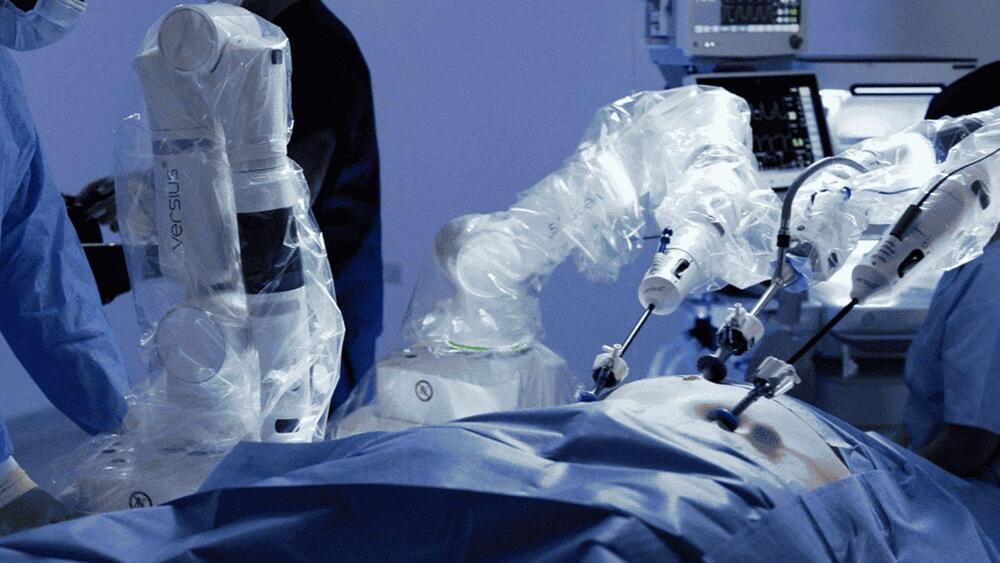
Using the Versius surgical robot permitted a keyhole, or minimal access surgical approach, in an otherwise open surgery.
A robot at Gloucestershire Royal Hospital (GRH), United Kingdom, saved the life of a 61-year-old patient by removing a cancerous tumor from their throat, in what can be called a first in the country.
“To have been given a second chance to see my grandchildren, my children, and my wife has meant so much to me. The team at the GRH saved my life, and I’ll be forever grateful to them for doing so,” Nugent told Gloucestershire Live in an interview.
Versius/CMR Surgical.
Grandfather Martin Nugent is in high spirits after a surgical team comprising Gloucestershire Royal Hospital surgeons Simon Higgs and Steve Hornby employed Versius, a modern, cutting-edge robot from CMR Surgical, to operate earlier in July.