😗
PMSC-mediated exocrine pancreas regeneration initiates recovery of endogenous pancreas to alleviate type 1 diabetes in mice.

This post is also available in:  עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)
How soon will we be seeing robots walking about the street? How soon will robots join medical staff in hospitals and aid real people in life or death situations? How soon will robots replace health staff? The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that we will see a global shortfall of 12 million health workers by 2025.
From lifting patients and delivering lab samples, to cleaning and providing companionship, care robots can help with a range of tasks across a hospital or care setting. With nurses spending up to a third of their shift on menial tasks such as collecting equipment, the expectation is that care robots will be able to take ownership of these more mundane jobs, letting health staff focus on more important tasks.

Imaging deep tissues with light is challenging. Visible light is often quickly absorbed and scattered by structures and molecules in the body, preventing researchers from seeing deeper than a millimeter within a tissue. If they do manage to probe further, substances like collagen or melanin often muddy the image, creating the equivalent of background noise through their natural fluorescence. As the authors explained, “Biological tissues have strong optical attenuation in the visible wavelength range (350–700 nm), due to the absorption of hemoglobin and melanin, as well as the tissue scattering, which fundamentally limits the imaging depth of high-resolution optical technologies.”
To wade out from these muddied waters, Yao and collaborator Vladislav Verkhusha, PhD, professor of genetics at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, developed a protein that absorbs and emits longer wavelengths of light in the near-infrared (NIR) spectrum. “Tissue is the most transparent in the 700‑1300 nm window of NIR light,” said Yao. “At those wavelengths, light can penetrate deeper into a tissue, and because there is less natural background fluorescence to filter out, we can take longer exposures and capture clearer images.”
Verkhusha and his lab used a process called directed molecular evolution to engineer their proteins, using photoreceptors normally found in bacteria as the basis for the structure. “The state-of-the-art NIR FPs were engineered from bacterial phytochrome photoreceptors (BphPs),” the team noted. “Applying rational design, we developed 17 kDa cyanobacteriochrome-based near-infrared (NIR-I) fluorescent protein, miRFP718nano.”


Everyone knows someone who has had cancer. In 2020, around 19 million new cases—and around 10 million deaths—were registered worldwide. Treatments are improving all the time, but can damage healthy cells or have severe side effects that are hard on patients. In the search for new, more targeted cancer drugs, traditional medicine offers many possible candidates.
A team of Polish scientists led by Magdalena Winkiel at Adam Mickiewicz University, publishing today in Frontiers in Pharmacology, has reviewed the bioactive compounds called glycoalkaloids, found in vegetables like potatoes and tomatoes, to demonstrate their potential to treat cancer.
“Scientists around the world are still searching for the drugs which will be lethal to cancer cells but at the same time safe for healthy cells,” said Winkiel.
Human beings can sometimes experience dissociative states, moments in which they feel disconnected from their body and the world around them. While these states have been linked to many psychiatric conditions, they can also be elicited by the intake of some legal and illegal drugs.
One of the most renowned dissociation-inducing drugs is ketamine, an anesthetic commonly used to sedate patients or reduce pain resulting from medical procedures. In recent years, ketamine has also been found to be a potentially valuable treatment for some cases of depression.
