How can a computer chip the size of a human hair enhance the future of quantum computing? This is what a recent study published in Nature Communications ho | Technology



Get Our Newsletter (It’s Free): https://www.optispan.life/
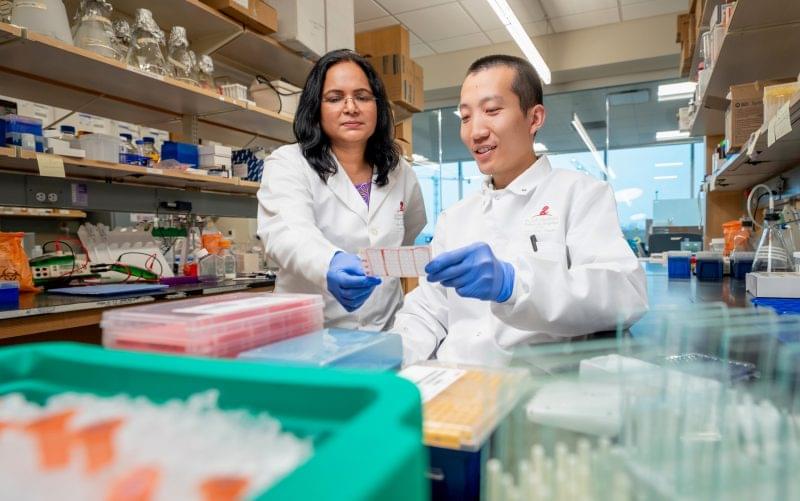
Dive into the future of longevity research with Dr. Ben Blue, CEO of Ora Biomedical. We explore how Ora’s high-throughput “Wormbot” platform is conducting the world’s largest unbiased search for longevity interventions, moving beyond the narrow focus on established pathways like mTOR.
In this episode, we discuss:
• The ambitious Million Molecule Challenge and why it could revolutionize the field.
• Surprising discoveries already made, including molecules that outperform rapamycin.
• Ora’s strategic pivot to radiation resistance, with applications for astronauts, pilots, and human health.
• How their data-driven approach is uncovering interventions for resilience against toxins and other stresses.
• The journey from worm models to potential clinical trials and what’s next for the company.
Learn how Ora is scaling drug discovery to tackle aging and age-related diseases.
https://twitter.com/OraBiomedical.
https://www.linkedin.com/company/ora-biomedical-inc/
This video was produced by One Billion Media, an agency that specializes in YouTube virality for health brands and experts. Learn more about their work here:

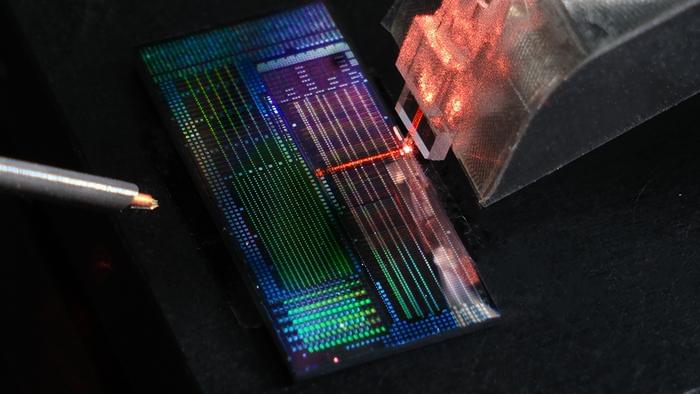
Quantum computers will need large numbers of qubits to tackle challenging problems in physics, chemistry, and beyond. Unlike classical bits, qubits can exist in two states at once—a phenomenon called superposition. This quirk of quantum physics gives quantum computers the potential to perform certain complex calculations better than their classical counterparts, but it also means the qubits are fragile. To compensate, researchers are building quantum computers with extra, redundant qubits to correct any errors. That is why robust quantum computers will require hundreds of thousands of qubits.
Now, in a step toward this vision, Caltech physicists have created the largest qubit array ever assembled: 6,100 neutral-atom qubits trapped in a grid by lasers. Previous arrays of this kind contained only hundreds of qubits.
This milestone comes amid a rapidly growing race to scale up quantum computers. There are several approaches in development, including those based on superconducting circuits, trapped ions, and neutral atoms, as used in the new study.
The neutral-atom platform shows promise for scaling up quantum computers.
