Category: biotech/medical – Page 1,450

The missing links: Finding function in lincRNAs
Genomes contain regions between protein-coding genes that produce lengthy RNA molecules that never give rise to a protein. These long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) are thought to have important functions, such as regulating responses to environmental change. However, a paucity of well-annotated lincRNA data, especially for crop plants, has precluded a deeper understanding of their roles.
Up until now, there have been no systematic genome-wide studies that both confirmed DNA sequences that produce lincRNAs and proposed functions for those lincRNAs. Plus, data are reported differently across studies, making direct comparisons among them difficult.
These barriers inspired researchers at the Boyce Thompson Institute to take a comprehensive look at the identity, production and function of lincRNAs in four species in the mustard family, including the model organism Arabidopsis thaliana, and Brassica rapa, a species that produces boy choy, turnips and other food crops.

Failures in large networks can be prevented with local focus
We live in an increasingly connected world, a fact underscored by the swift spread of the coronavirus around the globe. Underlying this connectivity are complex networks—global air transportation, the internet, power grids, financial systems and ecological networks, to name just a few. The need to ensure the proper functioning of these systems also is increasing, but control is difficult.
Now a Northwestern University research team has discovered a ubiquitous property of a complex network and developed a novel computational method that is the first to systematically exploit that property to control the whole network using only local information. The method considers the computational time and information communication costs to produce the optimal choice.
The same connections that provide functionality in networks also can serve as conduits for the propagation of failures and instabilities. In such dynamic networks, gathering and processing all the information necessary to make a better decision can take too much time. The goal is to diagnose a problem and take action before it leads to a system-wide issue. This may mean having less information but being timely.
The Devastating Destruction of the Human Race | The Killing Star
So, I think I uncovered a treasure. The Killing Star by Charles Pellegrino and George Zebrowski was originally published 1995 and it paints a dark and seemingly plausible depiction of humanity’s potential future. This book is about several things genetic engineering and cloning, it’s about the destructive power of fanaticism, It’s about the over confidence and hubris of humanity, and that gets really hammered home in this book with all it’s references to the titanic, which has for a very long time been thought of as one of the greatest symbols of human hubris, it’s about AI, and when it goes to far, it’s about our over dependence on technology, it’s about humanity’s indefinite survival outside of earth, and most importantly, it’s about the devastating annihilation of the vast majority of the human race.
Join Dune Club!
https://twitter.com/DanikaXIX/status/1540394079069999106
Music: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=63UR4xLiUNo.
Cover art: https://www.artstation.com/artwork/L3YP2w.
FOLLOW QUINN ON TWITTER: Twitter: https://twitter.com/IDEASOFICE_FIRE
Three-Body Playlist: https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLRXGGVBzHLUfIzEhovpQJ2ENiNvJoOD2A
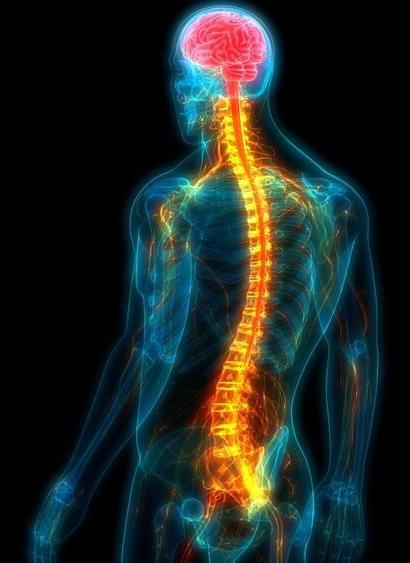
Research Shows Investigational Cancer Drug Can Boost Regeneration of Damaged Nerves After Spinal Cord Injury
Scientists have demonstrated that a brain-penetrating candidate drug currently in development as a cancer therapy can promote regeneration of damaged nerves after spinal trauma.
The research used cell and animal models to show that when taken orally the candidate drug, known as AZD1390, can block the response to DNA
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule composed of two long strands of nucleotides that coil around each other to form a double helix. It is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms that carries genetic instructions for development, functioning, growth, and reproduction. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA).

