The real opportunity lies in using AI to strengthen clinical work, not replace it.


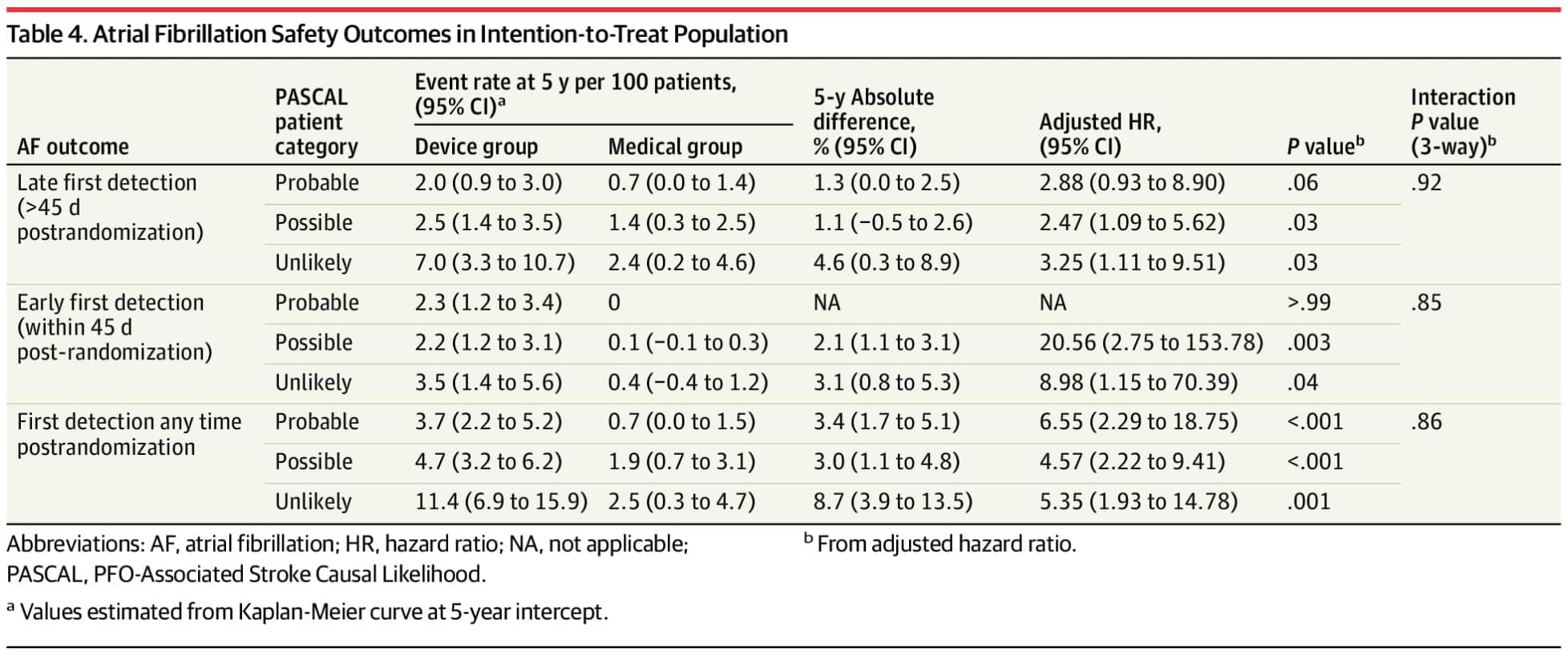
Among patients with Stroke and PatentForamenOvale, the PASCAL classification system identified those likely to benefit from closure and those at risk of increased atrial fibrillation.
Question Among young and middle-aged individuals (ages 18–60 years) with patent foramen ovale (PFO) and otherwise cryptogenic ischemic stroke enrolled in pivotal trials, can the PASCAL classification system identify those who will experience net benefit and those who will experience net harm from PFO closure in the next 5 years?
Finding This meta-analysis showed that in the PASCAL groups probable and possible, PFO closure reduced recurrent ischemic stroke more often than it caused atrial fibrillation, but in the unlikely group, closure did not reduce stroke and caused a larger amount of atrial fibrillation.
Meaning The PASCAL classification system may identify as many as 4 of 5 patients who will experience net benefit and 1 of 5 who will experience net harm from PFO closure.
