Circulate Health and Buck researchers find that TPE combined with immunoglobulin reduced biological age by more than 2.5 years on average.


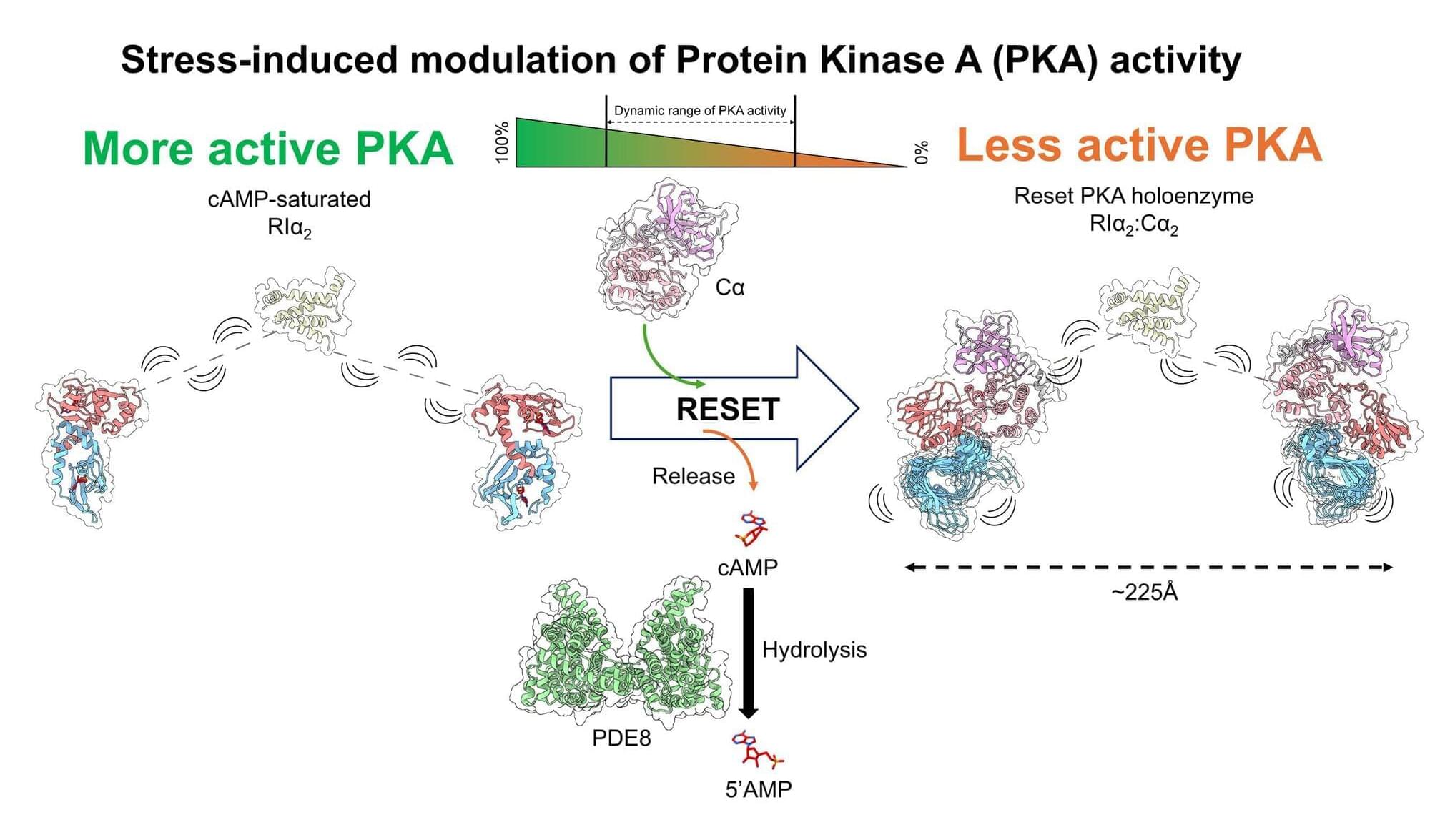
Being cut off in traffic, giving a presentation or missing a meal can all trigger a suite of physiological changes that allow the body to react swiftly to stress or starvation. Critical to this “fight-or-flight” or stress response is a molecular cycle that results in the activation of protein kinase A (PKA), a protein involved in everything from metabolism to memory formation. Now, a study by researchers at Penn State has revealed how this cycle resets between stressful events, so the body is prepared to take on new challenges.