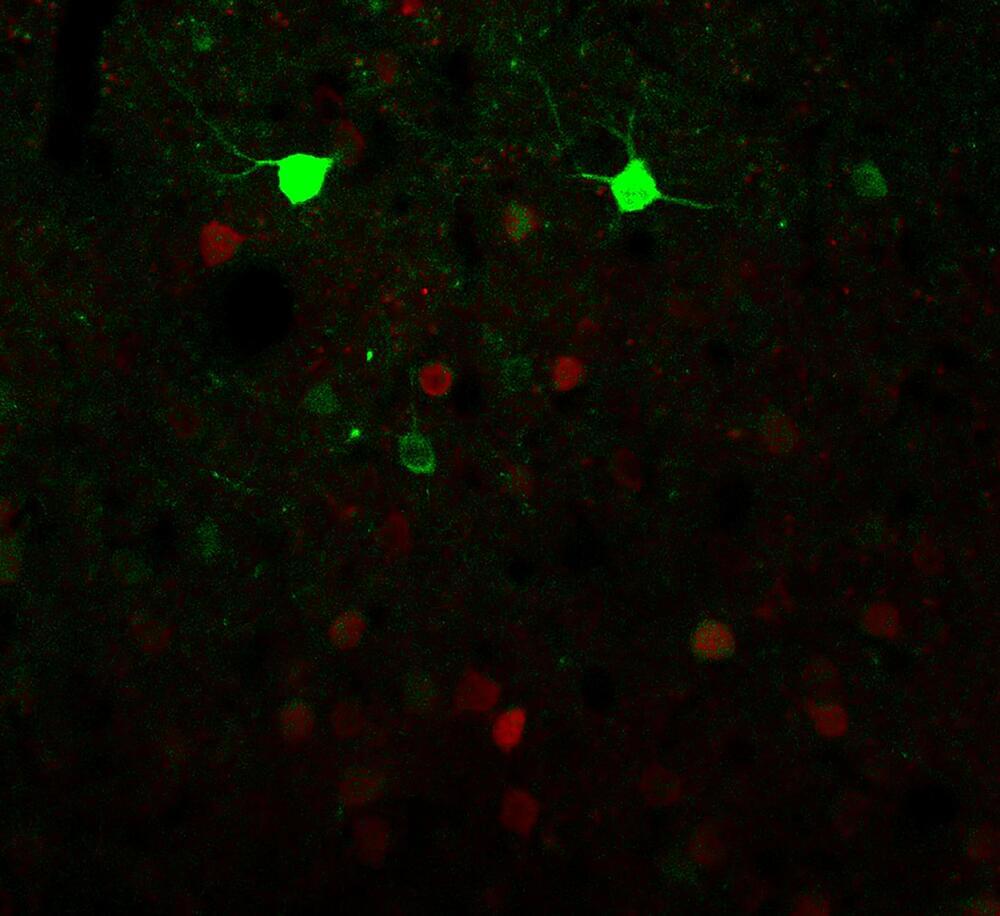
While several studies have investigated the therapeutic effects of this strong anesthetic, so far very little is known about the cellular and neuronal mechanisms behind the dissociative states it produces. A paper by a team of researchers at University of Pennsylvania, recently published in Nature Neuroscience, might shed some light on these so far elusive processes.
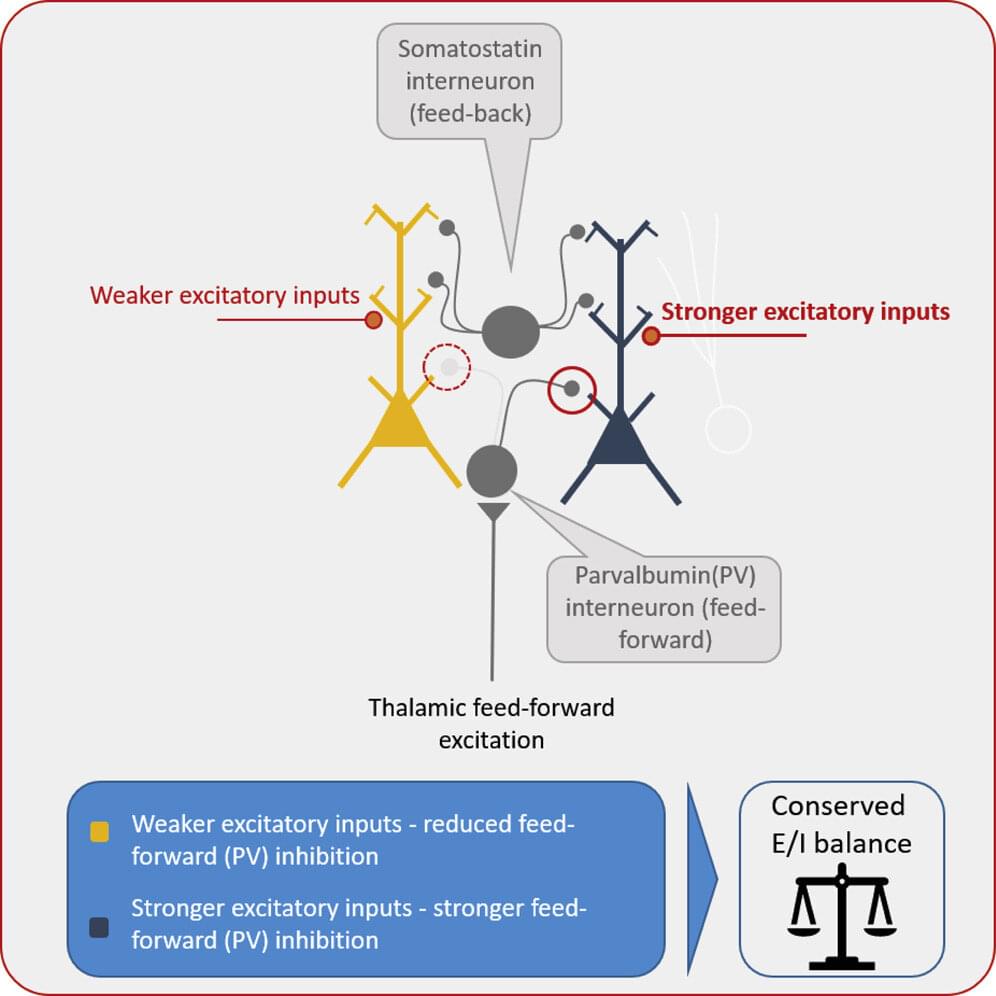
Nerve cells can regulate their sensitivity to incoming signals autonomously. A new study led by the University of Bonn has now discovered a mechanism that does just that. The German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases and the Max Planck Institute for Neurobiology of Behavior were involved in the work. The results have now been published in the journal Cell Reports.
Anyone who has ever sent a voice message with a cell phone knows how much the volume matters: Shouting into the microphone results in a distorted and unclear recording. But whispering is not a good idea either—then the result is too quiet and also difficult to understand. That is why sound engineers ensure the perfect sound at every concert and talk show: They regulate each microphone’s gain to match the input signal.