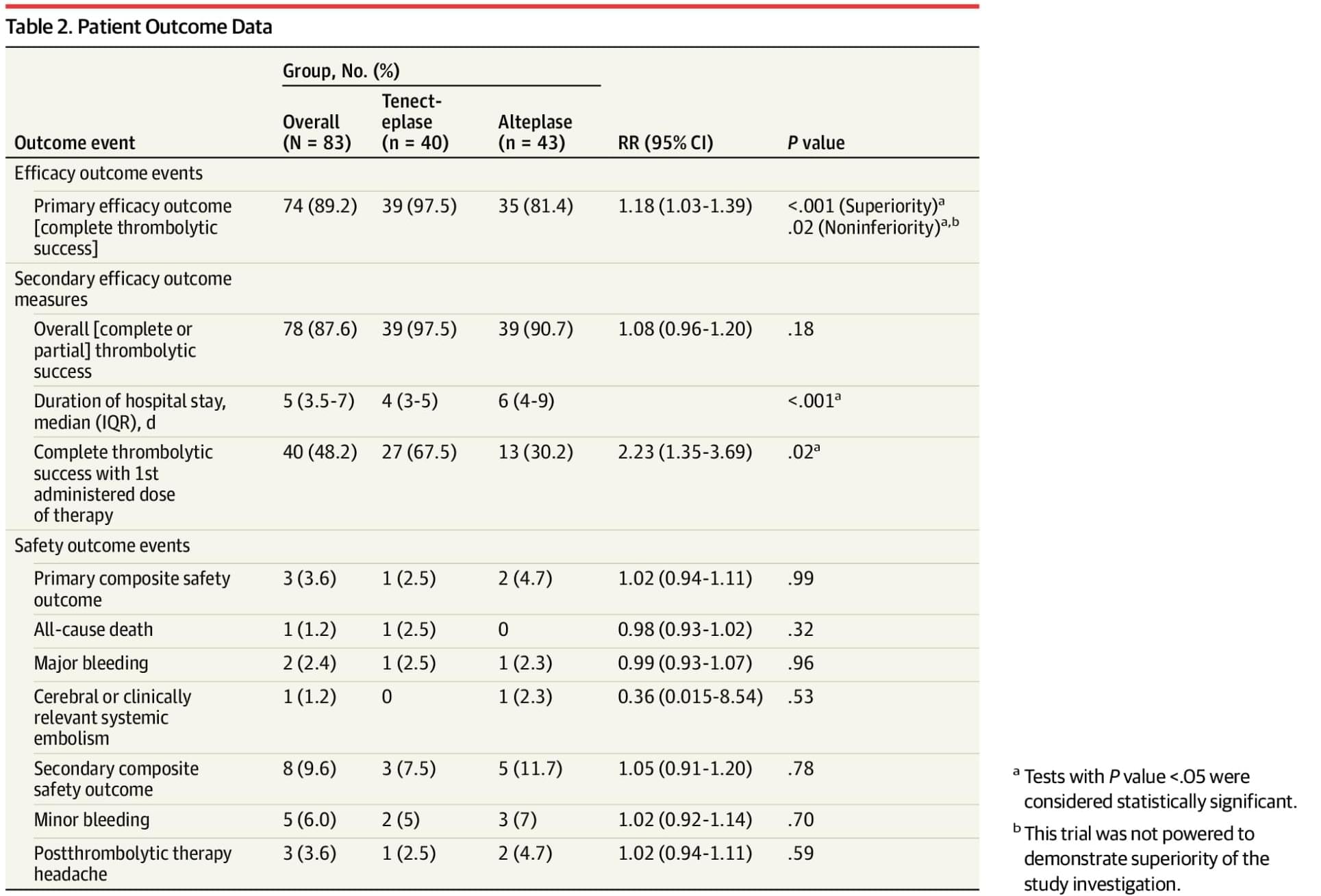
RCT: Among patients with obstructive prosthetic heart valve thrombosis, tenecteplase achieved higher complete thrombolytic success (97.5%) than alteplase (81.5%) and a shorter hospital stay.
Question What is the safety and efficacy of a single bolus of intravenous tenecteplase as compared with a low-dose slow-infusion protocol of alteplase in patients with obstructive mechanical prosthetic heart valve thrombosis?
Findings In this randomized clinical trial including 83 patients, tenecteplase was found to have noninferior rates of complete thrombolytic therapy success compared with alteplase. There was no difference in adverse events between the 2 groups.
