The experimental interface allows the patient to communicate through a digital avatar, and it’s faster than her current system.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 1,143
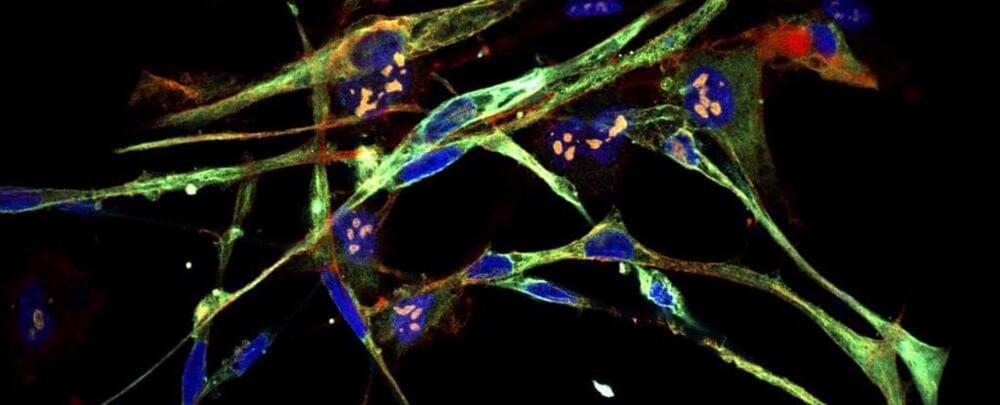
Aggressive Cancer Cells Transformed Into Healthy Cells in Breakthrough
This is good news! The article says this could lead to treatment of other cancers.
A particularly aggressive form of childhood cancer that forms in muscle tissue might have a new treatment option on the horizon.
Scientists have successfully induced rhabdomyosarcoma cells to transform into normal, healthy muscle cells. It’s a breakthrough that could see the development of new therapies for the cruel disease, and it could lead to similar breakthroughs for other types of human cancers.
“The cells literally turn into muscle,” says molecular biologist Christopher Vakoc of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
LiFi — This is the Fastest Internet in the World (224GBPS) — Easiest Explanation Ever!
#ted.
#wifi.
#internet.
What about 102,400 MBPS or 100GBPS. This is the speed of data transfer that you can achieve with LiFi Technology. With LiFi you can download 100 movies in just one second.
How’s this incredible internet speed possible?
It is possible with LED lights.
Watch this video till the end for a detailed introduction and truths of LiFi technology.
NEW HERE! TRY THIS STUFF
▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀
Warp Drive Technology.
Eye as a Camera.
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3Ur6HoAN3Vo.
Artificial Blood.
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MX3LU0ClFPw&t=24s.
Wireless Electricity.
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zGna5lTkBuc&t=65s.
📑 REFERENCES:
▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀
[1] The Technology of LiFi — E Ramadhani and G P Mahardika 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 325 012013
- https://bit.ly/3yMqSK9
[2] How Wireless Communication Works.
- https://bit.ly/3uUZZmq.
[3] Spectrum Crunch FAQ
- https://bit.ly/3AUCz47
[4] A Review Paper on LiFi Technology — Volume 5, Issue 23, International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
- https://bit.ly/3yCAEP6
[5] LiFi Study Paper Approved.
- https://bit.ly/3uOHLCL
[6] LiFi vs WiFI
- https://bit.ly/3II3zWt.
[7] LiFi Pros and Cons.
- https://bit.ly/3oaPsQd.
[8] How Does LiFi Work?
- https://bit.ly/3o8t3De.
[9] What is LiFi?
- https://bit.ly/3aJam5P
[10] LiFi Wikipedia.
- https://bit.ly/3cmhe9u.
WHO ARE WE?
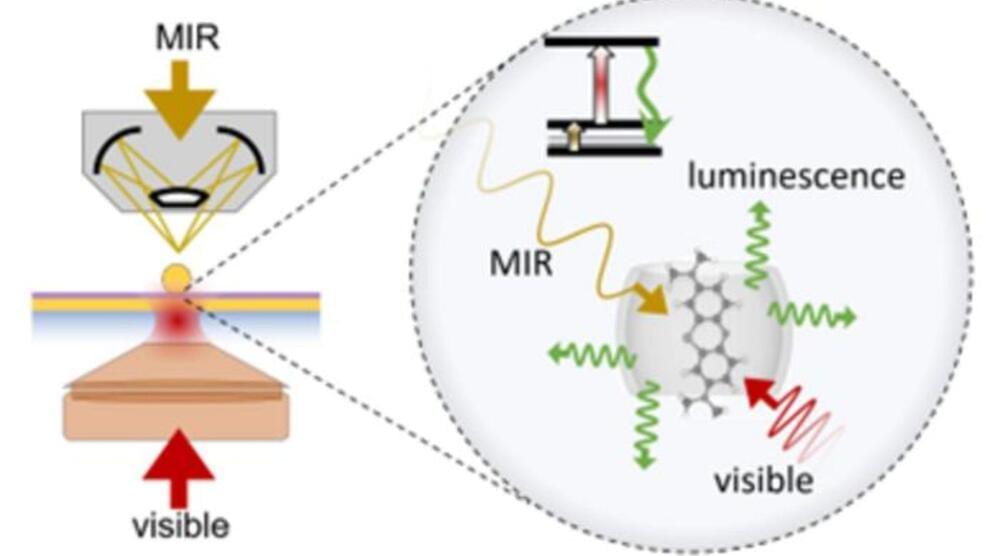
Visible infrared at room temperature achieved in a first
Rohit Chikkaraddy/ University of Birmingham.
