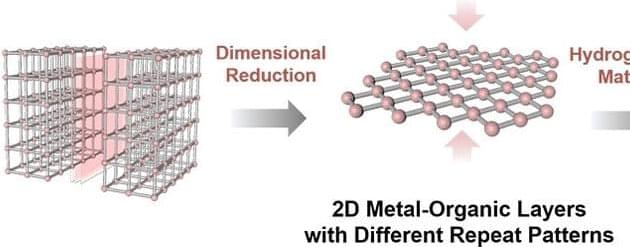
The concept of biological immortality challenges the belief that death gives meaning to life and raises questions about the potential societal implications and ethical considerations of living indefinitely.
Questions to inspire discussion.
What is biological immortality?
—Biological immortality refers to the potential for humans to live indefinitely due to advancements in science and technology, leading to the elimination of age-related diseases and the aging process.