Meaning Study results show that a regimen of bolus-dose tenecteplase may be a safe and efficacious alternative to current therapy for patients with prosthetic heart valve thrombosis.
In recent years, numerous landslides on hillsides in urban and rural areas have underscored that understanding and predicting these phenomena is more than an academic curiosity—it is a human necessity. When unstable slopes give way after intense rainfall, the consequences can be devastating, with both human and material losses. These recurring tragedies led us to a simple yet powerful question: Can we build landslide susceptibility maps that are more objective, transparent, and useful for local authorities and residents?
The answer led us to compare two susceptibility analysis methods: the traditional Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) and its statistical version, the Gaussian AHP. After months of multidisciplinary work, we found that the Gaussian AHP, which relies on data rather than subjective judgments, better identifies critical areas in a more balanced manner and is consistent with the landslide patterns observed in the field. We share here our journey and the lessons we learned. Our findings are published in Scientific Reports.
Traditional AHP is a decision-support technique widely used in geosciences and urban planning. It relies on pairwise comparisons of factors such as slope, soil type, and distance to rivers or roads to assign relative weights based on expert opinion. One advantage is that it allows the incorporation of accumulated experience; a disadvantage is the subjectivity and the effort required when many factors are involved. In our case, we worked with 16 physical and environmental variables that influence slope instability—from terrain morphometry to land cover and proximity to rivers.
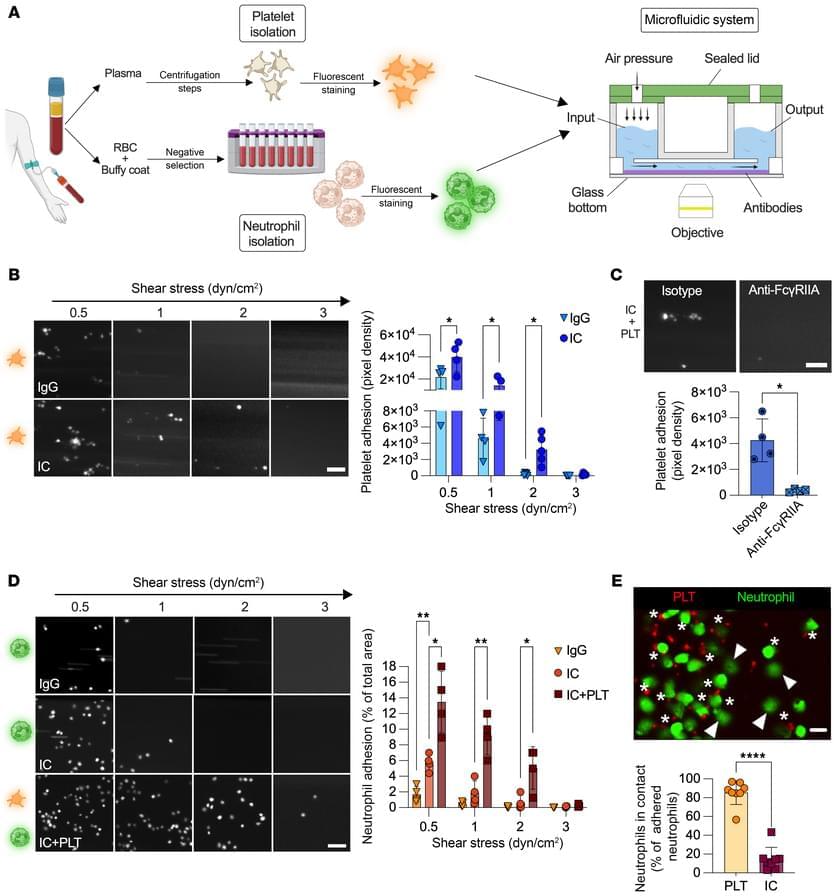
Eric Boilard & team now detail platelet-neutrophil interactions as being more abundant in arthritic mice than in healthy mice, reporting neutrophils migrate in tissue to play a pathogenic role in autoimmune arthritis and noting that they fail to migrate in the absence of platelets:
Image credit: Emma Bourgeault (emmabourgeault).
1Faculté de Médecine de l’Université Laval, Université Laval, Québec City, Québec, Canada.