Mid-infrared, as the name suggests, lies between the infrared spectrum’s near and far wavelengths, just outside those of visible light. The mid-infrared spectrum has gained particular importance as it has been useful for multiple applications ranging from military to environmental and medical treatments and studying celestial objects.
Mitochondria in Cancer Stem Cells: From an Innocent Bystander to a Central Player in Therapy Resistance
1 Department of Biotechnology, School of Science, GITAM (Deemed to be University), Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, 530,045, India; 2 Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, 61,801, USA
Correspondence: Sireesha V Garimella; Pankaj Chaturvedi, Email [email protected]; [email protected]
Abstract: Cancer continues to rank among the world’s leading causes of mortality despite advancements in treatment. Cancer stem cells, which can self-renew, are present in low abundance and contribute significantly to tumor recurrence, tumorigenicity, and drug resistance to various therapies. The drug resistance observed in cancer stem cells is attributed to several factors, such as cellular quiescence, dormancy, elevated aldehyde dehydrogenase activity, apoptosis evasion mechanisms, high expression of drug efflux pumps, protective vascular niche, enhanced DNA damage response, scavenging of reactive oxygen species, hypoxic stability, and stemness-related signaling pathways. Multiple studies have shown that mitochondria play a pivotal role in conferring drug resistance to cancer stem cells, through mitochondrial biogenesis, metabolism, and dynamics. A better understanding of how mitochondria contribute to tumorigenesis, heterogeneity, and drug resistance could lead to the development of innovative cancer treatments.
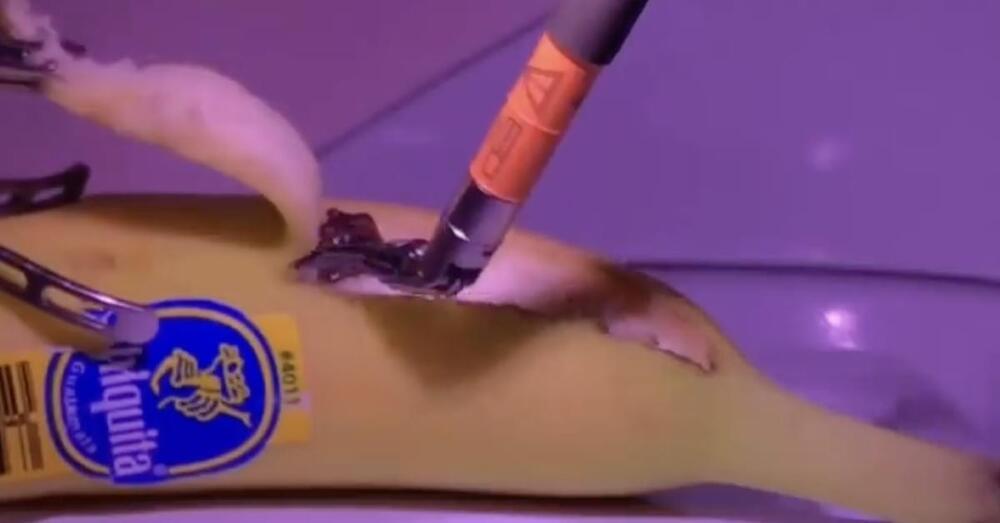

No, they did not do surgery on a banana over 5G
If your mother says she loves you: check it.
A couple weeks ago, I asked Vergecast.
What I was not expecting was for so many people to send me versions of a video that shows a banana getting stitches in a robotic surgery device, with the captions claiming that the surgery is being done remotely over 5G. This video has had an … More.
Meet Dr. Kais Rona, who is as befuddled by the lie appended to his video as anyone else.
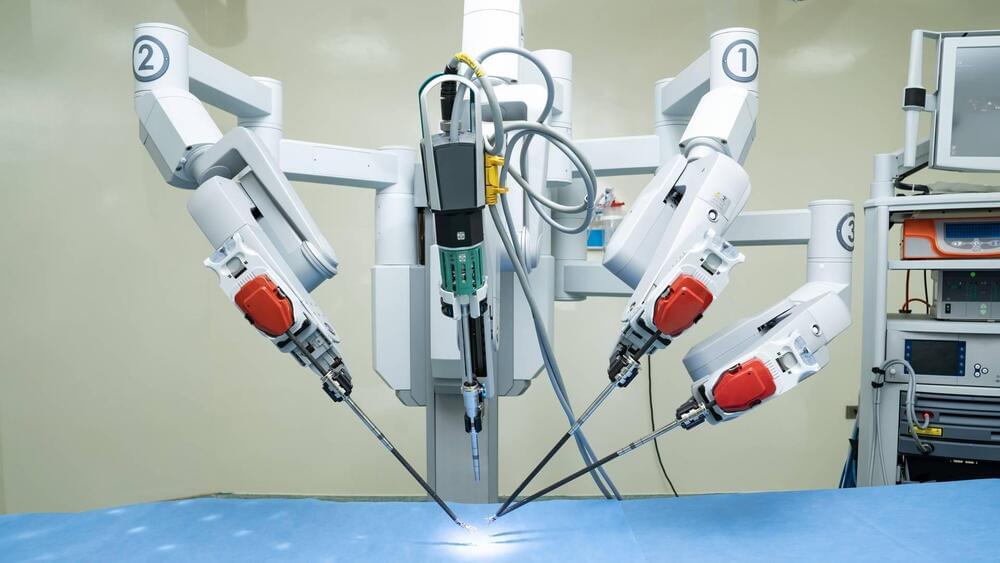
How one robot saved a patient from an inoperable tumor
The Da Vinci robot was able to undertake an operation no doctor would.
