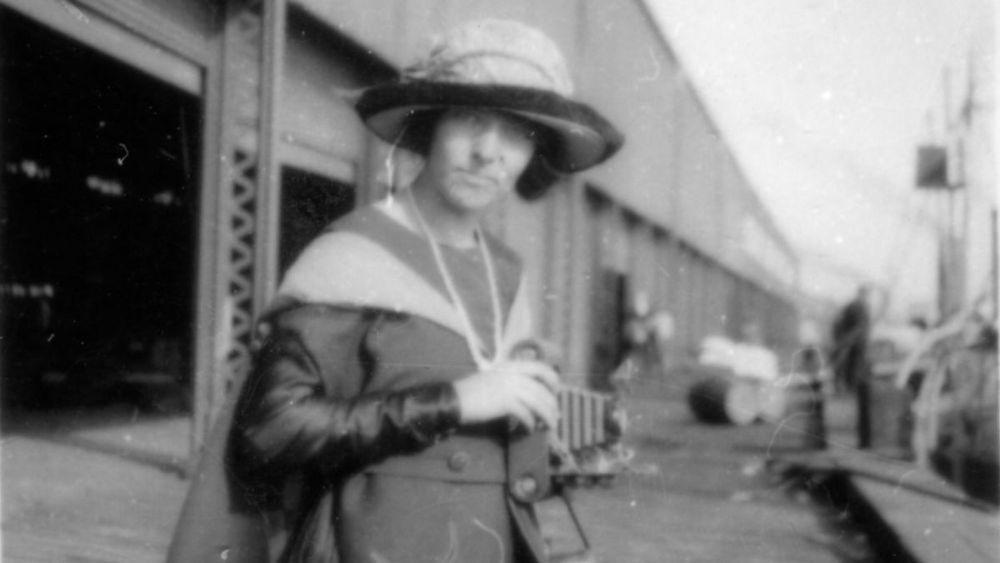
Astronomers are rediscovering how calculations made by the ‘human computer’ Elizabeth Williams contributed to the first observations of Pluto 90 years ago.
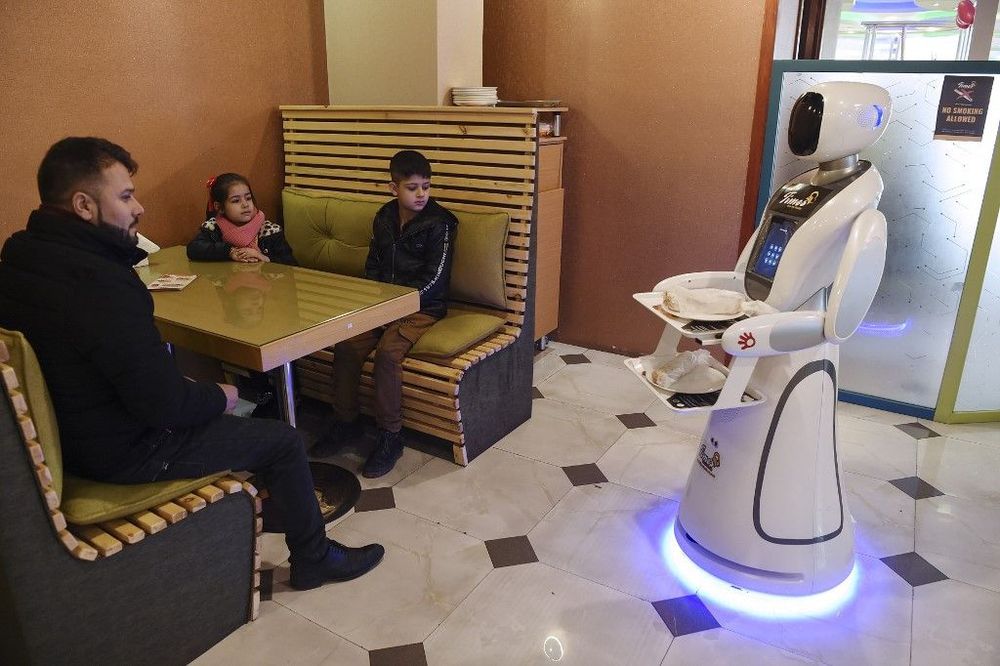



Afghanistan’s first-ever robot waitress glides up to a table of curious diners in central Kabul and presents them with a plate of French fries.
