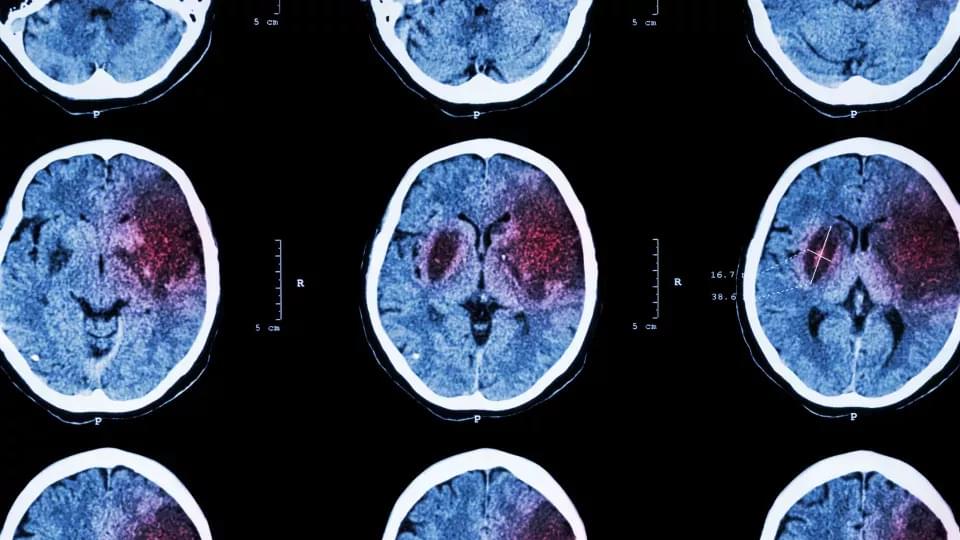
In 2001, Gina Arata was in her final semester of college, planning to apply to law school, when she suffered a traumatic brain injury in a car accident. The injury so compromised her ability to focus she struggled in a job sorting mail.
“I couldn’t remember anything,” said Arata, who lives in Modesto with her parents. “My left foot dropped, so I’d trip over things all the time. I was always in car accidents. And I had no filter—I’d get pissed off really easily.”
Her parents learned about research being conducted at Stanford Medicine and reached out; Arata was accepted as a participant. In 2018, physicians surgically implanted a device deep inside her brain, then carefully calibrated the device’s electrical activity to stimulate the networks the injury had subdued. The results of the clinical trial were published Dec. 4 in Nature Medicine.