The neurons in the brain can also fine-tune their sensitivity, and even do so autonomously. A new study led by the University of Bonn and the University Hospital Bonn shows how they do this. For this purpose, the participants investigated nerve cell networks that also play a role in vision, hearing and touch. The stimulus first travels to the so-called thalamus, a structure deep in the center of the brain. From there, it is then conducted to the cerebral cortex, where it is further processed.
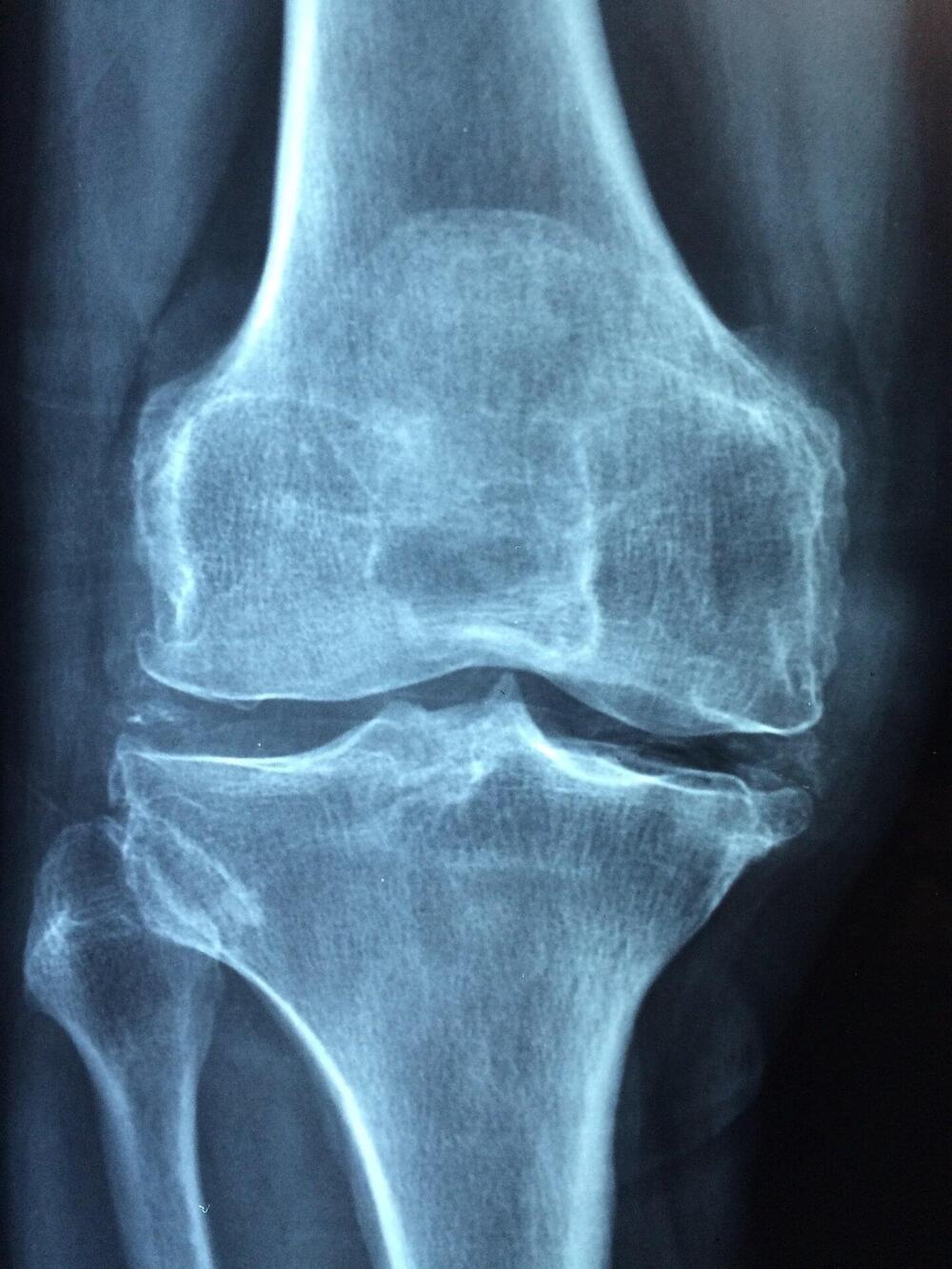
University of Central Florida researchers have created unique technology for treating osteoporosis that uses nanobubbles to deliver treatment to targeted areas of a person’s body.
The new technology was developed by Mehdi Razavi, an assistant professor in UCF’s College of Medicine and a member of the Biionix Cluster at UCF, and UCF biomedical sciences student Angela Shar at the Biomaterials and Nanomedicine Lab, as part of the lab’s focus on developing tools for diagnostics and therapeutics.
Osteoporosis is a disease marked by an imbalance between the body’s ability to form new bone tissue, or ossification, and break down, or remove, old bone, known as resorption.
Adopting and maintaining a healthy lifestyle might prevent up to 60% of inflammatory bowel disease cases—Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis—finds a large international study, published online in the journal Gut.
The findings prompt the study authors to suggest that subject to further research, particularly in those at high risk of developing these conditions, lifestyle changes may be a feasible option for future preventive strategies.
Inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD for short, affects an estimated 3 million adults in the U.S. and another 1.3 million in Europe, and diagnoses have been increasing, particularly in newly industrialized countries.

Breathing in common workplace dusts and fumes from agents such as vapors, gases, and solvents may heighten the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis, suggests research published online in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
What’s more, such vapors, gases, and solvents seem to boost the detrimental impact of smoking and genetic susceptibility to the disease, the findings indicate.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune joint disorder characterized by painful and disabling inflammation. It affects up to 1% of the world’s population.