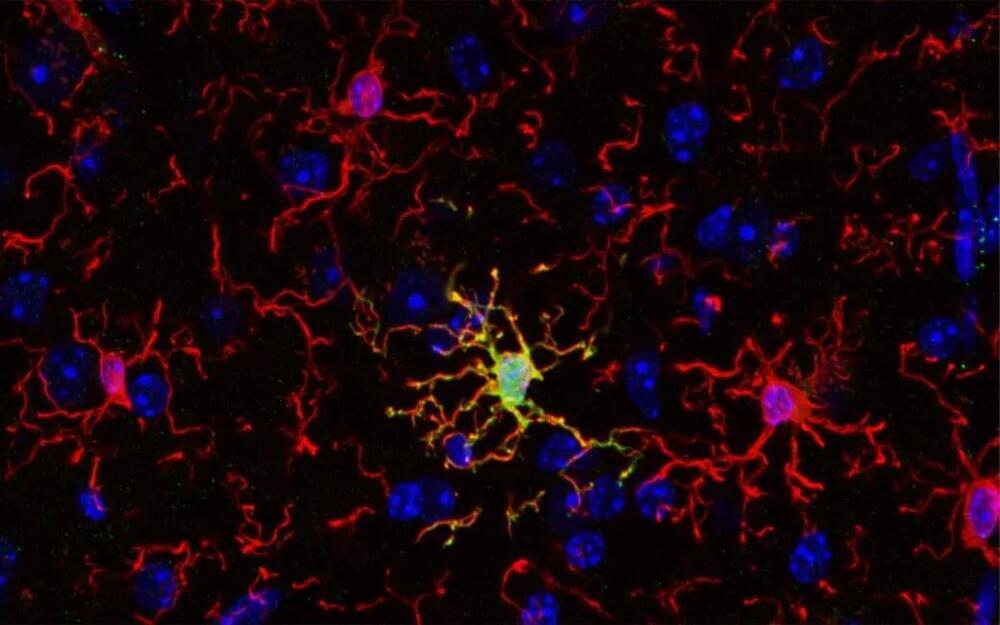
A recent study published in Nature Neuroscience indicates that, contrary to common belief, the immune cells of the brain, known as microglia, are not all the same. Researchers found that a unique microglial subset with unique features and function is important for establishing proper cognitive functions in mice. Evidence for such microglial subsets exists also for the human brain, opening exciting new possibilities for novel therapies.
An international collaboration led by researchers from University of Helsinki, Karolinska Institutet and University of Seville characterized ARG1+ microglia, a subset of microglial cells, that produces the enzyme called arginase-1 (ARG1). Using advanced imaging techniques, the team found that ARG1+ microglia are abundant during development and less prevalent in adult animals. Strikingly, these ARG1+ microglia are located in specific brain areas important for cognitive functions such as learning, thinking and memory.
“Cognition and memory are crucial components of what makes us human, and microglia are necessary for proper brain development and function. Cognitive decline is a common feature of neurodegenerative and psychiatric conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, schizophrenia and depression,” says Dr. Vassilis Stratoulias, senior researcher at the University of Helsinki and lead author of the study.