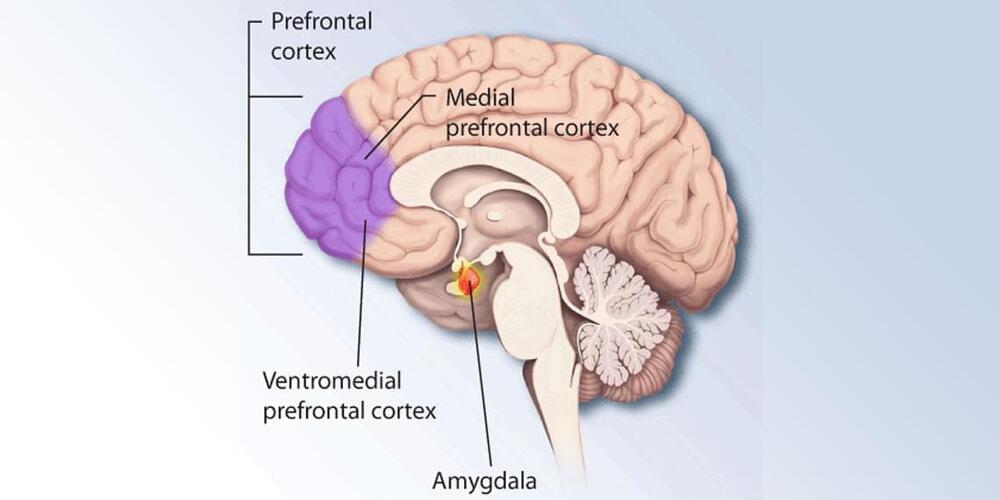
A study on a large sample of patients found chronic, long-lasting depression to be associated with reduced brain volume. The reduced volume was found in brain regions relevant for planning one’s behavior, focusing attention, thinking, learning and remembering and also in regions relevant for regulating emotions. The study was published in Neurobiology and Treatment of Depression.
Depression, also called major depressive disorder, is a mood disorder that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest. It changes the way a person feels, thinks and behaves. For many people suffering from it, depressive episodes become a recurring event. More than half of patients with depression experience a relapse after 2 years and the probability of recurrent depressive episodes rises to 90% after 3–4 episodes. Studies have indicated that recurring depressive episodes might be linked to structural changes in the brain, but the existing results are not uniform.
Ms. Hannah Lemke and her colleagues analyzed the data of 681 patients from the Marburg-Muenster-Affective-Cohort Study (MACS) in order to better link properties of the course of depressive disorder with specific changes in the brain structure. Patient data were collected at two sites in Germany – Muenster and Marburg.