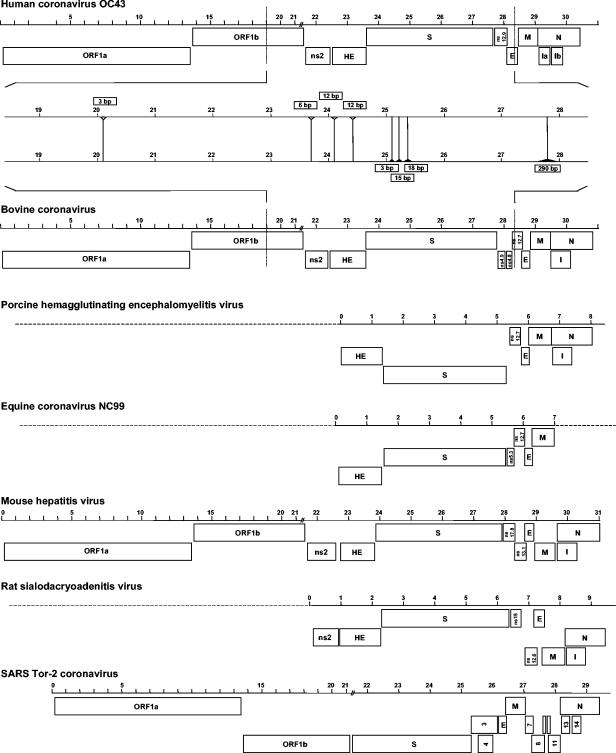
Coronaviruses are enveloped, positive-stranded RNA viruses with a genome of approximately 30 kb. Based on genetic similarities, coronaviruses are classified into three groups. Two group 2 coronaviruses, human coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43) and bovine coronavirus (BCoV), show remarkable antigenic and genetic similarities. In this study, we report the first complete genome sequence (30,738 nucleotides) of the prototype HCoV-OC43 strain (ATCC VR759). Complete genome and open reading frame (ORF) analyses were performed in comparison to the BCoV genome. In the region between the spike and membrane protein genes, a 290-nucleotide deletion is present, corresponding to the absence of BCoV ORFs ns4.9 and ns4.8. Nucleotide and amino acid similarity percentages were determined for the major HCoV-OC43 ORFs and for those of other group 2 coronaviruses. The highest degree of similarity is demonstrated between HCoV-OC43 and BCoV in all ORFs with the exception of the E gene. Molecular clock analysis of the spike gene sequences of BCoV and HCoV-OC43 suggests a relatively recent zoonotic transmission event and dates their most recent common ancestor to around 1890. An evolutionary rate in the order of 4 × 10−4 nucleotide changes per site per year was estimated. This is the first animal-human zoonotic pair of coronaviruses that can be analyzed in order to gain insights into the processes of adaptation of a nonhuman coronavirus to a human host, which is important for understanding the interspecies transmission events that led to the origin of the severe acute respiratory syndrome outbreak.
Coronaviruses are large (120- to 160-nm), roughly spherical particles with a linear, nonsegmented, capped, and polyadenylated positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome that is encapsidated in a helical nucleocapsid. The envelope is derived from intracellular membranes and contains a characteristic crown of widely spaced club-shaped spikes that are 12 to 24 nm long. The genus Coronavirus (International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses database [ICTVdb], virus code 03.019.0.1) belongs to the family Coronaviridae in the order Nidovirales (7, 8).
Before the 2002-to-2003 severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) epidemic, coronaviruses were somewhat neglected in human medicine, but they have always been of considerable importance in animal health. Coronaviruses infect a variety of livestock, poultry, and companion animals, in whom they can cause serious and often fatal respiratory, enteric, cardiovascular, and neurologic diseases (25). Most of our understanding about the molecular pathogenic properties of coronaviruses has been achieved by the veterinary virology community.