Researchers have developed a hackable and multi-functional 3D printer for soft materials that is affordable and open design. The technology has the potential to unlock further innovation in diverse fields, such as tissue engineering, soft robotics, food, and eco-friendly material processing—aiding the creation of unprecedented designs.
Category: bioengineering – Page 101
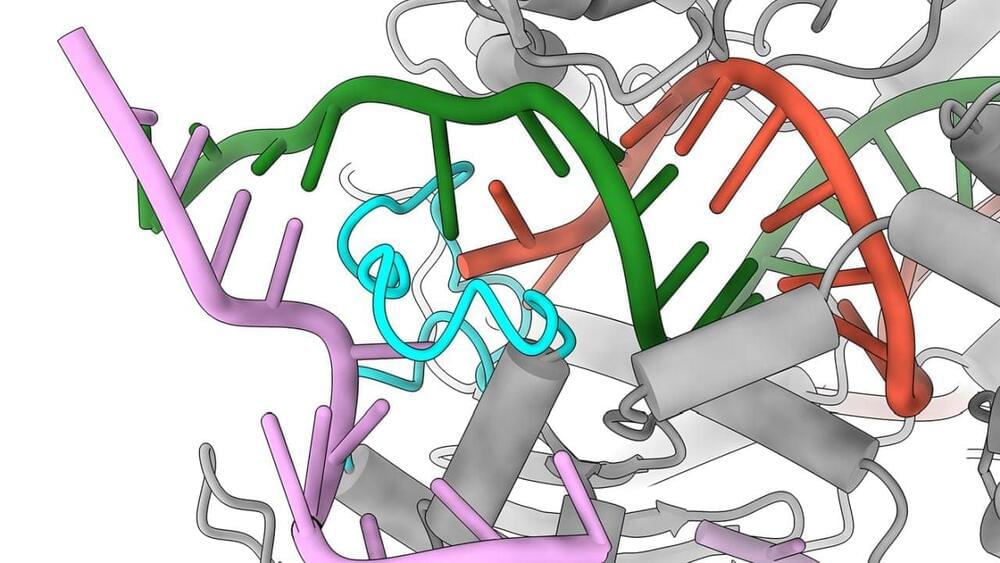
UT Austin scientists design safer Cas9 with improved CRISPR gene editing accuracy
The CRISPR system, which involves a Cas enzyme to cut DNA, is a powerful tool for gene editing. But the genetic scissors sometimes make changes at the wrong place, creating a major safety problem that could limit their therapeutic use.
Now, scientists at the University of Texas (UT) at Austin have refined the Cas9 protein used in the Nobel Prize-winning CRISPR-Cas9 tool. The new version, dubbed SuperFi-Cas9, was thousands of times less likely to perform off-target editing but just as efficient at on-target editing as the original version, the team said in a paper published in Nature.
“This really could be a game-changer in terms of a wider application of the CRISPR-Cas systems in gene editing,” Kenneth Johnson, Ph.D., the study’s co-senior author, said in a statement.

Weird ‘Borg’ DNA May Have Assimilated Microbes For Billions of Years
Strange libraries of supplementary genes nicknamed “Borg” DNA appear to supercharge the microbes that possess them, giving them an uncanny ability to metabolize materials in their environment faster than their competitors.
By learning more about the way organisms use these unusual extrachromosomal packets of information, researchers are hoping to find new ways of engineering life to take a big bite out of methane emissions.
In the wake of a study publicized last year (and now published in Nature), researchers have continued to analyze the diversity of sequences methane-munching microbes store in these unusual genetic depositaries in an effort to learn more about the evolution of life.
3D Printing With A Drone Swarm?
The goal is to enable the printing of large, complex shaped structures, on any surface, using a swarm of drones, each depositing whatever material is required. It’s a bit like a swarm of wasps building a nest, into whatever little nook they come across, but on the wing.
Even in technical disciplines such as engineering, there is much we can still learn from nature. After all, the endless experimentation and trials of life give rise to some of the most elegant solutions to problems. With that in mind, a large team of researchers took inspiration from the humble (if rather annoying) wasp, specifically its nest-building skills. The idea was to explore 3D printing of structures without the constraints of a framed machine, by mounting an extruder onto a drone.
As you might expect, one of the most obvious issues with this attempt is the tendency of the drone’s to drift around slightly. The solution the team came up with was to mount the effector onto a delta bot carrier hanging from the bottom of the drone, allowing it to compensate for its measured movement and cancel out the majority of the positional error.
