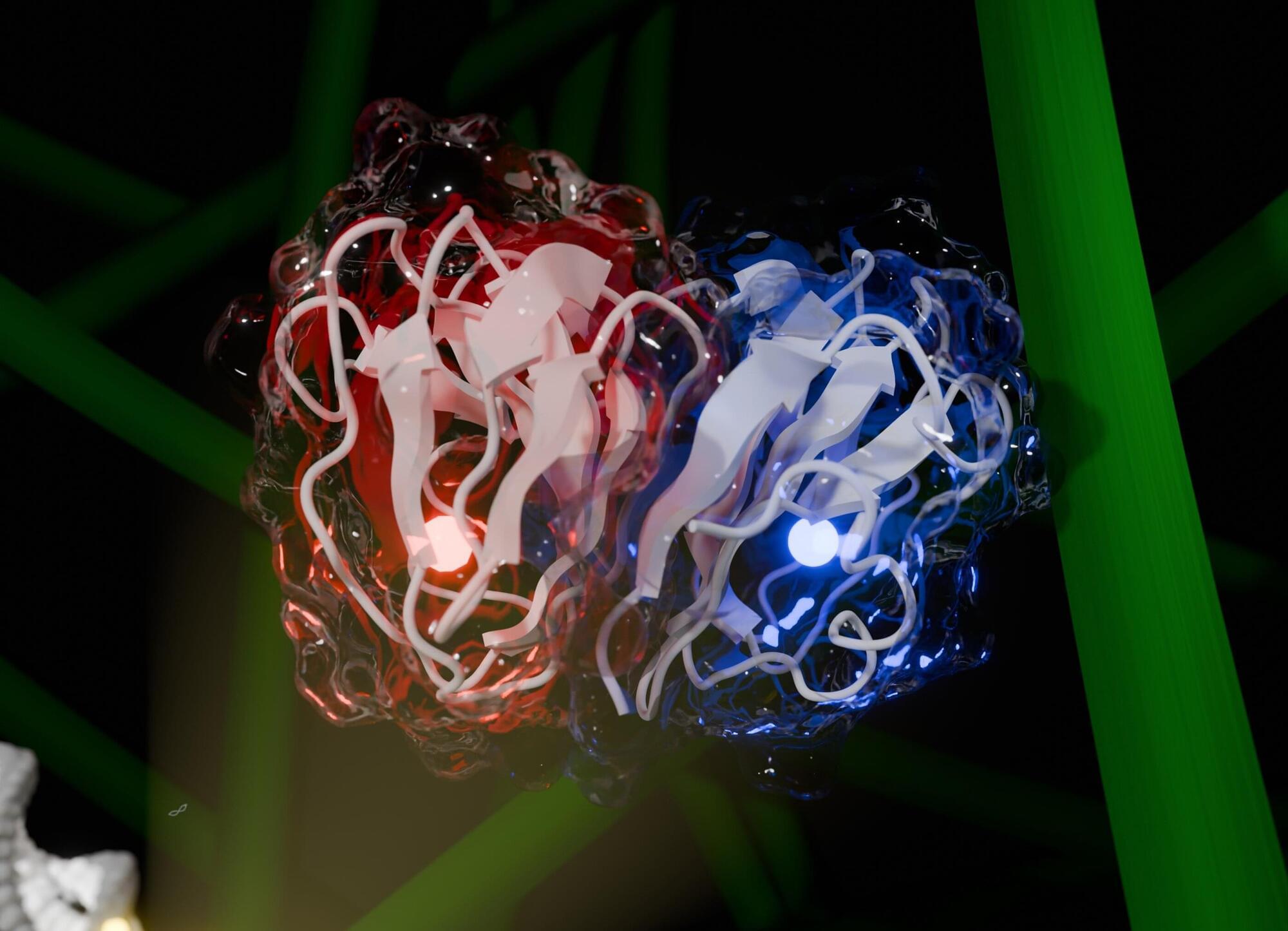
The deconstruction of cellulose is essential for the conversion of biomass into fuels and chemicals. But cellulose, the most abundant renewable polymer on the planet, is extremely recalcitrant to biological depolymerization. Although composed entirely of glucose units, its crystalline microfibrillar structure and association with lignin and hemicelluloses in plant cell walls make it highly resistant to degradation.
As a result, its degradation in nature is slow and requires complex enzymatic systems. The deconstruction of cellulose, which could, among other things, significantly increase the production of ethanol from sugarcane, has been a major technological challenge for decades.
Researchers from the Brazilian Center for Research in Energy and Materials (CNPEM), in partnership with colleagues from other institutions in Brazil and abroad, have just obtained an enzyme that could revolutionize the process of deconstructing cellulose, allowing, among other technological applications, the large-scale production of so-called second-generation ethanol, derived from agro-industrial waste such as sugarcane bagasse and corn straw. The study was published in the journal Nature.