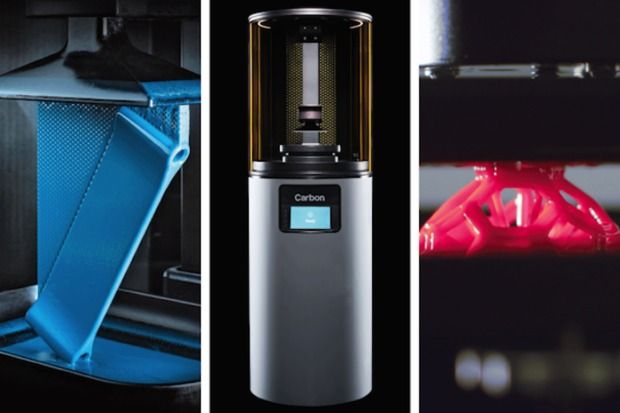
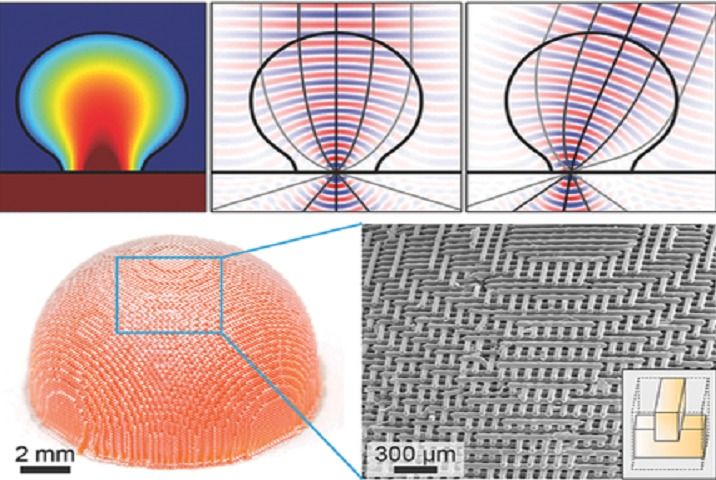
Disney Research has designed a new 3D printer that utilizes light on photosensitive resin so that models can be printed out as whole objects instead of by the layer, cutting down 3D printing from hours down to just minutes.
Disney Research has patented its design for “a nearly instantaneous” 3D printer that uses light to cure resin selectively to produce an entire model out of a stereolithography (STL) file all at once. Notably, this significantly cuts down printing time. Or at least, it will if it makes it to market.
“Presently, 3D printing is extremely slow and time consuming. For example, it may take several hours to print a single 3D object even if the 3D object is relatively small (e.g., several inches in diameter and four to 12 inches tall),” the patent stated. It continues, “the 3D printing process that uses conventional 3D printers such as an FFF-based 3D printer is limited in its speed by the speed of the mechanism moving the print head to each new position on a print layer.”