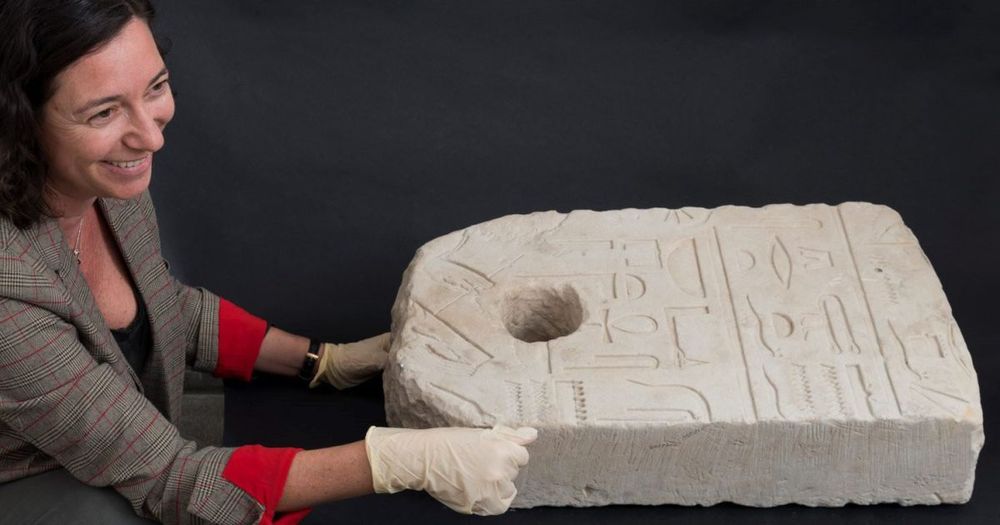
A veterinarian taking a morning swim found what turned out to be an anchor engraved with hieroglyphs on the seafloor. But who defaced the Egyptian goddess?


“It’s very, very transmissible, and it almost certainly is going to be a pandemic,” said Dr. Anthony S. Fauci, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease.
Rapidly rising caseloads alarm researchers, who fear the virus may make its way across the globe. But scientists cannot yet predict how many deaths may result.
Braintree founder Bryan Johnson, MBA’07, invests in bold ventures on the next frontier.
Bryan Johnson is determined to explore the depths of your mind and help save humanity from its direst threats.
“The biggest revolutions that have happened over the past couple of decades have largely been done on silicon—the transistors we build, the computers we have, the internet, our smartphones,” said Johnson, MBA’07. “The next great revolutions will be evolving our cognition and predictably engineering atoms, molecules, organisms and complex systems.”

If you’re interested in mind uploading, then I have an excellent article to recommend. This wide-ranging article is focused on neuromorphic computing and has sections on memristors. Here is a key excerpt:
“…Perhaps the most exciting emerging AI hardware architectures are the analog crossbar approaches since they achieve parallelism, in-memory computing, and analog computing, as described previously. Among most of the AI hardware chips produced in roughly the last 15 years, an analog memristor crossbar-based chip is yet to hit the market, which we believe will be the next wave of technology to follow. Of course, incorporating all the primitives of neuromorphic computing will likely require hardware solutions even beyond analog memristor crossbars…”
Here’s a web link to the research paper:
Computers have undergone tremendous improvements in performance over the last 60 years, but those improvements have significantly slowed down over the last decade, owing to fundamental limits in the underlying computing primitives. However, the generation of data and demand for computing are increasing exponentially with time. Thus, there is a critical need to invent new computing primitives, both hardware and algorithms, to keep up with the computing demands. The brain is a natural computer that outperforms our best computers in solving certain problems, such as instantly identifying faces or understanding natural language. This realization has led to a flurry of research into neuromorphic or brain-inspired computing that has shown promise for enhanced computing capabilities. This review points to the important primitives of a brain-inspired computer that could drive another decade-long wave of computer engineering.
New Research Estimates 75,000 People in Wuhan Are Infected With Coronavirus.
Everyone is aware of the fact that Coronavirus is spreading across China and the world quickly. By far, the virus has affected over 11,800 people and the global death toll has risen to at least 250.
Now, the Government of China has urged its people to give up non-veg because scientists believe that eating slaughtered animals’ flesh may be the cause of the disease. The virus is believed to have spread from animals to humans.
One research from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows that more than 75% of emerging diseases originate in animals. Experts believe that the dangerous virus might have originated in a market in Wuhan, China, where humans have direct contact with live animals and animal flesh. So far, many dangerous viruses have originated in animals such as the new coronavirus, SARS, bird flu, and more.

