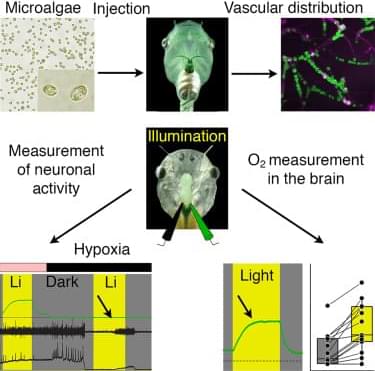
Classification Description: Animal physiology; Neuroscience; Microbiology; Biotechnology.

The central principle of superconductivity is that electrons form pairs. But can they also condense into foursomes? Recent findings have suggested they can, and a physicist at KTH Royal Institute of Technology today published the first experimental evidence of this quadrupling effect and the mechanism by which this state of matter occurs.
Reporting today in Nature Physics, Professor Egor Babaev and collaborators presented evidence of fermion quadrupling in a series of experimental measurements on the iron-based material, Ba1−x Kx Fe2As2. The results follow nearly 20 years after Babaev first predicted this kind of phenomenon, and eight years after he published a paper predicting that it could occur in the material.
The pairing of electrons enables the quantum state of superconductivity, a zero-resistance state of conductivity which is used in MRI scanners and quantum computing. It occurs within a material as a result of two electrons bonding rather than repelling each other, as they would in a vacuum. The phenomenon was first described in a theory by, Leon Cooper, John Bardeen and John Schrieffer, whose work was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1972.
Forward-looking: The service department can seem like the slowest part of a dealership, especially when it’s your car getting worked on. But Mercedes-Benz is infusing its dealerships with AR technology to speed up the diagnosis and repair of tricky and complex issues with its Virtual Remote Support, powered by Microsoft’s HoloLens 2 and Dynamics 365 Remote Assist. I visited one of Mercedes’ showcases last week to check out the implementation and get some hands-on time with the HoloLens 2.
For customers that bring in a hard-to-solve problem, it was common for Mercedes-Benz to call in a flying doctor, an expert from HQ that would fly in and get hands-on with an issue. That could take days to arrange, not to mention the costs and environmental impacts associated with flying in these technical specialists from all over the country. All the while, the customer is left without their luxury automobile.
While many shoppers go with a Mercedes for the styling and performance, it’s the service experience that impacts their future purchases. Long waits could see someone changing brands in the future.
Integrated And Cross-Disciplinary Research Focused on Diagnosing, Treating And Curing Cancers — Dr. Antonio Giordano MD, PhD, President & Founder, Sbarro Health Research Organization.
Dr. Antonio Giordano, MD, Ph.D., (https://www.drantoniogiordano.com/) is President and Founder of the Sbarro Health Research Organization (https://www.shro.org/), which conducts research to diagnose, treat and cure cancer, but also has diversified into research beyond oncology, into the areas of cardiovascular disease, diabetes and other chronic illnesses.
Dr. Giordano is also a Professor of Molecular Biology at Temple University in Philadelphia, a ‘Chiara fama’ Professor in the Department of Pathology & Oncology at the University of Siena, Italy, and Director of the Sbarro Institute for Cancer Research and Molecular Medicine, and the Center for Biotechnology, at Temple’s College of Science & Technology.
In his research throughout the years, Dr. Giordano has identified numerous tumor suppressor genes, including Rb2/p130, which has been found to be active in lung, endometrial, brain, breast, liver and ovarian cancers, as well as interesting synergistic effects of gamma radiation in combination with this gene, accelerating the death of tumor cells.
Dr. Giordano went on to discover Cyclin A, Cdk9 (which is known to play critical roles in HIV transcriptions, inception of tumors, and cell differentiation), and Cdk10. Dr. Giordano also developed patented technologies for diagnosing cancer.
Interview with a very important researcher who gives a reality check on a few things (Sirtuins) and explains how effective Rapamycin has been.
Professor Matt Kaeberlein discusses aspects of aging and proposed interventions to improve health. He gives an in-depth review on sirtuins, resveratrol, fasting, NAD precursors, and rapamycin.
Timestamps.
0:00 Intro.
0:25 Discovery of Sirtuins.
7:30 Resveratrol & Health.
11:05 Calorie Restriction & Fasting.
17:07 What Is A Healthy Diet?
21:46 NAD+ Precursors.
29:07 Rapamycin & Lifespan.
32:50 Rapamycin & Dog Aging Project.
38:45 Intermittent Fasting In Dogs.
40:45 Rapamycin Human Clinical Studies.
50:30 DNA Methylation Clocks.
54:15 What Areas Are Exciting For Healthspan Extension?
56:25 Yamanaka Factors.
59:55 How Do We Avoid Hype Over Substance?
1:06:50 Senolytics.
1:17:36 What Supplements Does Professor Kaeberlein Take?
My full supplement stack: http://bit.ly/39vRnXX
Supplements I source from Amazon: http://amzn.to/3o2ULOV
✨10% Discounts✨

The central principle of superconductivity is that electrons form pairs. But can they also condense into foursomes? Recent findings have suggested they can, and a physicist at KTH Royal Institute of Technology today published the first experimental evidence of this quadrupling effect and the mechanism by which this state of matter occurs.
Reporting in Nature Physics, Professor Egor Babaev and collaborators presented evidence of fermion quadrupling in a series of experimental measurements on the iron-based material, Ba1−xKxFe2As2. The results follow nearly 20 years after Babaev first predicted this kind of phenomenon, and eight years after he published a paper predicting that it could occur in the material.
The pairing of electrons enables the quantum state of superconductivity, a zero-resistance state of conductivity which is used in MRI scanners and quantum computing. It occurs within a material as a result of two electrons bonding rather than repelling each other, as they would in a vacuum. The phenomenon was first described in a theory by, Leon Cooper, John Bardeen and John Schrieffer, whose work was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1972.
For most of the time since the first description of multiple sclerosis (MS) in 1,868 the causes of this disabling disease have remained uncertain. Genes have been identified as important, which is why having other family members with MS is associated with a greater risk of developing the disease.
A recent study my colleagues and I conducted found that several types of infection during the teenage years are associated with MS after age 20. Our study didn’t investigate whether people who are more likely to have genetic risks for MS were also more likely to have worse infections.
This might explain why people with MS also have more infections that need hospital treatment.

If the properties of materials can be reliably predicted, then the process of developing new products for a huge range of industries can be streamlined and accelerated. In a study published in Advanced Intelligent Systems, researchers from The University of Tokyo Institute of Industrial Science used core-loss spectroscopy to determine the properties of organic molecules using machine learning.
The spectroscopy techniques energy loss near-edge structure (ELNES) and X-ray near-edge structure (XANES) are used to determine information about the electrons, and through that the atoms, in materials. They have high sensitivity and high resolution and have been used to investigate a range of materials from electronic devices to drug delivery systems.
However, connecting spectral data to the properties of a material—things like optical properties, electron conductivity, density, and stability—remains ambiguous. Machine learning (ML) approaches have been used to extract information for large complex sets of data. Such approaches use artificial neural networks, which are based on how our brains work, to constantly learn to solve problems. Although the group previously used ELNES/XANES spectra and ML to find out information about materials, what they found did not relate to the properties of the material itself. Therefore, the information could not be easily translated into developments.

While the pandemic is still raging, the chaos of the past 18 months has calmed a bit, and the dust is starting to settle. Now the time has come for healthcare CIOs and other health IT leaders to look forward and plan their IT investments – shaped, in no small part, by the lessons of the recent past.