“Thank you very much,” the machine says in Dari, one of Afghanistan’s two main languages.
Restaurant manager Mohammad Rafi Shirzad says the humanoid robot, imported from Japan and designed to look vaguely like a women wearing a hijab, has already pulled in new customers since it started working last month.
Newborn screening covers more than 30 conditions. Yet, with genome sequencing, we could screen newborns for several thousand genetic conditions.
In the surveys’ open-ended responses about risks of genome sequencing, parents and clinicians both expressed concerns about psychological distress related to difficult or uncertain results. Clinicians were more likely to raise concerns about returning results for adult-onset conditions, unnecessary parental stress over health problems that might never actually occur, and the possibility of future discrimination against the child on the basis of their genomic information.
On the other hand, parents mentioned a broader range of benefits than clinicians. Both parents and clinicians saw potential health benefits of genome sequencing, such as the ability to search for more conditions compared to standard newborn screening and the ability to predict a child’s future disease risks. Parents went further, though, seeing benefits in family planning, preparing for the child’s future, and knowledge just for the sake of knowing. Those potential benefits fall outside of traditional definitions of clinical utility, which means they are less likely to be considered in the professional guidelines that steer adoption of practices like genome sequencing.
This brings us into a debate that may be central to the near future of genome sequencing, not only for newborns but for ostensibly healthy adults as well: how to define the utility of genomic technologies. How much weight, if any, should patients’ perceptions carry? If they think genomic information will have utility, should that count for something, even if clinicians and researchers have their doubts? Should the idea of “clinical utility” be expanded beyond information that directly affects medical care, perhaps including perceived quality of life impacts for patients?
Researchers at Haifa’s Technion–Israel Institute of Technology say they have developed a standalone system capable of producing water from air, including in desert regions.
Described as the “first technology of its kind in the world,” the energy-efficient system aims to assist small and isolated communities far from freshwater and saltwater sources.
Superb piece.
“But, I say we should pursue science and technology because, like Prometheus, the fires of invention burn bright, and although we may not always know where it leads us, a world darkened by the fear of treading upon the unknown, is unimaginable.”
Yet we can look to a brighter side, one I could never have imagined in the ’60’s when the chromosomes we karyotyped would be uncoiled to lay bare the genome as an instrument for critical medical diagnoses, to set free those erroneously convicted of crime, or enlighten us about Mitochondrial Eve our common mother, and the long journey that began two hundred thousand years ago; the journey that brought me into the world of physical things, air, table and chairs, and beyond into the space of the geometries and cohorts, like Golay and Bolsey, who helped me better understand my Universe, the one either too small or too far to see, unless aided by the eyes of science and technology. I once wondered how I got here, and now I think I know, but I am afraid my second query, “where will it lead,” will remain an open question.
One cannot predict with any precision where technology will lead us, although it has the indisputable potential to reduce suffering, extend life, and increase living standards. And, in the hands of the powerful, we witness its misuse altering natural patterns: ecosystems, the sustainability of organisms, to kill with greater efficiency. If we were separated from modern inventions, we would remain alive not more than a few days, weeks for survivalists. Invention does not only express our ingenuity, it expresses a societal conscience commensurate with the kind of world we collectively choose to live in.
Ingenuity itself has little control over where it leads, and I have long wondered whether one might in the words of Hamlet, “bear those ills we have than fly to others that we know not of.” But, I say we should pursue science and technology because, like Prometheus, the fires of invention burn bright, and although we may not always know where it leads us, a world darkened by the fear of treading upon the unknown, is unimaginable.