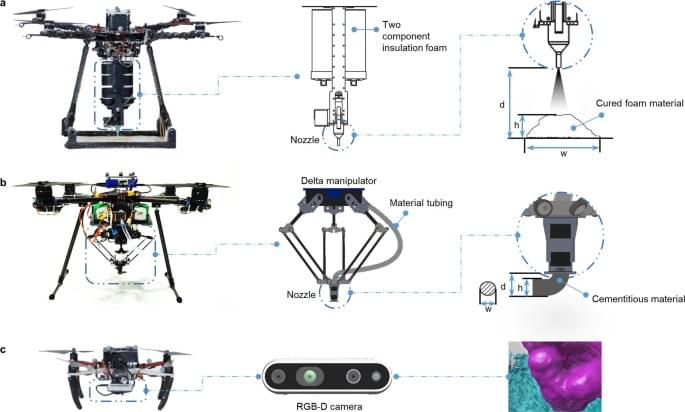
The printing method relies upon the use of two kinds of drone. The first done operates as a scanner, measuring the print surface and any printing already completed. The second drone then approaches and lays down a single layer, before they swap places and repeat until the structure is complete.
Michael Levin: Intelligence Beyond the Brain
*Intelligence Beyond the Brain: morphogenesis as an example of the scaling of basal cognition*
*Description:*
Each of us takes the remarkable journey from physics to mind: we start life as a quiescent oocyte (collection of chemical reactions) and slowly change and acquire an advanced, centralized mind. How does unified complex cognition emerge from the collective intelligence of cells? In this talk, I will use morphogenesis to illustrate how evolution scales cognition across problem spaces. Embryos and regenerating organs produce very complex, robust anatomical structures and stop growth and remodeling when those structures are complete. One of the most remarkable things about morphogenesis is that it is not simply a feed-forward emergent process, but one that has massive plasticity: even when disrupted by manipulations such as damage or changing the sizes of cells, the system often manages to achieve its morphogenetic goal. How do cell collectives know what to build and when to stop? Constructing and repairing anatomies in novel circumstances is a remarkable example of the collective intelligence of a biological swarm. I propose that a multi-scale competency architecture is how evolution exploits physics to achieve robust machines that solve novel problems. I will describe what is known about developmental bioelectricity — a precursor to neurobiology which is used for cognitive binding in biological collectives, that scales their intelligence and the size of the goals they can pursue. I will also discuss the cognitive light cone model, and conclude with examples of synthetic living machines — a new biorobotics platform that uses some of these ideas to build novel primitive intelligences. I will end by speculating about ethics, engineering, and life in a future that integrates deeply across biological and synthetic agents.

‘Near-limitless CRISPR therapies’: This drug delivery breakthrough helps gene editing technology infiltrate cells
A team of researchers at Northwestern University has devised a new platform for gene editing that could inform the future application of a near-limitless library of CRISPR-based therapeutics.
Using chemical design and synthesis, the team brought together the Nobel-prize winning technology with therapeutic technology born in their own lab to overcome a critical limitation of CRISPR. Specifically, the groundbreaking work provides a system to deliver the cargo required for generating the gene editing machine known as CRISPR-Cas9. The team developed a way to transform the Cas-9 protein into a spherical nucleic acid (SNA) and load it with critical components as required to access a broad range of tissue and cell types, as well as the intracellular compartments required for gene editing.

The Search for a Pill That Can Help Dogs—and Humans—Live Longer
Celine halioua drops into a crouch and greets Bocce, a Chihuahua-dachshund mix with soulful brown eyes, like a long-lost friend. “Oh my God, you’re so beautiful!” she chirps. The two have just met in an upstairs room at Muttville Senior Dog Rescue in San Francisco, where light streams in through the open windows and urine occasionally streams onto the floor. About a dozen elderly dogs, none taller than a kneecap, putter around on the gray linoleum or nap on blankets. When Halioua kneels, her dark hair tumbling over her shoulder, Bocce rests his head blissfully in her lap.
A tragedy of human-canine relations is that a 10-year-old dog such as Bocce is old, while a 28-year-old person such as Halioua is in the prime of life. Bocce is one of the lucky ones. Many dogs can only dream of living as long as he likely will, because dog lifespan is inversely correlated with body size. It’s the opposite of the wider pattern in the animal kingdom, where elephants easily outlast mice, which in turn outlive mosquitoes. A Chihuahua can expect roughly 15 years of life; an Irish wolfhound or Great Dane around seven or eight.
Halioua hopes that the startup whose name is emblazoned on her slim black T-shirt— Loyal —can start to fix this bug in humanity’s 14,000-year-plus wolf bioengineering project. The company, which she founded in 2019 and leads as CEO, is developing drugs to delay aging in dogs and extend their healthy lifespan. She has raised around $58 million and has two drugs in development. In a few years, she hopes to have the first commercial drug—for any species—to state on the label that it delays aging or extends lifespan. That alone would be a triumph, but Halioua sees it as a springboard to a still greater feat: creating similar drugs for humans.