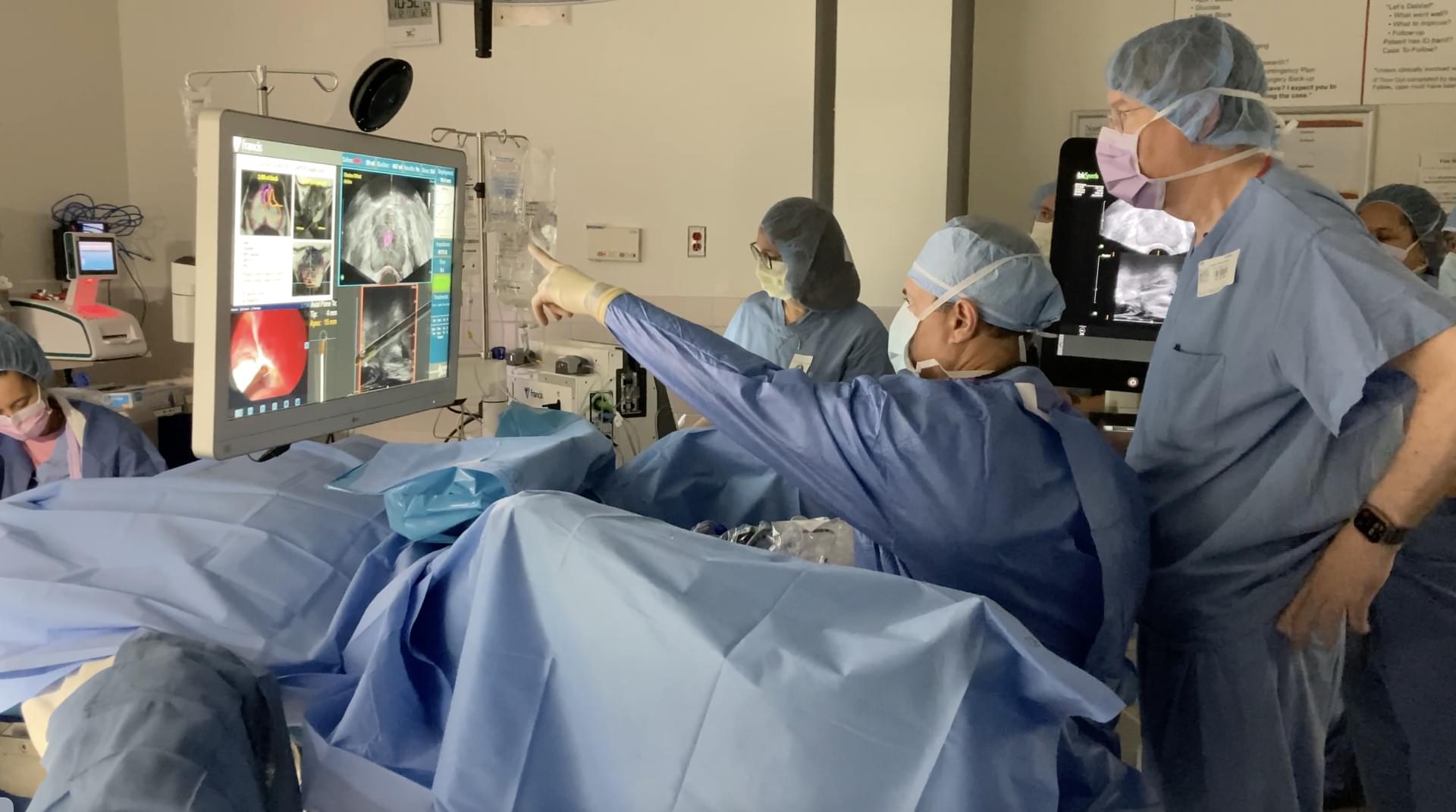
Heat is one therapy to help damage and kill cancer cells, according to the National Cancer Institute. Steam offers a targeted way to deliver heat into the body, according to Abreu.
Before the procedure, physicians use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to locate the tumor cells in the patient’s prostate. During the procedure, doctors use an ultrasound and prostate mapping to guide a thin catheter through the patient’s urethra and into the area of the prostate where the tumor is located.
Once the catheter is positioned, a fine needle is deployed in the tumor. Doctors then release a quick, targeted 10-second burst of steam from the needle, and more bursts as needed, to destroy the tumor.
‘This procedure is thought to be much gentler on the body than traditional therapies and is designed to target the cancerous tissue within the prostate,’ said Abreu. ‘We are exploring if steam may be effective at destroying cancer cells without damaging the surrounding organs.’
B-roll video available for download below.