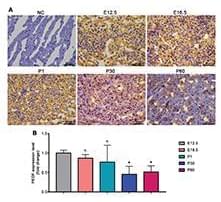
A cell’s identity is based on the genes it expresses, and scientists have been studying gene expression mechanisms for many years. But the process involves molecules that are too small to see, until the recent development of a technique called expansion microscopy. With expansion microscopy, scientists preserve tissue, and then enlarge it; this can make very small structures much easier to see. Researchers have now improved the technology, and even after increasing the size of zebrafish embryonic cell nuclei by 4,000 times, they were able to see the influence of individual molecules on gene expression. The findings, which have enhanced our understanding of gene regulation, have been reported in Science.
With this technique, investigators can now visualize the fundamental processes of the cell that form the basis of life. “We can see processes that we could only imagine before,” said co-senior study author Antonio Giraldez, Ph.D., Fergus F. Wallace Professor of Genetics at Yale School of Medicine.