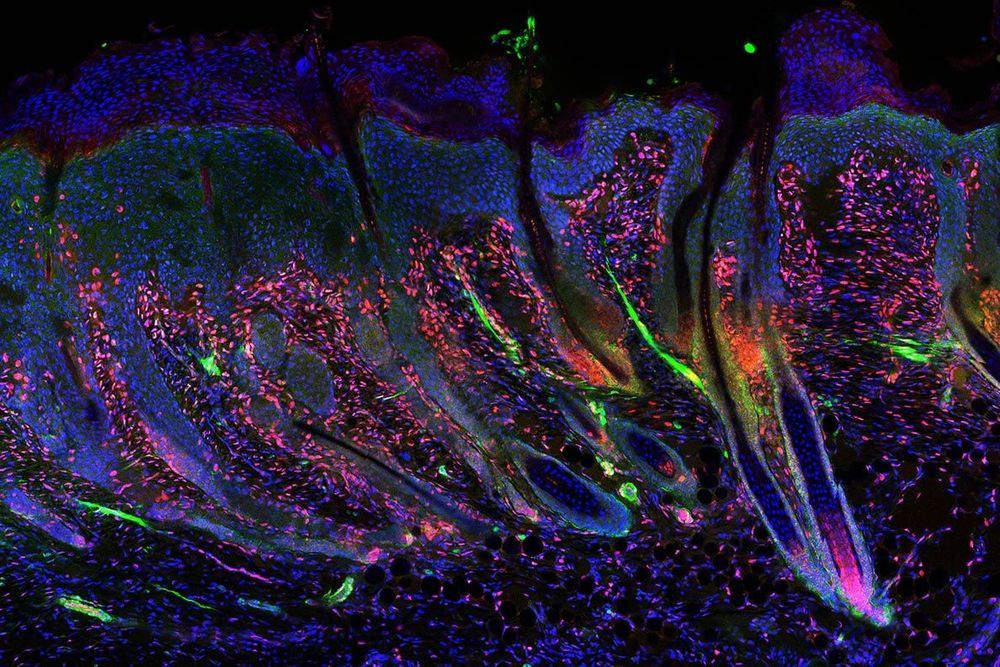
A newly identified genetic factor allows adult skin to repair itself like the skin of a newborn babe. The discovery by Washington State University researchers has implications for better skin wound treatment as well as preventing some of the aging process in skin.
In a study, published in the journal eLife on September 29, 2020, the researchers identified a factor that acts like a molecular switch in the skin of baby mice that controls the formation of hair follicles as they develop during the first week of life. The switch is mostly turned off after skin forms and remains off in adult tissue. When it was activated in specialized cells in adult mice, their skin was able to heal wounds without scarring. The reformed skin even included fur and could make goosebumps, an ability that is lost in adult human scars.
“We were able to take the innate ability of young, neonatal skin to regenerate and transfer that ability to old skin,” said Ryan Driskell, an assistant professor in WSU’s School of Molecular Biosciences. “We have shown in principle that this kind of regeneration is possible.”