Huntington’s disease is a genetic disorder that is caused by an unusual number of repeats in the huntingtin gene; there make the gene too long, and lead to the production of a toxic protein in brain cells. Symptoms of the disease tend to arise when a person is in their 30s or 40s and it is typically fatal within 20 years. New work may change that, however.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 190
Sugar fingerprints offer faster, more reliable diagnoses for fungal infections
Hospitals worldwide, including Germany, face a growing problem with fungal infections, with an estimated 6 million cases and 3.8 million deaths each year. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), Candida—a common fungus most people encounter at least once in life—is a top concern. While many know it from mild, superficial infections such as thrush, Candida (especially C. auris and C. albicans) can also reach the bloodstream and cause life-threatening disease.
This is increasingly happening in clinics around the world, where Candida finds an ideal target in weakened patients—after major surgery or chemotherapy, for example. Candida can also cling to medical equipment, like catheters, tubes, or prostheses, forming slimy biofilms that are highly resistant to antifungal drugs.
The European Center for Disease Prevention and Control has recently echoed the WHO in sounding the alarm and calling for better prevention, faster diagnosis, and more effective treatment.
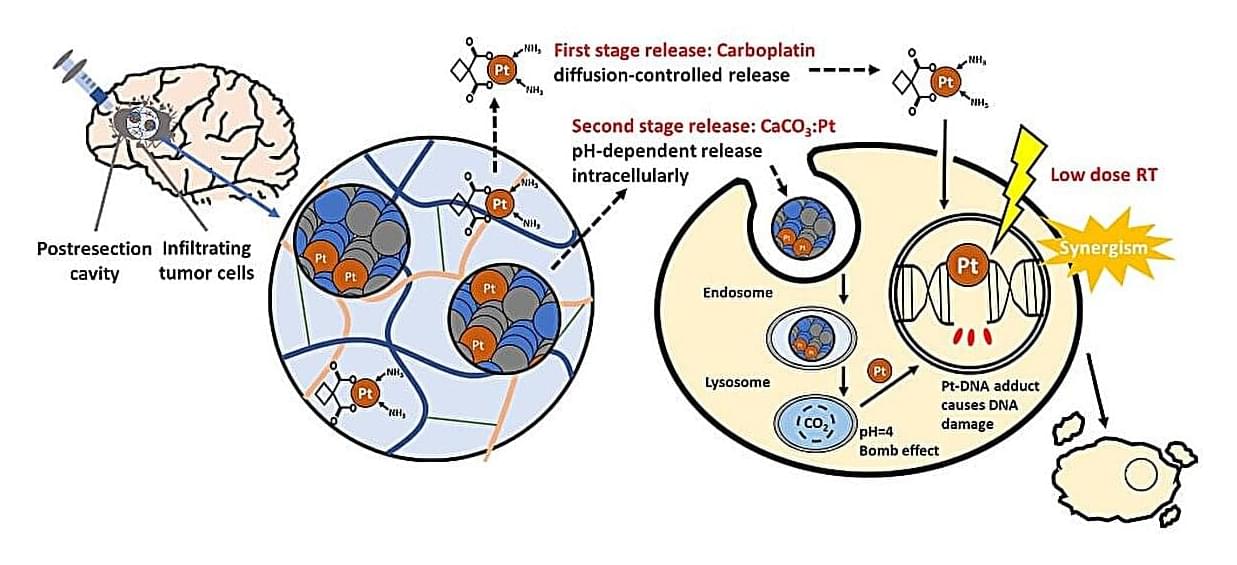
Time-released gel packs a one-two punch against aggressive brain tumors
High-grade gliomas are aggressive brain tumors with poor prognosis, largely because even after surgical removal, infiltrative residual tumor cells often regrow during the latency before radiotherapy, leading to recurrence. The standard chemoradiotherapy only modestly improves survival. A crucial window of vulnerability arises post-surgery, before radiotherapy begins, where residual tumor cells are not well addressed by systemic chemotherapy.
Prof. Feng-Huei Lin and Dr. Jason Lin from National Taiwan University have designed a local post-surgical gel packing with sequential delivery of platinum agents that could maintain therapeutic drug concentrations intracranially and synergize with subsequent radiotherapy to eliminate glioma tissue. Their study is published in the Chemical Engineering Journal.
The cutting-edge drug-delivery gel can be directly injected into the surgical cavity following tumor resection. This gel provides sustained local delivery of platinum-based anticancer agents, ensuring effective eradication for residual glioma tissue that remain after surgery. The gel is designed to maximize the therapeutic impact while minimizing systemic exposure.
New Study Finds Evidence of Hepatitis C Virus in Cells Lining Human Brain
Observational studies of psychiatric diseases such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and major depression have long tied viral infections with behavioral symptoms in these disorders, but scientists have been unable to find direct evidence of suspected viruses in the brain. Experts say that’s possibly because viruses may not get directly inside the brain, but may target the brain lining instead.
