With funds from national grants and private philanthropy, Duke University scientists are working to develop a universal flu vaccine that would last last much longer than the current flu vaccines.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 1,046
Synthetic Evolution: Genetically Minimal Artificial Cells Prove “Life Finds a Way”
Scientists discovered that a synthetic cell with a reduced genome could evolve as quickly as a normal cell. Despite losing 45% of its original genes, the cell adapted and demonstrated resilience in a laboratory experiment lasting 300 days, effectively showcasing that evolution occurs even under perceived limitations.
“Listen, if there’s one thing the history of evolution has taught us is that life will not be contained. Life breaks free. It expands to new territories, and it crashes through barriers painfully, maybe even dangerously, but… ife finds a way,” said Ian Malcolm, Jeff Goldblum’s character in Jurassic.
The Jurassic period is a geologic time period and system that spanned 56 million years from the end of the Triassic Period about 201.3 million years ago to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period 145 million years ago. It constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic Era and is divided into three epochs: Early, Middle, and Late. The name “Jurassic” was given to the period by geologists in the early 19th century based on the rock formations found in the Jura Mountains, which were formed during the Jurassic period.

Google’s medical AI chatbot is already being tested in hospitals
The Mayo Clinic has reportedly been testing the system since April.
Google’s Med-PaLM 2, an AI tool designed to answer questions about medical information, has been in testing at the Mayo Clinic research hospital, among others, since April, The Wall Street Journal.
WSJ reports that an internal email it saw said Google believes its updated model can be particularly helpful in countries with “more limited access to doctors.” Med-PaLM 2 was trained on a curated set of medical expert demonstrations, which Google believes will make it… More.
Google says doctors prefer its answers, even if they’re less accurate.
Researchers successfully implanted the first artificial tubular muscle in vivo
In January 2021, EPFL engineers announced in Advanced Science their concept of a novel cardiac assist device that is devoid of rigid metallic components. It consists of a soft, artificial muscle wrapped around the aorta that can constrict and dilate the vessel, ultimately enhancing the aorta’s natural function and aiding the heart to pump blood to the rest of the body.
Now June 2021, EPFL engineers led by Yves Perriard of the Laboratory of Integrated Actuators in collaboration with University of Bern, have successfully implanted their first artificial tubular muscle, in vivo, in a pig. During the 4-hour long operation, their cardiac assist device maintained 24 000 pulsations, of which 1,500 were activated artificially by the augmented aorta.
More information with downloadable pdf:
https://infoscience.epfl.ch/record/296049
In January of this year, EPFL engineers announced in Advanced Science their concept of a novel cardiac assist device that is devoid of rigid metallic components. It consists of a soft, artificial muscle wrapped around the aorta that can constrict and dilate the vessel, ultimately enhancing the aorta’s natural function and aiding the heart to pump blood to the rest of the body.
Now, EPFL engineers led by Yves Perriard of the Laboratory of Integrated Actuators in collaboration with University of Bern, have successfully implanted their first artificial tubular muscle, in vivo, in a pig. During the 4-hour long operation, their cardiac assist device maintained 24 000 pulsations, of which 1,500 were activated artificially by the augmented aorta.

When it comes to health care, will AI be helpful or harmful?
Artificial intelligence algorithms, such as the sophisticated natural language processor ChatGPT, are raising hopes, eyebrows and alarm bells in multiple industries. A deluge of news articles and opinion pieces, reflecting both concerns about and promises of the rapidly advancing field, often note AI’s potential to spread misinformation and replace human workers on a massive scale. According to Jonathan Chen, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine, the speculation about large-scale disruptions has a kernel of truth to it, but it misses another element when it comes to health care: AI will bring benefits to both patients and providers.
Chen discussed the challenges with and potential for AI in health care in a commentary published in JAMA on April 28. In this Q&A, he expands on how he sees AI integrating into health care.
The algorithms we’re seeing emerge have really popped open Pandora’s box and, ready or not, AI will substantially change the way physicians work and the way patients interact with clinical medicine. For example, we can tell our patients that they should not be using these tools for medical advice or self-diagnosis, but we know that thousands, if not millions, of people are already doing it — typing in symptoms and asking the models what might be ailing them.
Newfound CRISPR-Like System In Animals Could Be Used To Manipulate Human Genomes
A genetic editing system similar to CRISPR-Cas9 has been uncovered for the first time in eukaryotes – the group of organisms that include fungi, plants, and animals. The system, based on a protein called Fanzor, can be guided to precisely target and edit sections of DNA, and that could open up the possibility of its use as a human genome editing tool.
The research team, led by Professor Feng Zhang at the McGovern Institute for Brain Research at MIT and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, began to suspect that Fanzor proteins might act as nucleases – enzymes that can chop up nucleic acids, like DNA – during a previous investigation.
They were looking into the origins of proteins like Cas9. This is the enzyme part of the CRISPR-Cas9 system. CRISPR (short for clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) sequences are the guide to particular regions of DNA, and Cas9 makes the cut. We hear a lot about CRISPR-Cas systems and their applications in medicine and biotechnology, but you may not be aware that they originate in bacteria, where they play a key role in immunity against viruses.

