Solving a notorious quantum quandary could require abandoning some of science’s most cherished assumptions about the physical world.


The Forever Healthy Foundation is pleased to announce the second edition of the Rejuvenation Startup Summit, following the inaugural Rejuvenation Startup Summit in 2022 with more than 400 participants from over 30 countries. It will take place on 10–11 May 2024 in Berlin. The Rejuvenation Startup Summit is the world’s largest in-person gathering of longevity startups. It brings together startups, members of the longevity venture capital / investor ecosystem, and researchers interested in starting or joining a startup – all with the goal of accelerating the development of the rejuvenation biotech industry.
At Blueprint we’ve explored and evaluated hundreds of anti-aging therapies.
Recently, we had a daring idea: what if my father, son and I completed the world’s first ever multi-generational plasma exchange?
Plasma is the yellowish, liquid part of your blood. There is emerging evidence that plasma exchanges may offer various health benefits.
Nervous but excited, we travelled to a transfusion centre in Dallas Texas to make it happen.
I’ve invested millions of dollars building the world’s leading anti-aging protocol, becoming the most measured human in history. Blueprint is an algorithm, built by science, that takes better care of me than I can myself.
And it’s available to you for free. Check out the Blueprint website for recipes, exercise, and other protocols. Become the next evolution of human.

The other day a friend proudly told me she wrote a heartwarming graduation card to her teenage son. “Okay,” she confessed. “I
How long was your card? I asked her.
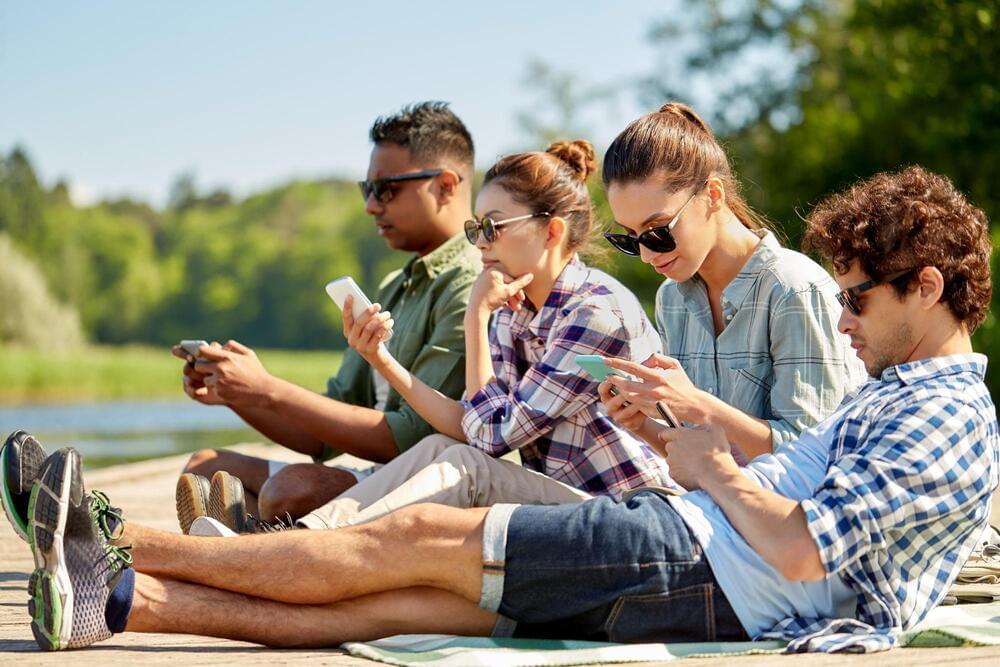
Not only that, but many also couldn’t even generate a topic on their own. They lacked creativity to dream up their own ideas, much less the critical thinking skills to put themselves in the shoes of their audience, imagining what would land. But they all had 4.0 GPAs or higher and came from private schools in Orange County and LA, reflecting our watered-down educational system.
And now we’re being told ChatGPT is a boon for our students?
Despite these concerns, our best days are ahead of us. As a positive futurist, I see the AI surge as a wakeup call. Especially in corporate America. For too long, we’ve outsourced too much. As just one example, the COVID-19 pandemic exposed how reliant we are on countries like China for manufacturing, including our critical medical supply chain.

