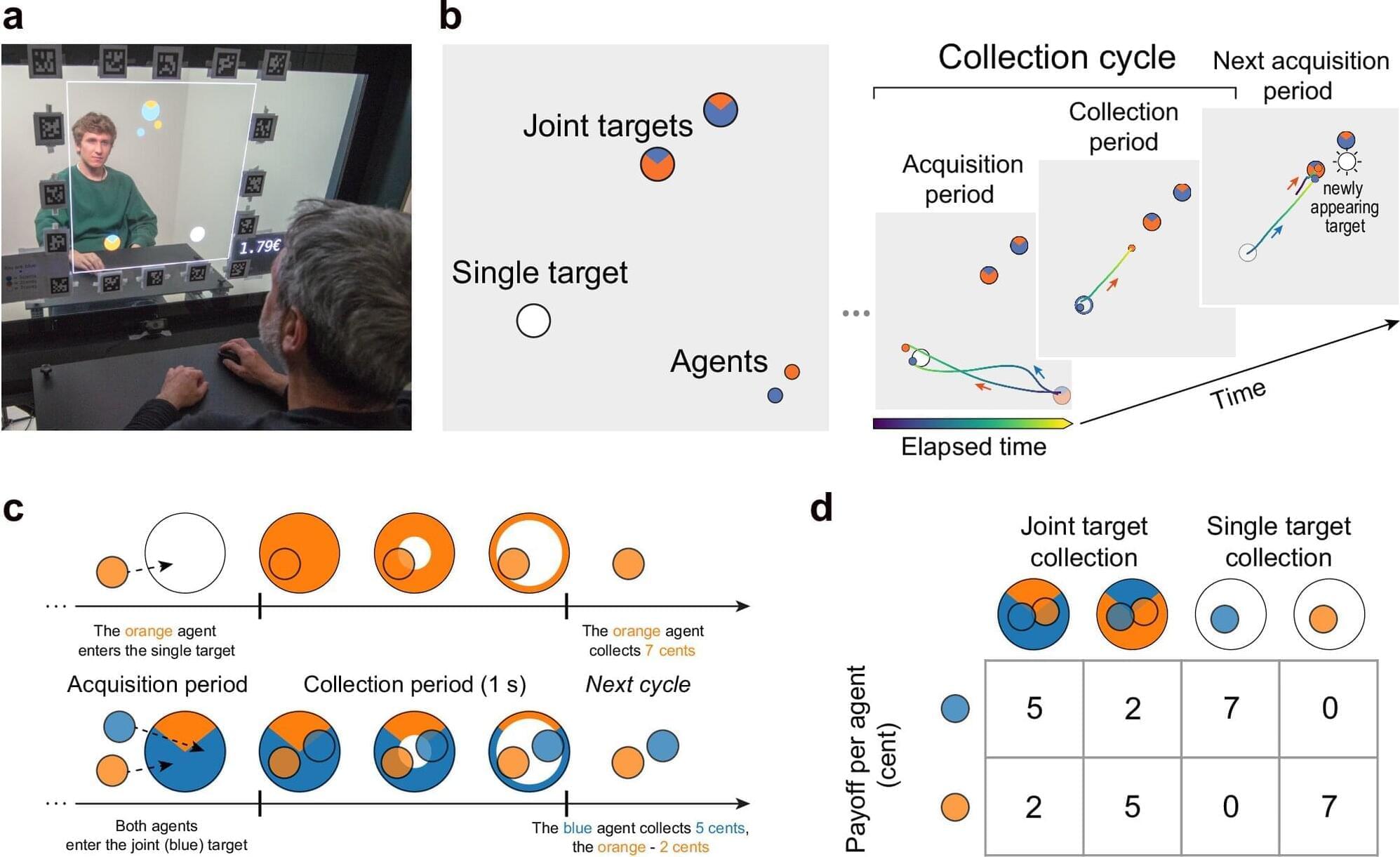
When people reach for the same object, walk through a narrow doorway, forage for food, or work together on a shared task, they continuously negotiate—often without noticing—how much to cooperate or compete. Unlike classical laboratory games that force players to choose between fixed options in advance, real-life interactions unfold dynamically, with movement timing and subtle cues shaping social behavior from one moment to the next.
A collaborative research team from the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPI), the University of Göttingen, and the German Primate Center—Leibniz Institute for Primate Research (DPZ) has developed a novel experimental framework that captures this natural complexity. Their study, published in Communications Psychology, reveals how human pairs spontaneously settle into stable cooperative, intermediate or competitive roles—and how these strategies arise from the interplay between social motives, cost-benefit constraints, and sensorimotor skills.