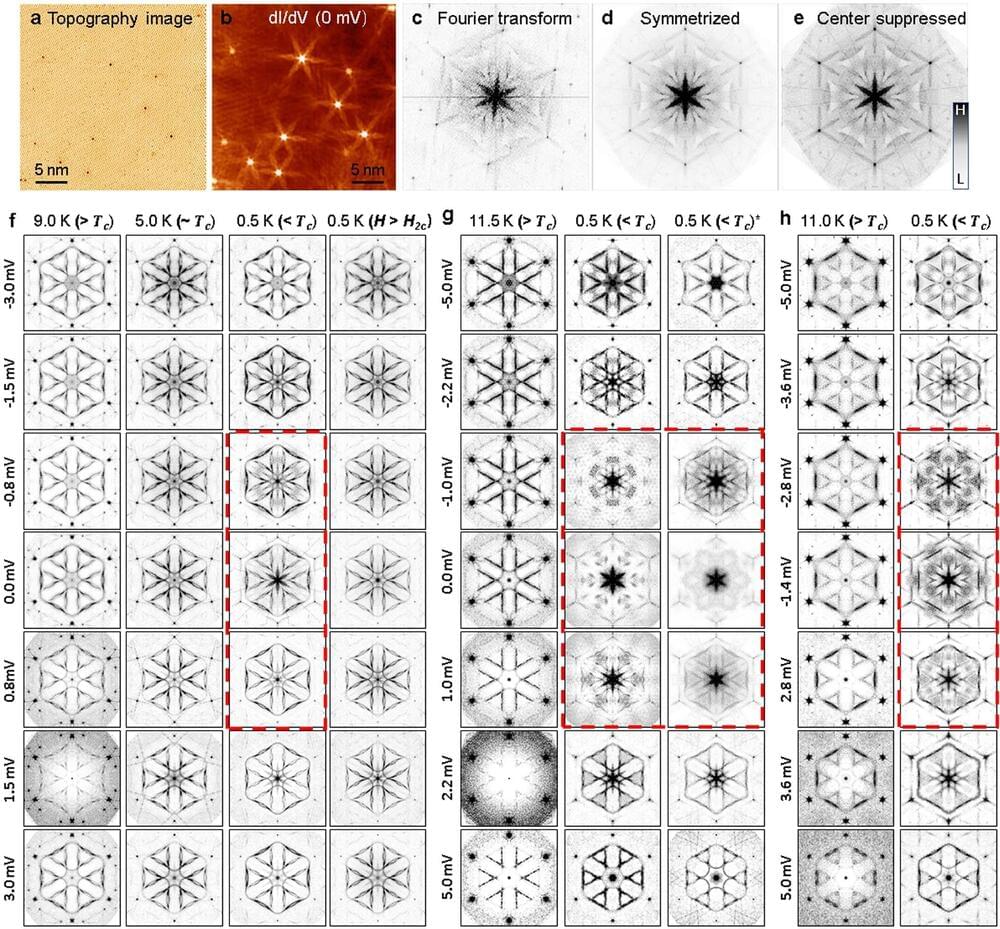
The University of Tennessee’s physicists have led a scientific team that found silicon—a mainstay of the soon-to-be trillion-dollar electronics industry—can host a novel form of superconductivity that could bring rapidly emerging quantum technologies closer to industrial scale production.
The findings are reported in Nature Physics and involve electron theft, time reversal, and a little electronic ambidexterity.
Superconductors conduct electric current without resistance or energy dissipation. Their uses range from powerful electromagnets for particle accelerators and medical MRI devices to ultrasensitive magnetic sensors to quantum computers. Superconductivity is a spectacular display of quantum mechanics in action on a macroscopic scale. It all comes down to the electrons.