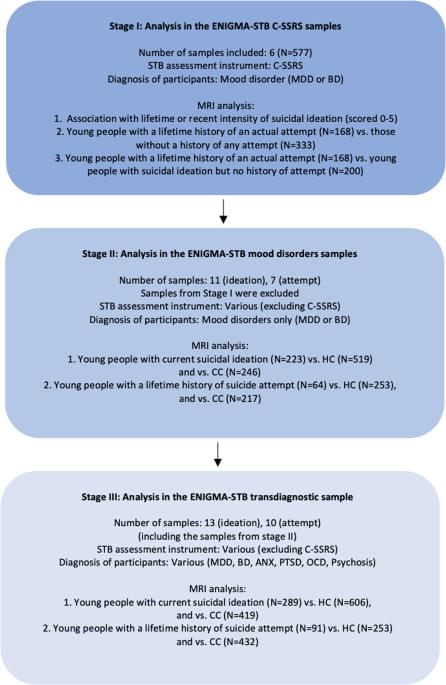
Suicide is the second leading cause of death for young people aged between 15 and 29 [1]. Suicidal thoughts and behaviors (STBs) typically emerge during adolescence [2]. It has been estimated that between 11 and 29% of adolescents report suicidal ideation (suicidal thoughts), and 2–10% of adolescents attempted suicide in the past year [3]. Unfortunately, the number of suicide attempts among children and adolescents has continued to increase sharply despite national and international prevention efforts [4].
To improve targeting of prevention and intervention efforts and thereby reduce the number of deaths by suicide in this age group, we must increase our understanding of the mechanisms underlying both suicidal thoughts and suicidal behaviors (including suicide attempts) in young people. Neuroimaging, including Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), is a useful tool with which to identify biological risk markers for STBs in vivo and non-invasively. Many neuroimaging studies have been published examining the neural substrates of STBs in the past 20 years, but few have focused on STBs in youth (for a review, see [5]). Although several of these studies support lower regional brain volumes, particularly in ventral and dorsal prefrontal and also in temporal regions [6,7,8,9] in suicide attempters with mood disorders, negative findings have also been reported [10, 11].