Why ‘panspermia theory’ – the wild idea of microbes ‘hitchhiking’ on meteoroids through the cosmos – is now taken seriously.


A talk on “Diverse Intelligence: understanding and relating to unconventional biological, engineered, and hybrid agents” by Michael Levin.
Generative AI represents a big breakthrough towards models that can make sense of the world by dreaming up visual, textual and conceptual representations, and are becoming increasingly generalist. While these AI systems are currently based on scaling up deep learning algorithms with massive amounts of data and compute, biological systems seem to be able to make sense of the world using far less resources. This phenomenon of efficient intelligent self-organization still eludes AI research, creating an exciting new frontier for the next wave of developments in the field. Our panelists will explore the potential of incorporating principles of intelligent self-organization from biology and cybernetics into technical systems as a way to move closer to general intelligence. Join in on this exciting discussion about the future of AI and how we can move beyond traditional approaches like deep learning!
Year 2021 face_with_colon_three
For decades, scientists suspected that bacteria known as Geobacter could clean up radioactive uranium waste, but it wasn’t clear how the microbes did it.

Evolution’s rapid pace after the Cambrian explosion
Though the work of Schopf and other paleobiologists continues to fill in the Precambrian fossil record, questions remain about the pace of the Cambrian explosion. What triggered life to evolve so fast?
The question has intrigued scientists of many disciplines for decades. Interdisciplinary collaboration has wrought a wealth of evidence from diverse perspectives — geochemical, paleoenvironmental, geological, anatomical, and taxonomic — that describes how biological organisms evolved in concert with changing environmental conditions.
Keep exploring at http://brilliant.org/ArtemKirsanov/
Get started for free, and hurry—the first 200 people get 20% off an annual premium subscription.
My name is Artem, I’m a computational neuroscience student and researcher. In this video we will see why individual neurons essentially function like deep convolutional neural networks, equipped with insane information processing capabilities as well as some of the physiological mechanisms, that account for such computational complexity.
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/artemkirsanov.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/ArtemKRSV
OUTLINE:
00:00 Introduction.
01:42 — Perceptrons.
03:43 — Electrical excitability and action potential.
07:12 — Cable theory: passive dendrites.
09:03 — Active dendritic properties.
12:10 — Human neurons as XOR gates.
19:11 — Single neurons as deep neural networks.
22:32 — Brilliant.
23:57 — Recap and outro.
REFERENCES (in no particular order):
1. Bicknell, B. A., Bicknell, B. A. & Häusser, M. A synaptic learning rule for exploiting nonlinear dendritic computation. Neuron (2021) doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2021.09.044.
2. Matthew Larkum. Are dendrites conceptually useful? Neuroscience (2022) doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.03.008.
3. Polsky, A., Mel, B. W. & Schiller, J. Computational subunits in thin dendrites of pyramidal cells. Nature Neuroscience 7621–627 (2004).
4. Tran-Van-Minh, A. et al. Contribution of sublinear and supralinear dendritic integration to neuronal computations. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 9, 67–67 (2015).
5. Gidon, A. et al. Dendritic action potentials and computation in human layer 2/3 cortical neurons. Science 367, 83–87 (2020).
6. London, M. & Häusser, M. DENDRITIC COMPUTATION. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 28503–532 (2005).
7. Branco, T., Clark, B. A. & Häusser, M. Dendritic Discrimination of Temporal Input Sequences in Cortical Neurons. Science 329, 1671–1675 (2010).
8. Stuart, G. J. & Spruston, N. Dendritic integration: 60 years of progress. Nat Neurosci 18, 1713–1721 (2015).
9. Smith, S. L., Smith, I. T., Branco, T. & Häusser, M. Dendritic spikes enhance stimulus selectivity in cortical neurons in vivo. Nature 503115–120 (2013).
10. Beniaguev, D., Segev, I. & London, M. Single cortical neurons as deep artificial neural networks. Neuron 109, (2021).