A New Technology Could Help Solve a DNA Mystery
Researchers from Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Weill Cornell Medicine, and the New York Genome Center have created a new technique to evaluate the three-dimensional structure of the human DNA
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule composed of two long strands of nucleotides that coil around each other to form a double helix. It is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms that carries genetic instructions for development, functioning, growth, and reproduction. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA).
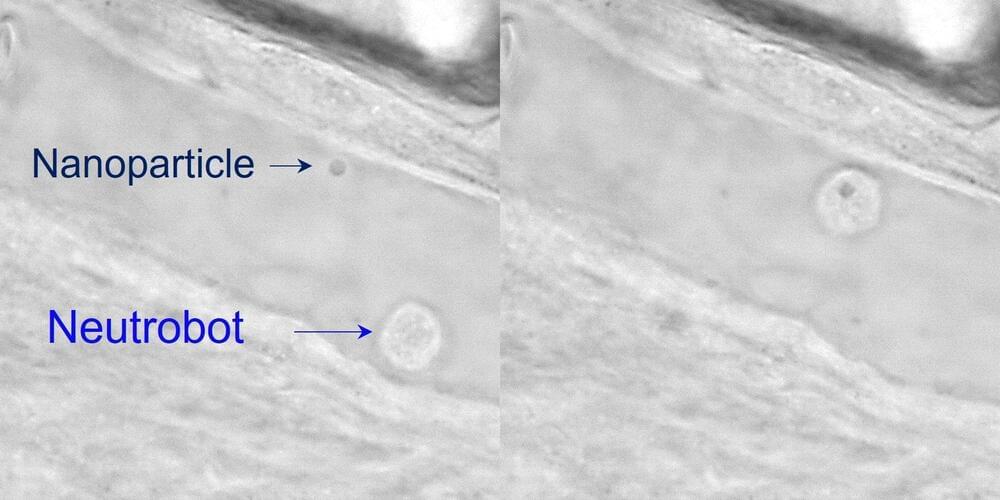
Researchers Use Lasers to Transform Neutrophils into Medicinal Microrobots
Medical microrobots could aid doctors in providing better illness prevention and treatment. However, the majority of these gadgets are created from synthetic materials that incite in vivo immunological reactions.
Scientists have now successfully utilized lasers to precisely manipulate neutrophils, a type of white blood cell, in living fish as a natural, biocompatible microrobot for the first time, as reported in ACS Central Science.
Microrobots that are now being developed for medical use need to be injected into an animal or ingested as capsules. However, scientists have discovered that these tiny items frequently cause immunological reactions in small animals, which prevents the elimination of microrobots from the body before they can carry out their functions.
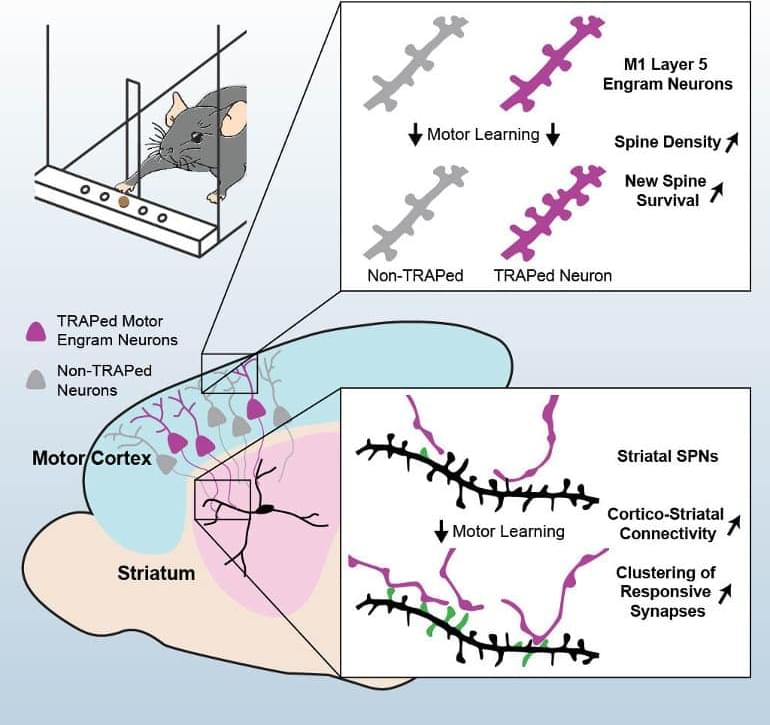
Observing Memory Formation in Real Time
Summary: Study reveals how motor memories are formed and how they remain persistent. The findings may help illuminate the root cause of motor disorders like Parkinson’s disease.
Source: Stanford.
Why is it that someone who hasn’t ridden a bicycle in decades can likely jump on and ride away without a wobble, but could probably not recall more than a name or two from their 3rd grade class?