2Centre de Recherche ARThrite – Arthrite, Recherche, Traitements, Université Laval, Québec City, Québec, Canada.
3Axe maladies infectieuses et immunitaires du Centre de recherche du Centre hospitalier universitaire de Québec-Université Laval, Québec City, Québec, Canada.
New preprint reports 17-month lifespan extension in mice with some living nearly 5 years. The intervention targets immune aging through CD4+ T cells and is expected to enter human trials in 2026.
Some links are affiliate links so we will earn a commission when they are used to purchase products.
If you would like to support our channel please consider joining our patreon / modernhealthspan.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Renue By Science (10% off: MHS) https://tinyurl.com/bdew4bfs NMN Powder • Lipo NR
BiOptimizers (15% off: MHBIO) https://bit.ly/47VAa8f — Magnesium Breakthrough.
Seeking Health (10% off: Richard10) https://crrnt.app/SEEK/-dm0MyrQ, Histamine Nutrients https://crrnt.app/SEEK/EpM7paAO
Stemregen (15% off: MODERN) US only https://tinyurl.com/45z968yr.
Wellness Extract (10% off: MODERNWE) http://wellnessextract.com/RICHARDWE Geranylgeraniol • Vit E
AX3 Life (20% off: MODERN20) https://tinyurl.com/2t3w26nw — Astaxanthin.
Oxford Healthspan (15% off: MHS) https://tinyurl.com/hrxfnzpn — Spermidine.
Qitone (10% off: HEALTH10) https://tidd.ly/4jGklry Qitone Esters Powder.
ProHealth (15% off: MODERN) https://prohealth.pxf.io/aObQRR NMNH 500mg.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
A new preprint by Lanna et al. reports one of the largest lifespan extensions ever seen in mice; approximately 17 months, with some mice living close to 5 years. The study focuses on metabolically reprogramming CD4+ T cells from aged mice using a peptide called DOS, which enables these cells to produce \.

“Foundry-Enabled Patterning of Diamond Quantum Microchiplets for Scalable Quantum Photonics” was published by researchers at MIT, KAUST, PhotonFoundries and MITRE.
Abstract
Quantum technologies promise secure communication networks and powerful new forms of information processing, but building these systems at scale remains a major challenge. Diamond is an especially attractive material for quantum devices because it can host atomic-scale defects that emit single photons and store quantum information with exceptional stability. However, fabricating the optical structures needed to control light in diamond typically relies on slow, bespoke processes that are difficult to scale. In this work, we introduce a manufacturing approach that brings diamond quantum photonics closer to industrial production. Instead of sequentially defining each device by lithography written directly on diamond, we fabricate high-precision silicon masks using commercial semiconductor foundries and transfer them onto diamond via microtransfer printing.

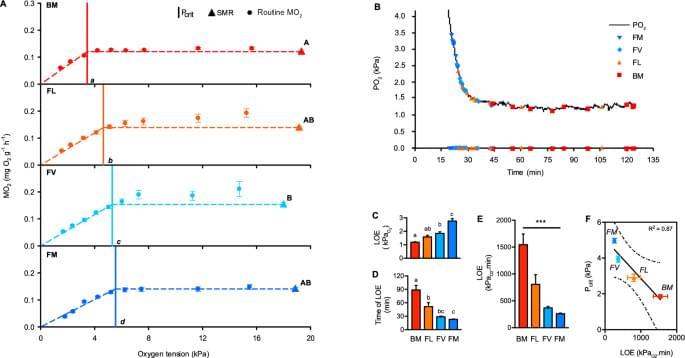
At the terminus of the O2 cascade, mitochondria play an important role in O2 utilisation and energy conservation, with adaptive modifications occasionally shared among hypoxia-tolerant species. Here, we sought to determine whether mitochondrial adaptations in brain tissue explain the hypoxia tolerance of New Zealand triplefin fishes (Tripterygiidae). We compared two intertidal species (Bellapiscis medius and Forsterygion lapillum), both likely adapted to hypoxia-reoxygenation exposures, and two subtidal species (F. varium and F. malcomi), which inhabit normoxic waters. To assess hypoxia tolerance, we determined loss of equilibrium (LOE) during hypoxia exposure and measured the critical O2 tension (Pcrit). Intertidal species displayed superior hypoxia tolerance as assessed by LOE and also had lower Pcrit (LOE versus Pcrit R2 = 0.99).