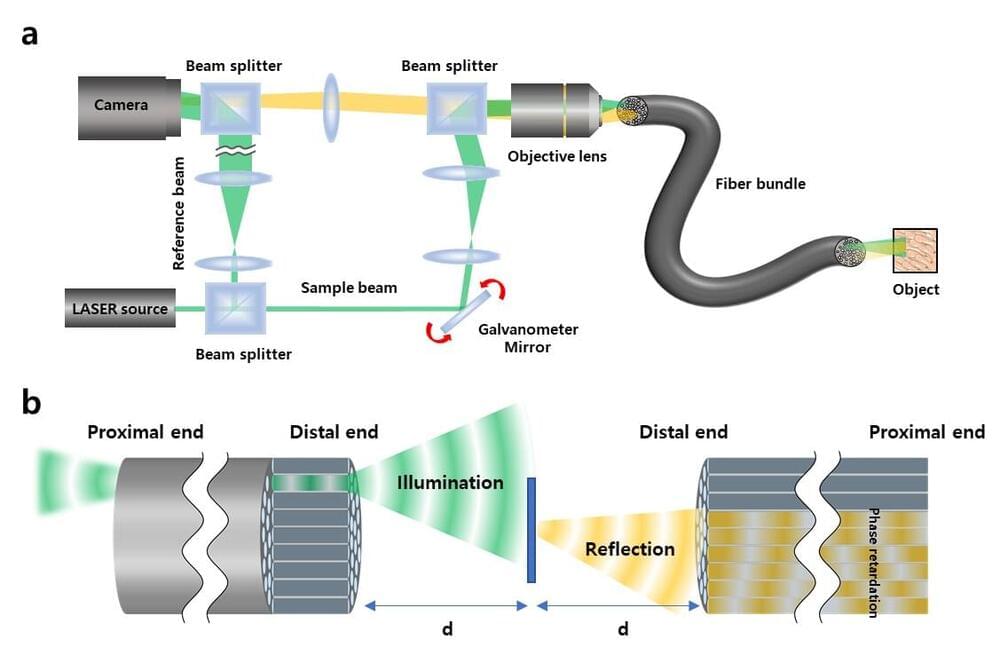
If you are used to getting regular health checkups, you might be familiar with endoscopes. The endoscope is an imaging device consisting of a camera and a light guide attached to a long flexible tube. It is particularly useful for acquiring images of the inside of a human body. For example, stomach and colon endoscopy are widely used for the early detection and diagnosis of diseases such as ulcers and cancers.
In general, an endoscope is manufactured by attaching a camera sensor to the end of a probe or using an optical fiber, which allows for information to be transmitted using light. In the case of an endoscope that uses a camera sensor, the thickness of the probe increases, which makes the endoscopy rather invasive. In the case of an endoscope using an optical fiber bundle, it can be manufactured in a thinner form factor, which minimizes invasiveness and results in much less discomfort to the patients.
However, the downside is that in a conventional fiber-bundle endoscope, it is difficult to perform high-resolution imaging, because the resolution of the obtained image is limited by the size of the individual fiber cores. Much of the image information is also lost due to reflection from the probe tip. Furthermore, in fiber endoscopy, it is often necessary to label the target with fluorescence, especially in biological samples with low reflectivity, due to strong back-reflection noise generated from the tip of the thin probe.