The details of this reset mechanism, uncovered through a combination of imaging, structural and biochemical techniques, are published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
“Some of the early changes in the fight-or-flight response include the release of hormones, like adrenaline from stress or glucagon from starvation,” said Ganesh Anand, associate professor of chemistry and of biochemistry and molecular biology in the Penn State Eberly College of Science and lead author of the paper.
A new study, led by San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance, Smithsonian’s National Zoo & Conservation Biology Institute, and additional researchers, offers a unique lens for understanding the unprecedented extinction crisis of native Hawaiian forest birds.
Just 17 out of approximately 60 species of the iconic honeycreeper remain, most of which are facing rapid decline due to avian malaria. The findings, published in Current Biology, include new evidence that there is still time to save the critically endangered honeycreeper ‘akeke’e—but the window is rapidly closing.
“In a race against time to save the remaining honeycreepers, necessary insights about their survival are found in their genetic makeup,” said Christopher Kyriazis, Ph.D., lead author and postdoctoral researcher from San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance. “Our findings provide a new understanding of the last remaining individuals as recovery efforts forge on in their native forests and in human care.”

Scientists call for halt on ‘mirror life’. A new study suggests that creating a new tree of life could put the earth at unprecedented risk. paper: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.ads9158 #science #breakthrough #biology #mirrorlife #shorts 🚀 JOIN US for members-only content: https://www.patreon.com/DrBenMiles 🤘👨🔬 ROCKSTAR SCIENTIST Merch: https://www.rockstarscientist.org/ 📸 INSTAGRAM https://www.instagram.com/drbenmiles A few people have asked so I’ve added the