Remember when eggs were so high? A vaccine for birds, now that can make money. 🤔
In the past two years, a viral disease has swept across much of the planet — not Covid but a type of avian flu. It’s devastated the poultry industry in the US, Europe, and elsewhere, sickening millions of farmed birds, which either die from infection or are killed by farmers seeking to stem the spread.
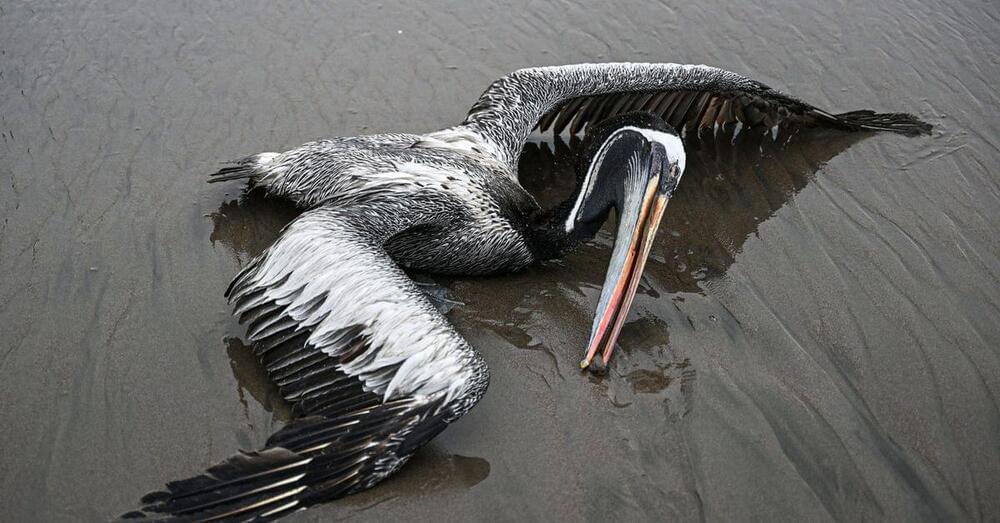
The ongoing outbreak of avian flu has killed hundreds of thousands — if not millions — of wild birds, including endangered species like the California condor. It’s one of the worst wildlife disease outbreaks in history. Having now spread across five continents and hundreds of wildlife species, scientists call the current outbreak a panzootic, meaning a pandemic among animals.
“What we’re seeing right now is uncharted territory,” said Andrew Ramey, a wildlife geneticist at the US Geological Survey, one of the federal agencies involved in testing wild birds for the virus.
The number of dead birds in itself is historic, but so is the virus’s biology. Typically, avian influenza viruses only cause severe disease and death in domestic birds like chickens and farmed ducks; they sweep through populations, killing upward of 90 percent of the flock.