Summary: Neurons in the hippocampus vary in function depending on their exact genetic identity. The study revealed these neurons, once believed to be homogeneous, are quite diverse and encode task-related information differently based on their location. This newfound understanding of neuronal diversity could lead to better comprehension of brain functions, memory capacity, and potentially advance disease treatment strategies.
Key Facts:
Summary: Researchers used artificial intelligence to predict how enzymes interact with various substrates. The team developed an AI model that can accurately predict whether an enzyme can work with a particular molecule.
Their enzyme substrate prediction (ESP) model provides a valuable tool for drug research and biotechnology, with applications ranging from the creation of new drugs to the production of biofuels.
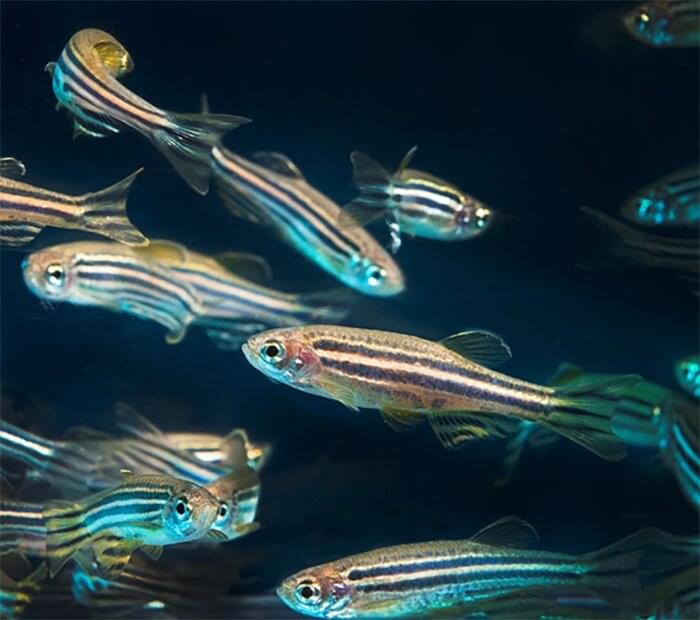


Lifespan by simply slowing the aging of an organ, such as the intestine? CNRS researchers have discovered how to extend the life expectancy of zebrafish by reactivating a gene within intestinal cells. The results were published in the journal Nature Aging on May 4, 2023.
The intestine plays a crucial role in an anti-aging approach as well as general health. Over a century ago, Elie Metchnikov observed that aging ensued from increased inflammation of the intestine and microbial infiltration within blood circulation. The more we age, the less the digestive tract serves as a barrier, allowing the undesirable particles and bacteria that cause the more rapid aging of the organism to pass through.
In a new study, Miguel Godinho Ferreira and his team at the Institute for Research on Cancer and Aging (Ircan) in Nice (CNRS/Inserm/Université Côte d’Azur) have studied the impact on aging of telomere length in the intestinal cells of zebrafish. As with humans, these chromosome extremities shrink faster in the intestine than in other organs during the course of a life, which is why this process plays such an important role in aging.

Join us at 6:00 pm EST (11:00 pm UTC) for our Perpetual Life Hybrid Party live from our new location at 950 South Cypress Road in Pompano Beach, FL, & socialize with Immortalists from Around the World, hosted by hosted by Tonya Scholz & Rudi Hoffman.
Stay “In Zoom” for our 7:00 pm (12:00 am-midnight UTC) YouTube Streaming Service. This month, we are excited to have two speakers. First, Erik Nelson, Director of Clinical Programs at The Healthy Longevity Clinic, will present “Into the World of Longevity Medicine.”
Second, Bill Faloon: A founder of The Church of Perpetual Life and a leader in the Global Age Reversal movement, Bill will give a NEW Age Reversal Update at this service.
Quantum biology explores how quantum effects influence biological processes, potentially leading to breakthroughs in medicine and biotechnology. Despite the assumption that quantum effects rapidly disappear in biological systems, research suggests these effects play a key role in physiological processes. This opens up the possibility of manipulating these processes to create non-invasive, remote-controlled therapeutic devices. However, achieving this requires a new, interdisciplinary approach to scientific research.
Imagine using your cell phone to control the activity of your own cells to treat injuries and diseases. It sounds like something from the imagination of an overly optimistic science fiction writer. But this may one day be a possibility through the emerging field of quantum biology.
Over the past few decades, scientists have made incredible progress in understanding and manipulating biological systems at increasingly small scales, from protein folding to genetic engineering. And yet, the extent to which quantum effects influence living systems remains barely understood.