info below. Some of these are affiliate links. If you make a purchase it doesn’t cost you anything extra, but a percentage of the sale will help support this channel and my work to bringing entrepreneurship into science. Camera : Sony A7III https://amzn.to/3OWrmGd Lens: Sigma 402,965 16 mm F1.4 https://amzn.to/49BNJdq Mics: Shure SM7B https://youtu.be/lVTS_J7Xmxs Zoom H4n Pro https://amzn.to/3OXsklB Sennheiser AVX https://amzn.to/4geWnBi …
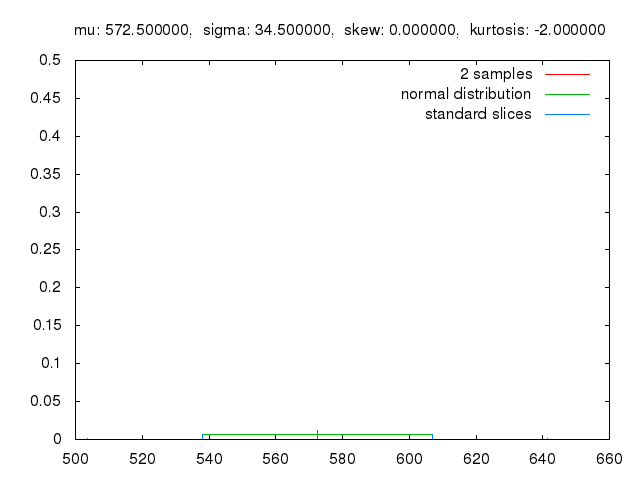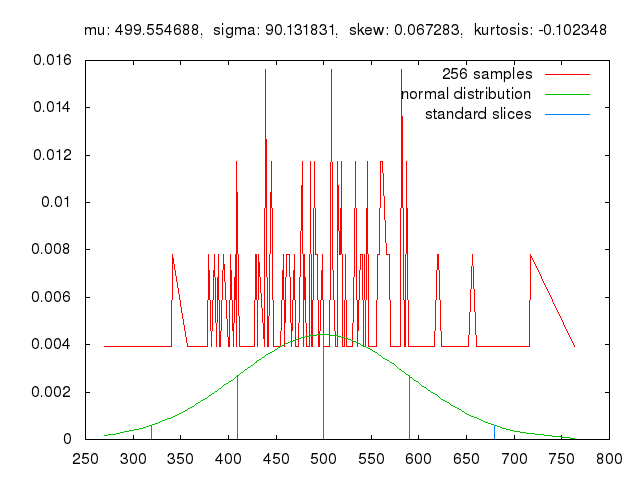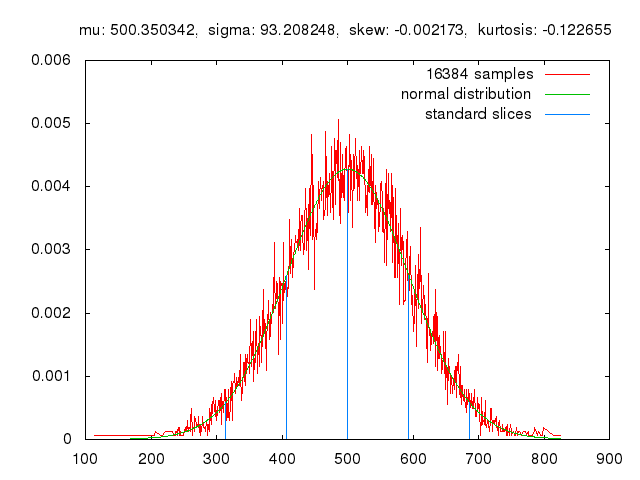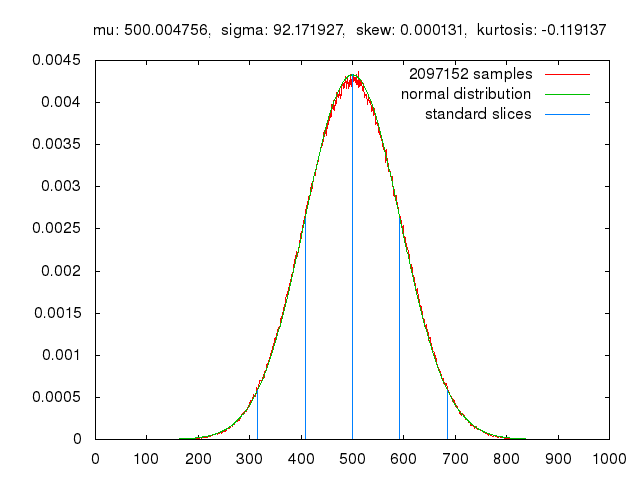
Monte Carlo methods, or Monte Carlo experiments, are a broad class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to obtain numerical results. The underlying concept is to use randomness to solve problems that might be deterministic in principle. The name comes from the Monte Carlo Casino in Monaco, where the primary developer of the method, mathematician Stanisław Ulam, was inspired by his uncle’s gambling habits.
Monte Carlo methods are mainly used in three distinct problem classes: optimization, numerical integration, and generating draws from a probability distribution. They can also be used to model phenomena with significant uncertainty in inputs, such as calculating the risk of a nuclear power plant failure. Monte Carlo methods are often implemented using computer simulations, and they can provide approximate solutions to problems that are otherwise intractable or too complex to analyze mathematically.
Monte Carlo methods are widely used in various fields of science, engineering, and mathematics, such as physics, chemistry, biology, statistics, artificial intelligence, finance, and cryptography. They have also been applied to social sciences, such as sociology, psychology, and political science. Monte Carlo methods have been recognized as one of the most important and influential ideas of the 20th century, and they have enabled many scientific and technological breakthroughs.
