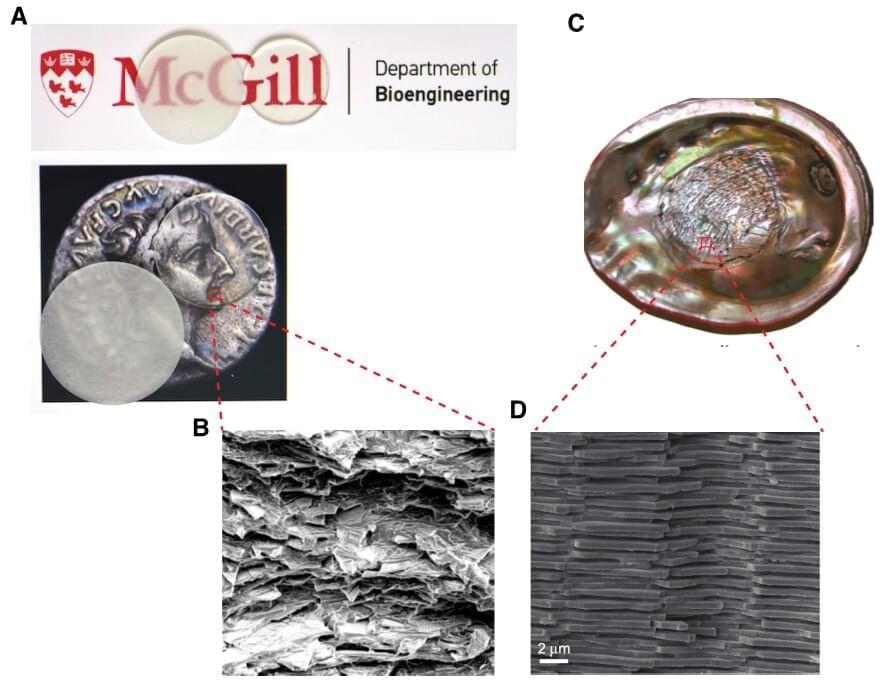
Amazingly, nacre has the rigidity of a stiff material and durability of a soft material, giving it the best of both worlds,” he explains. “It’s made of stiff pieces of chalk-like matter that are layered with soft proteins that are highly elastic. This structure produces exceptional strength, making it 3,000 times tougher than the materials that compose it.
Scientists from McGill University develop stronger and tougher glass, inspired by the inner layer of mollusk shells. Instead of shattering upon impact, the new material has the resiliency of plastic and could be used to improve cell phone screens in the future, among other applications.
While techniques like tempering and laminating can help reinforce glass, they are costly and no longer work once the surface is damaged. “Until now there were trade-offs between high strength, toughness, and transparency. Our new material is not only three times stronger than the normal glass, but also more than five times more fracture resistant,” says Allen Ehrlicher, an Associate Professor in the Department of Bioengineering at McGill University.
Nature as master of design
Drawing inspiration from nature, the scientist created a new glass and acrylic composite material that mimics nacre or mother of pearl. “Nature is a master of design. Studying the structure of biological materials and understanding how they work offers inspiration, and sometimes blueprints, for new materials,” says Ehrlicher.