After testing that idea using postmortem human brain samples and the electronic medical records of 285 million patients, a team of Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists says it has found such evidence in the form of the liver-damaging hepatitis C virus in the human brain’s choroid plexus, a collection of cells that make up the lining of the fluid-filled cavities, or ventricles, and — notably — produce the cerebrospinal fluid that protects the brain and spinal cord…
…’Our findings show that it’s possible that some people may be having psychiatric symptoms because they have an infection, and since the hepatitis C infection is treatable, it might be possible for this patient subset to be treated with antiviral drugs and not have to deal with psychiatric symptoms,’ Sabunciyan says.
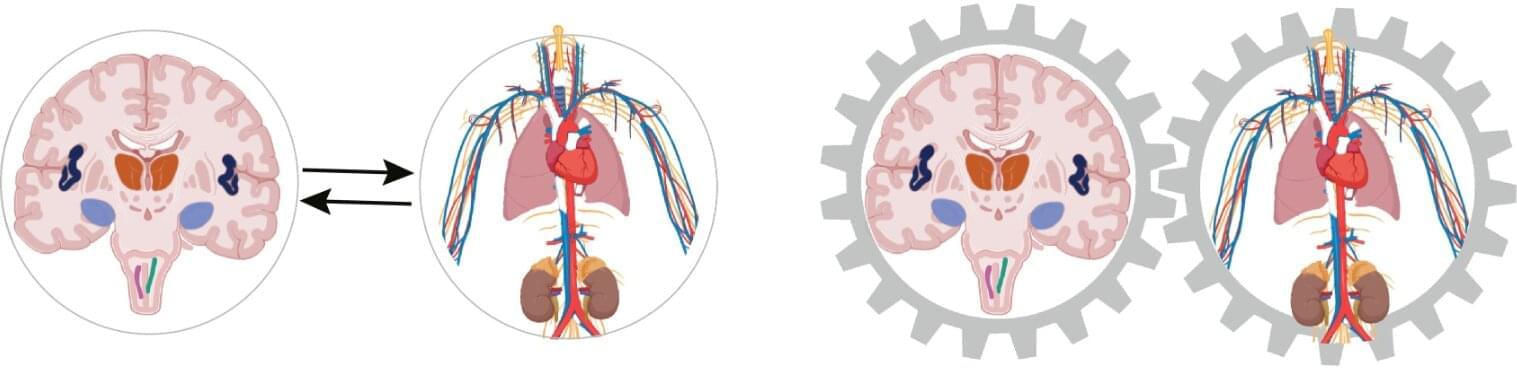
Growing evidence that the heart has a strong influence on thinking and feeling
The influence of the heart and circulatory system occurs within milliseconds, and every single heartbeat plays a role. The role of the heart in the psyche and cognition is evident in the high coincidence of cardiovascular diseases, such as high blood pressure and heart attack, and mental illnesses, such as depression and anxiety disorders.
There are a number of explanations for this high coincidence, but none of them have been definitively proven yet. For example, negative psychological reactions to a diagnosis of cardiovascular disease are cited as a reason for the development of mental illness. On the other hand, an unhealthy lifestyle in the presence of mental illness is considered a risk factor for the development of cardiovascular disease.
The concept is based on integrated brain–body states. Every physical process, such as a heartbeat or any change in blood pressure or metabolism, is automatically accompanied by a mental or psychological process. This means that the two are inextricably linked.
Chronic Insomnia May Spark Changes in The Brain That Trigger Dementia
Staring at the ceiling while the clock blinks 3am doesn’t only sap energy for the next day. A large, long-running US study of older adults has now linked chronic insomnia to changes inside the brain that set the stage for dementia.
The researchers, from the Mayo Clinic in the US, followed 2,750 people aged 50 and over for an average of five and a half years. Every year the volunteers completed detailed memory tests and many also had brain scans that measured two telltale markers of future cognitive trouble: the buildup of amyloid plaques, and tiny spots of damage in the brain’s white matter – known as white-matter hyperintensities.
Participants were classed as having chronic insomnia if their medical records contained at least two insomnia diagnoses a month apart – a definition that captured 16 percent of the sample.

Cambridge scientists created a gel that could end arthritis pain
Cambridge scientists have created a breakthrough material that can sense tiny chemical changes in the body, such as the increased acidity during an arthritis flare-up, and release drugs exactly when and where they’re needed. By mimicking cartilage while delivering medication, this smart gel could ease pain, reduce side effects, and provide continuous treatment for millions of arthritis sufferers.
Huntington’s progression slowed by experimental gene therapy
Even hearing the phrase “Huntington’s disease” will make a room suddenly somber. So the joy that accompanied a recent announcement of results of an experimental gene therapy for the deadly diseases signaled an unfamiliar sense of hope.
In a small clinical trial, brain injections of a virus that codes for a tiny segment of RNA may have prevented the formation of the rogue proteins that make Huntington’s so devastating. The early results, announced September 24 in a news release, show that over three years, the treatment slowed Huntington’s progression by up to 75 percent. While not a cure, the treatment could potentially give people living with Huntington’s disease, who might otherwise face early disability and death, the gift of many more years of life.