Robots are increasingly showing up in operating rooms and they are saving lives. As one patient in Canada reports in a CBC
Glenn Deir recounts the story of how his inoperable tumor nearly cost him his life and thanks the robot that saved him.
Are we failing to bridge the gap in HPV vaccine coverage globally?
Study reveals stark global inequities in HPV vaccine coverage across 84 countries, finding that nations with the highest burden of cervical cancer often have the lowest vaccination rates. However, new WHO recommendations and an increase in vaccine supply may help narrow this gap and improve equitable access.
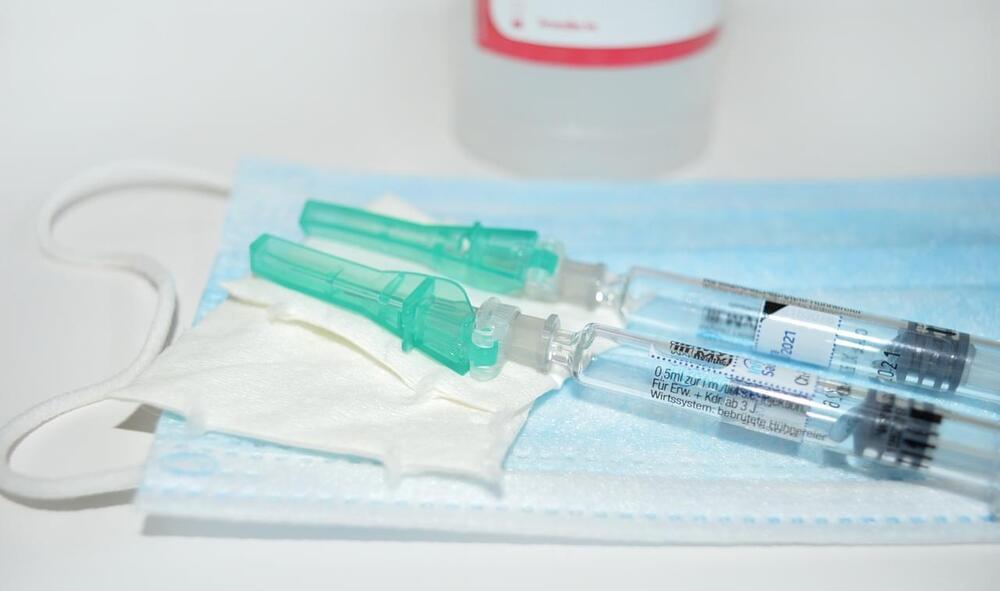
A universal influenza vaccine
The article titled “Evaluation of OVX836: A Promising Universal Influenza Vaccine Candidate” published in The Lancet presents a comprehensive assessment of OVX836, a novel influenza vaccine candidate targeting the nucleoprotein of influenza A virus. Authored by a team of researchers led by IL-R at CEVAC Clinical Unit and Laboratory, the study aims to investigate the safety, immunogenicity, and potential efficacy of OVX836 at different doses, shedding light on its potential as a universal influenza vaccine.
Influenza remains a significant global health concern, with seasonal epidemics and occasional pandemics causing substantial morbidity and mortality. Current influenza vaccines primarily focus on the viral surface protein hemagglutinin, but their efficacy is limited by antigenic variation and the emergence of new strains. Current vaccines are developed for the season based on what strains were prominent in the last season. Additionally, vaccine efficacies can vary from season to season. OVX836 takes a different approach by targeting the highly conserved nucleoprotein, which plays a crucial role in the influenza virus life cycle.
OVX836 elicited a robust immune response, characterized by significant increases in nucleoprotein-specific CD4 and CD8 T-cell responses, as well as the production of anti-nucleoprotein IgG antibodies. The magnitude of these immune responses displayed a dose-dependent relationship, with higher doses of OVX836 leading to stronger immune reactions. Of particular interest was the induction of a CD8 T-cell response, a rare achievement for influenza vaccines and a crucial component of comprehensive immune protection.
What’s Next For AI In Healthcare In 2023? — The Medical Futurist
AI is the undoubted buzzword of the year, so let’s take a look at what we can expect from AI in healthcare in the coming period.