11. Michalikova, M., Remme, M. W. H., Schmitz, D., Schreiber, S. & Kempter, R. Spikelets in pyramidal neurons: generating mechanisms, distinguishing properties, and functional implications. Reviews in the Neurosciences 31101–119 (2019).
12. Larkum, M. E., Wu, J., Duverdin, S. A. & Gidon, A. The Guide to Dendritic Spikes of the Mammalian Cortex In Vitro and In Vivo. Neuroscience 489, 15–33 (2022).
CREDITS:
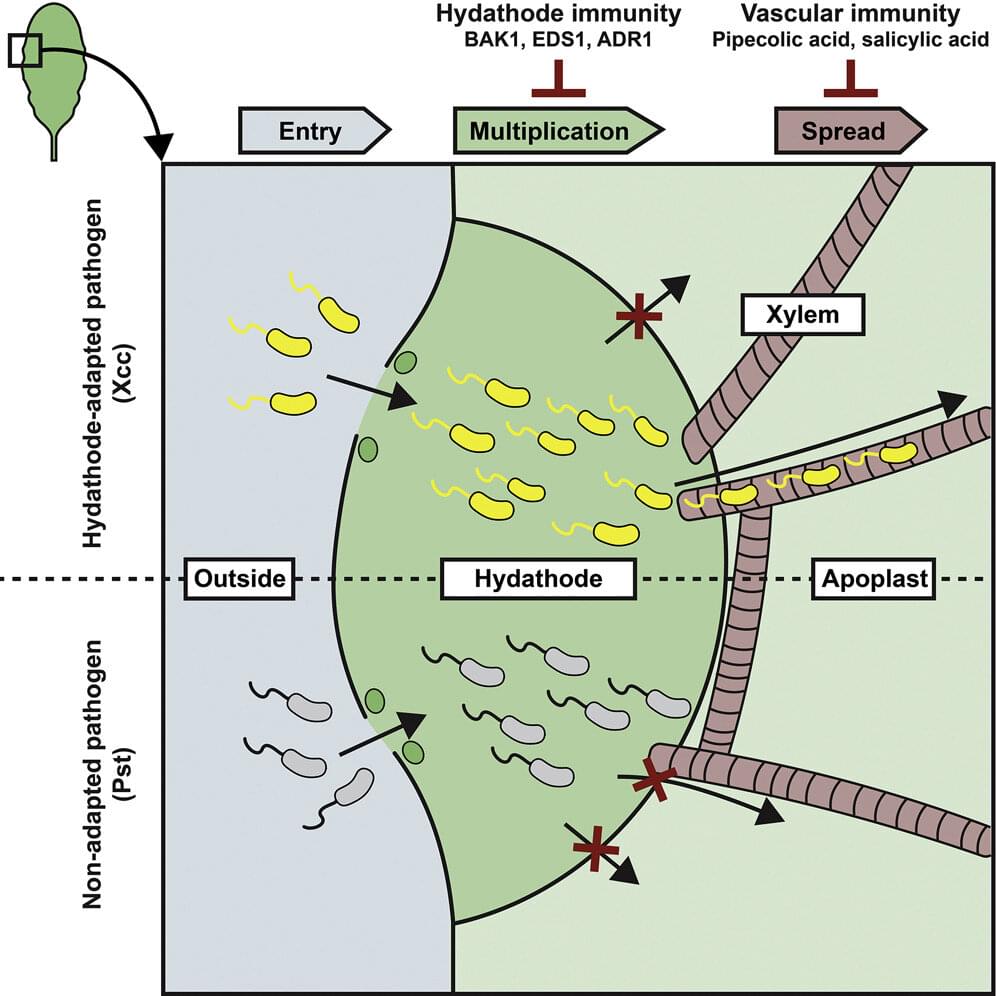
How do plants defend themselves against pathogenic microorganisms? This is a complex puzzle, of which a team of biologists from the University of Amsterdam has solved a new piece. The team, led by Harrold van den Burg, discovered that while the water pores (hydathodes) in leaves provide an entry point for bacteria, they are also an active part of the defense against these invaders. The team’s research has now been published in the journal Current Biology.