China’s advances with RNA gene editing
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Pr5aRhEIE9A&feature=share
Researchers from the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) claimed in a recently published study to have developed a gene editing method that is supposed to be “more efficient and safer” than the technique used so far.
But there is a lot behind gene editing, so let’s look at what it is all about and its risks and applications.
—————————
#ChinaRevealed #ChinaNews
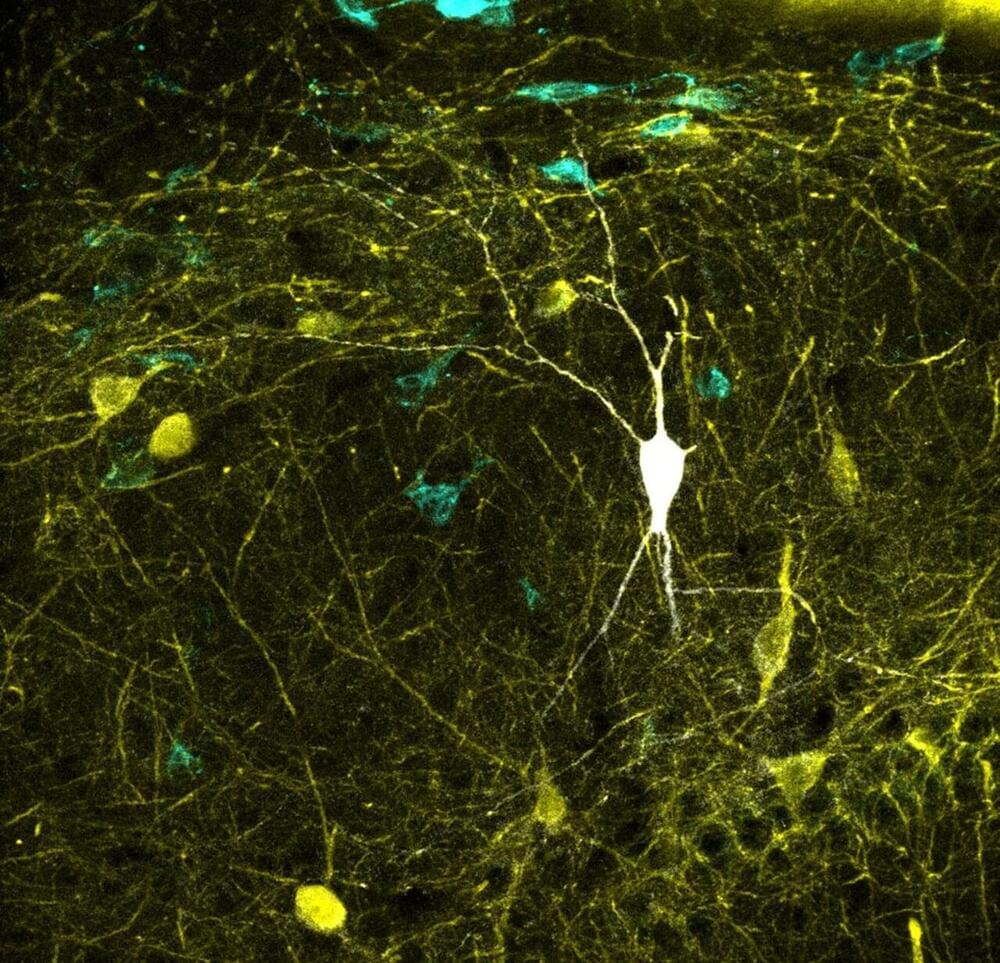
Study upgrades one of the largest databases of neuronal types
A study led by researchers from the Institute Cajal of Spanish Research Council (CSIC) in Madrid, Spain in collaboration with the Bioengineering Department of George Mason University in Virginia, U.S. has updated one of the world’s largest databases on neuronal types, Hippocampome.org.
The study, which is published in the journal PLOS Biology, represents the most comprehensive mapping performed to date between neural activity recoded in vivo and identified neuron types. This major breakthrough may enable biologically meaningful computer modeling of the full neuronal circuit of the hippocampus, a region of the brain involved in memory function.
Circuits of the mammalian cerebral cortex are made up of two types of neurons: Excitatory neurons, which release a neurotransmitter called glutamate, and inhibitory neurons, which release GABA (gamma-aminobutanoic acid), the main inhibitor of the central nervous system. “A balanced dialogue between the ‘excitatory’ and ‘inhibitory’ activities is critical for brain function. Identifying the contribution from the several types of excitatory and inhibitory cells is essential to better understand brain operation,” explains Liset Menendez de la Prida, the Director of the Laboratorio de Circuitos Neuronales at the Institute Cajal who leads the study at the CSIC.