Machine learning enables accurate electronic structure calculations at large scales for material modeling
The arrangement of electrons in matter, known as the electronic structure, plays a crucial role in fundamental but also applied research, such as drug design and energy storage. However, the lack of a simulation technique that offers both high fidelity and scalability across different time and length scales has long been a roadblock for the progress of these technologies.
Researchers from the Center for Advanced Systems Understanding (CASUS) at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) in Görlitz, Germany, and Sandia National Laboratories in Albuquerque, New Mexico, U.S., have now pioneered a machine learning–based simulation method that supersedes traditional electronic structure simulation techniques.
Their Materials Learning Algorithms (MALA) software stack enables access to previously unattainable length scales. The work is published in the journal npj Computational Materials.
Artificial Muscles Flex for the First Time: Ferroelectric Polymer Innovation in Robotics
Interesting discovery! I’d love to see it in action.
A new ferroelectric polymer that efficiently converts electrical energy into mechanical strain has been developed by Penn State researchers. This material, showing potential for use in medical devices and robotics, overcomes traditional piezoelectric limitations. Researchers improved performance by creating a polymer nanocomposite, significantly reducing the necessary driving field strength, expanding potential applications.
A new type of ferroelectric polymer that is exceptionally good at converting electrical energy into mechanical strain holds promise as a high-performance motion controller or “actuator” with great potential for applications in medical devices, advanced robotics, and precision positioning systems, according to a team of international researchers led by Penn State.
Mechanical strain, how a material changes shape when force is applied, is an important property for an actuator, which is any material that will change or deform when an external force such as electrical energy is applied. Traditionally, these actuator materials were rigid, but soft actuators such as ferrroelectric polymers display higher flexibility and environmental adaptability.
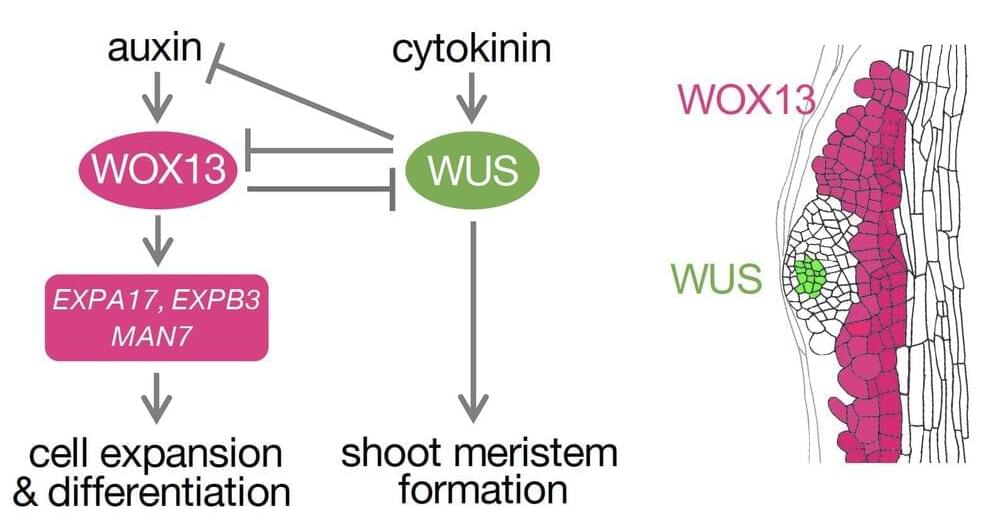
Study uncovers the secrets of plant regeneration
Plants have the unique ability to regenerate entirely from a somatic cell, i.e., an ordinary cell that does not typically participate in reproduction. This process involves the de novo (or new) formation of a shoot apical meristem (SAM) that gives rise to lateral organs, which are key for the plant’s reconstruction.
At the cellular level, SAM formation is tightly regulated by either positive or negative regulators (genes/protein molecules) that may induce or restrict shoot regeneration, respectively. But which molecules are involved? Are there other regulatory layers that are yet to be uncovered?
To seek answers to the above questions, a research group led by Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST), Japan studied the process in Arabidopsis, a plant commonly used in genetic research. Their research—which was published in Science Advances —identified and characterized a key negative regulator of shoot regeneration.