Anyone who is used to giving plants plenty of water might know the phenomenon: small droplets of plant sap that sometimes appear at the edge of the leaves, especially at nighttime. When plants take up more water via their roots than they lose through evaporation, they can use their water pores on the leaf margins to release excess water. The pores literally prevent root water pressure from becoming too high. This is an important mechanism, but at the same time, risky. Pathogenic microorganisms can enter the plant’s veins through these sap droplets to colonize the water pores.
Biologists have therefore been asking themselves for a long time: How do plants defend themselves against this wide-open entry point? Are those water pores, the hydathodes, defenseless glands that allow ample entry of harmful pests? Or have they evolved in such a way that they are part of the plant’s line of defense against pathogens?
A team of researchers from Illinois Institute of Technology and the University of Washington is trying to change the way that the field of biology understands how muscles contract.
In a paper published on January 25, 2023, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences titled “Structural OFF/ON Transition of Myosin in Related Porcine Myocardium Predict Calcium Activated Force,” Illinois Tech Research Assistant Professor Weikang Ma and Professor of Biology and Physics Thomas Irving—working in collaboration with Professor of Bioengineering Michael Regnier’s group at Washington—make the case for a second, newly discovered aspect to muscle contraction that could play a significant role in developing treatments for inherited cardiac conditions.
The consensus for how muscle contraction occurs has been that the relationship between the thin and thick filaments that comprise muscle tissue was a more straightforward process. When targets on thin filaments were activated, it was thought that the myosin motor proteins that make up the thick filaments would automatically find their way to those thin filaments to start generating force and contract the muscle.
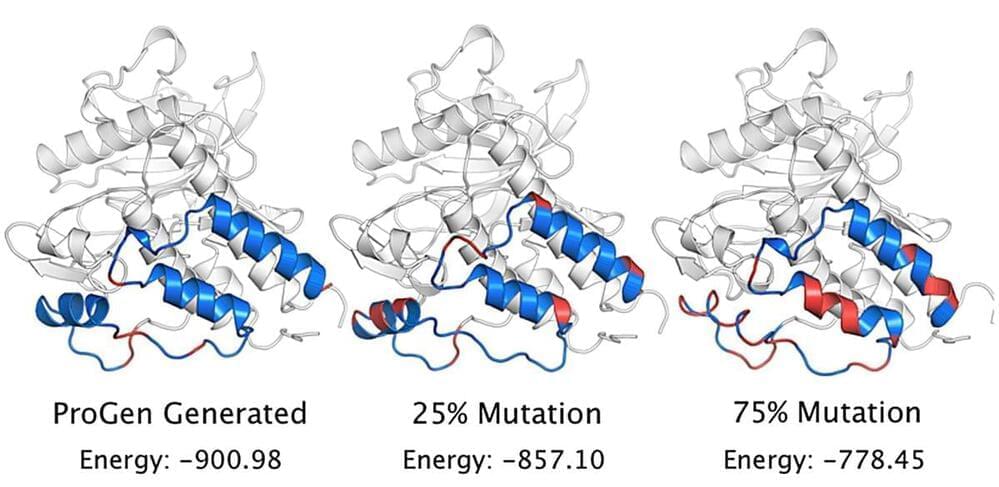

The first time a language model was used to synthesize human proteins.
Of late, AI models are really flexing their muscles. We have recently seen how ChatGPT has become a poster child for platforms that comprehend human languages. Now a team of researchers has tested a language model to create amino acid sequences, showcasing abilities to replicate human biology and evolution.
The language model, which is named ProGen, is capable of generating protein sequences with a certain degree of control. The result was achieved by training the model to learn the composition of proteins. The experiment marks the first time a language model was used to synthesize human proteins.