginning to test them in people. Vaccines developed against TB and polio have already been used in millions of people and could offer a low-risk way to rev up the body’s first line of defense — the innate immune system — against a broad array of pathogens, including the coronavirus.