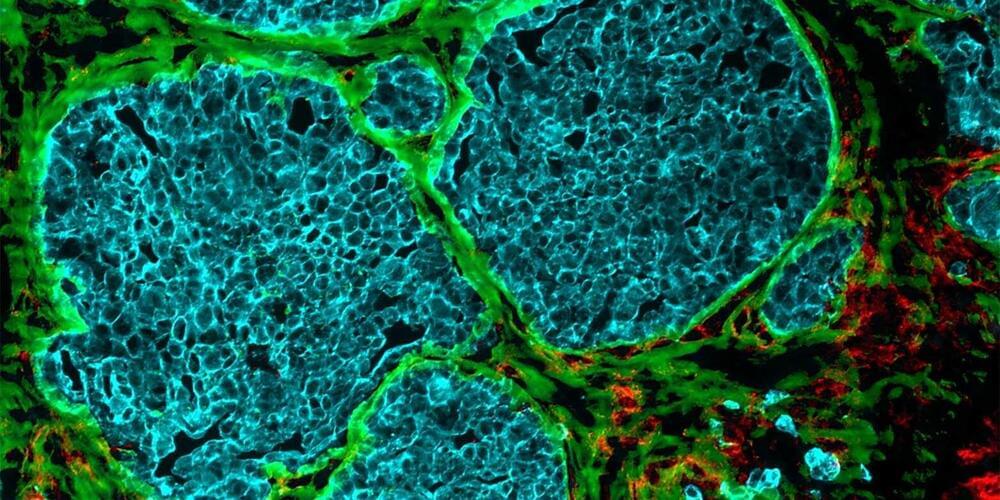
Increasingly dense cell clusters in growing tumors convert blood vessels into fiber-filled channels. This makes immune cells less effective, as findings by researchers from ETH Zurich and the University of Strasbourg suggest. Their research is published in Matrix Biology.
It was almost ten years ago that researchers first observed that tumors occurring in different cancers—including colorectal cancer, breast cancer and melanoma—exhibit channels leading from the surface to the inside of the cell cluster. But how these channels form, and what functions they perform, long remained a mystery.
Through a series of elaborate and detailed experiments, the research groups led by Viola Vogel, Professor of Applied Mechanobiology at ETH Zurich, and Gertraud Orend from the University of Strasbourg have found possible answers to these questions. There is a great deal of evidence to suggest that these channels, which the researchers have dubbed tumor tracks, were once blood vessels.