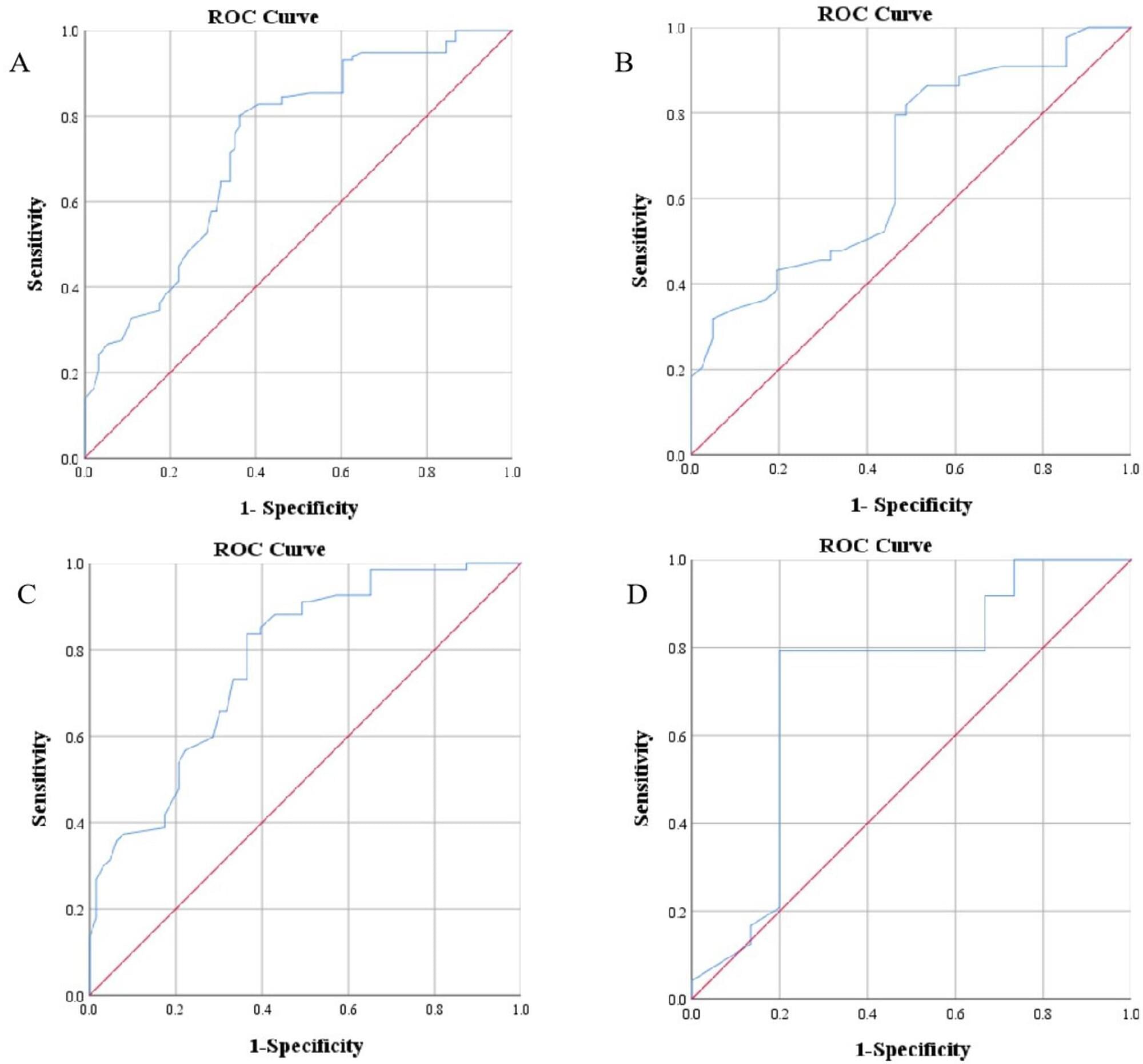
Timing of treatment with oral propranolol for infantile hemangioma
Early oral propranolol for infantile hemangioma (IH) can improve the success rate. However, few studies have been conducted on the specific age threshold for initiating treatment with propranolol. This study aimed to determine the cutoff value of treatment success for IH with oral propranolol.
This was a retrospective study involving 207 patients with IH and clinical data. The primary outcome measure was treatment success with oral propranolol at months 6 to 12.
Multivariate analysis showed that age at treatment initiation (P 0.001), high-risk IH (P = 0.002), and segmental IH (P = 0.012) were independent risk factors for treatment unsuccess with oral propranolol at months 6 to 12. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis indicated that the cutoff value for age at treatment initiation was 69.5 days for all patients, 65.5 days for patients with segmental IH or high-risk IH, and 93.5 days for patients with non-high-risk and nonsegmental IH. Patients who started treatment before 69.5 days had a success rate of 73.8%, which was higher than the 28.4% success rate of patients who started treatment after 69.5 days. The median time to treatment success for patients who started treatment before 69.5 days was 11.5 months, which was shorter than the 15 months for patients who started treatment after 69.5 days.