O.o!
Portfolio manager and crypto analyst Mati Greenspan says billions of dollars are essentially sitting on the sidelines, ready to move into Bitcoin, Ethereum, XRP and the altcoin market at large.
Greenspan is using data from the crypto research firm Messari, which shows that the total value of all stablecoins is just shy of $6 billion. Stablecoins are digital currencies that are pegged to traditional assets like fiat. They’re designed to maintain a steady value and offer crypto traders an easy way to sidestep the extreme volatility of the crypto markets.
Greenspan’s theory implies that the billions of dollars in the stablecoin market represent traders who have decided to exit their positions in BTC, ETH, XRP and other crypto assets and are waiting for the optimal time to re-enter the market.
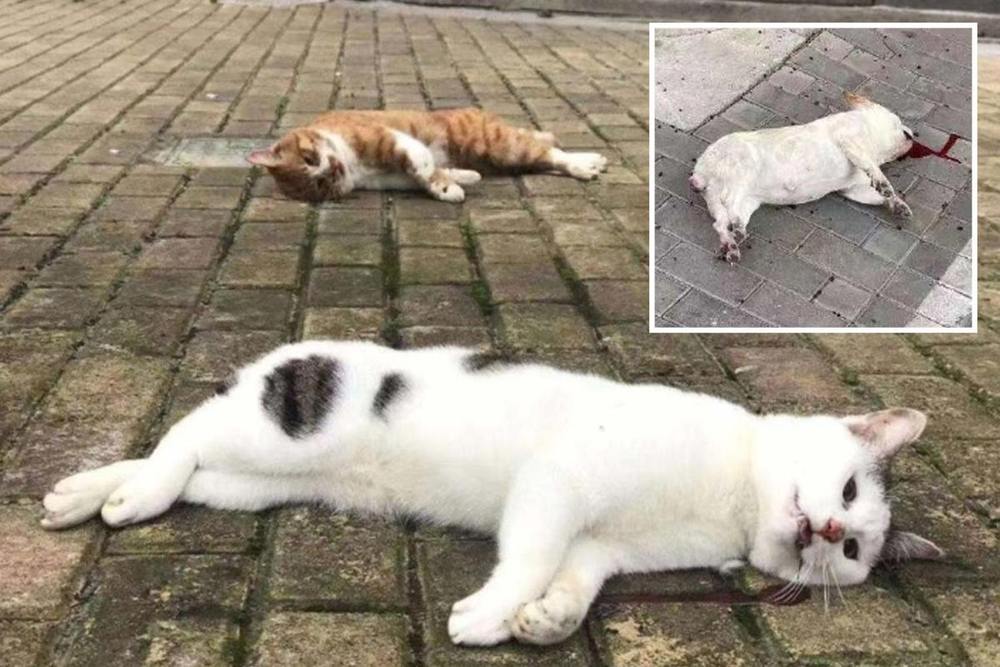
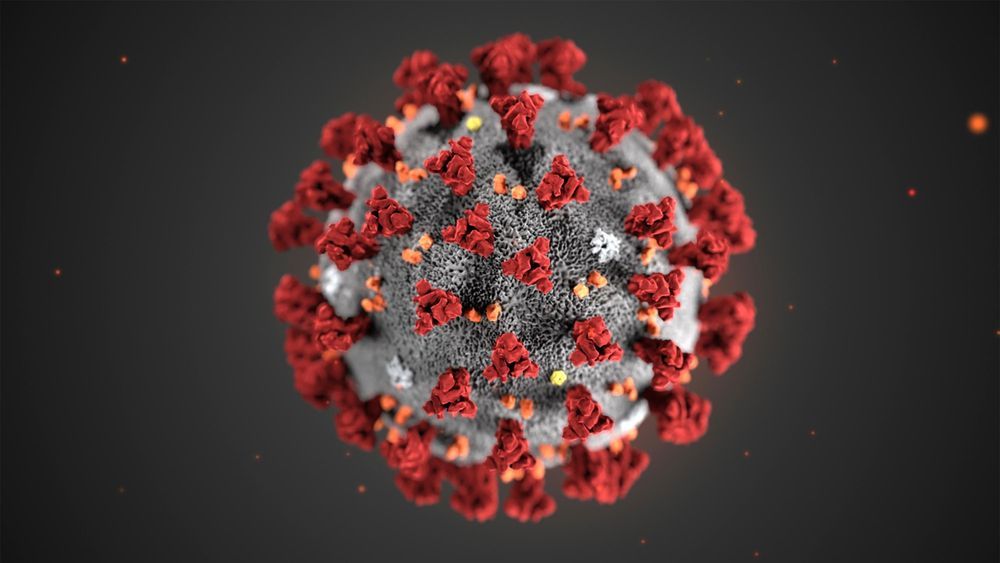

PANICKING pet owners are reportedly throwing cats and dogs out of towerblocks following bogus claims deadly coronavirus can be passed on by animals.
Chilling pictures coming out of crisis-hit China are said to show the bloodied corpses of animals lying in the road after being hurled to their death.
One dog was found dead after allegedly being thrown from one block of flats in Tianjin City in Hebei Province — home to the outbreak epicentre Wuhan.