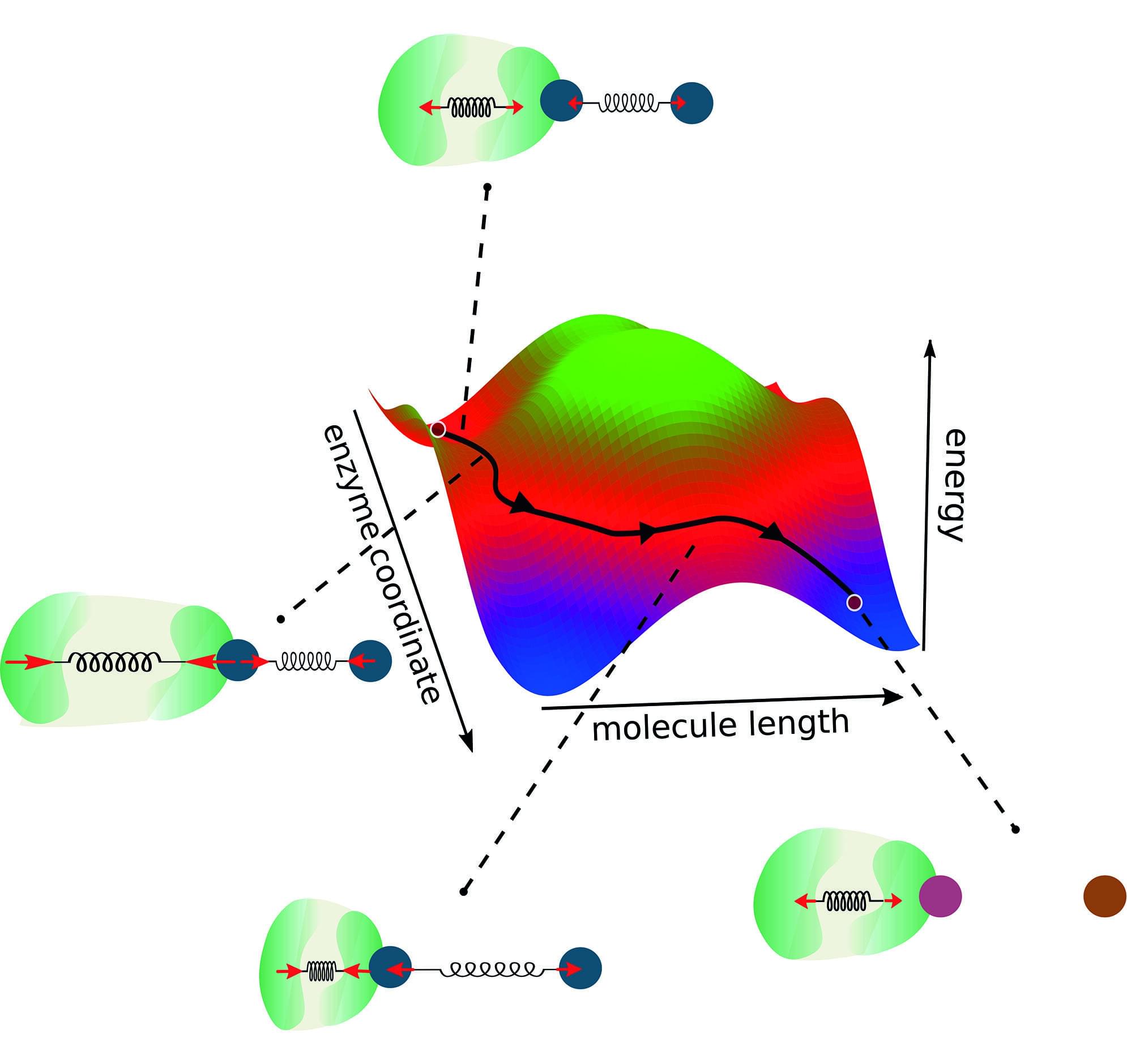
In biology, enzymes have evolved over millions of years to drive chemical reactions. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPI-DS) have now derived universal rules to enable the de novo design of optimal enzymes.
The paper is published in the journal Chem Catalysis.
As an example, they considered the enzymatic reaction of breaking a dimer into two monomer molecules. Considering the geometry of such an enzyme-substrate-complex, they identified three golden rules that should be considered to build a functional enzyme.
