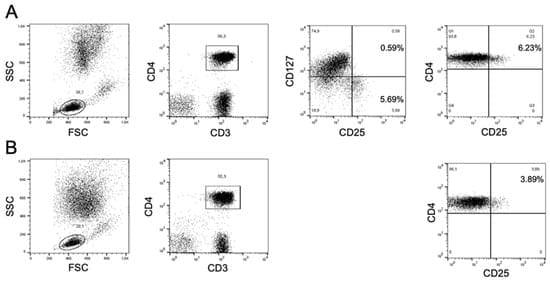
New-generation mRNA and adenovirus vectored vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein are endowed with immunogenic, inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties. Recently, BioNTech developed a noninflammatory tolerogenic mRNA vaccine (MOGm1Ψ) that induces in mice robust expansion of antigen-specific regulatory T (Treg) cells. The Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 is identical to MOGm1Ψ except for the lipid carrier, which differs for containing lipid nanoparticles rather than lipoplex. Here we report that vaccination with BNT162b2 led to an increase in the frequency and absolute count of CD4posCD25highCD127low putative Treg cells; in sharp contrast, vaccination with the adenovirus-vectored ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine led to a significant decrease of CD4posCD25high cells.