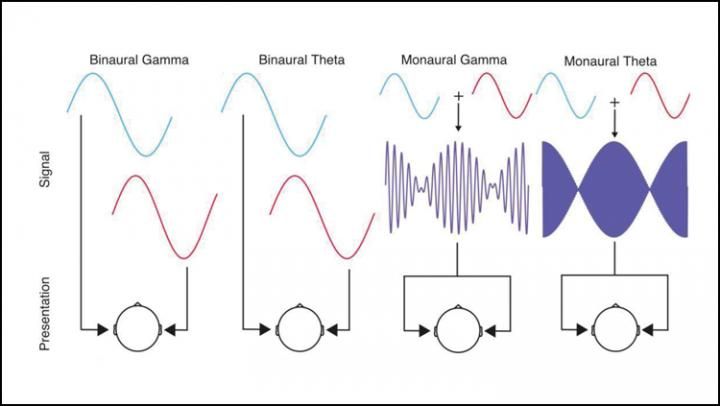
An auditory illusion thought to synchronize brain waves and alter mood is no more effective than other sounds, according to research in adults recently published in eNeuro. The effect reported in other studies might be a placebo but could still have helpful effects for some people.
Binaural beats are an auditory illusion caused by listening to two tones of slightly different frequency, one in each ear. The difference in frequencies creates the illusion of a third sound — a rhythmic beat. Neurons throughout the brain begin to send electrical messages at the same rate as the imaginary beat. Many unsupported claims surround binaural beats, including that listening to them decreases anxiety, increases focus, and improves mood.
Orozco Perez et al. played binaural and monoaural beats to healthy adults and measured their brain activity with electroencephalography. Monoaural beats don’t rely on the illusion to create the beats because they consist of edited audio tracks of the two different tones together. Both ears hear all three sounds. Brain activity synchronized with both types of beats, but the effect was stronger with monoaural beats. Neither type of beat affected mood. When the binaural beat played, far apart brain areas synchronized with each other at a different frequency than the beat. This may be how binaural beats improve memory and focus.
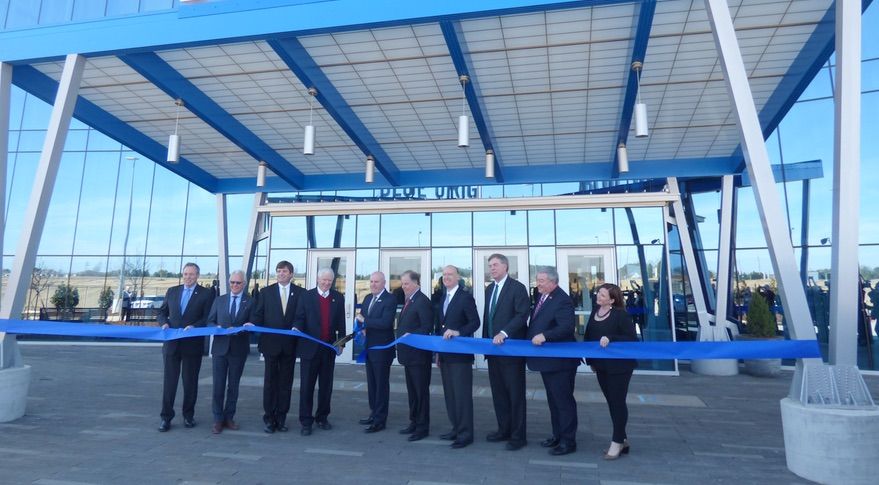

HUNTSVILLE, Ala. — Blue Origin formally opened a factory Feb. 17 that the company plans to use to produce engines both for its vehicles and for United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket.
A ribbon-cutting ceremony marked the completion of a 350,000-square-foot factory here that will produce BE-4 and BE-3U engines. The factory, built in a little more than a year, will host more than 300 employees and produce up to 42 engines a year.
“You can see we can get some things done really quickly,” said Bob Smith, chief executive of Blue Origin, in remarks at the ceremony. “Twelve months to actually build this kind of facility is an amazing accomplishment for our team.”

Despite a federal judge’s ruling last September that the U.S. government’s terror watch list violates constitutional rights, an FBI report obtained by Yahoo News shows local and state law enforcement agencies are being used to gather intelligence on individuals to collect information about those already in the database.
Law enforcement “encounters of watchlisted individuals almost certainly yield increased opportunities for intelligence collection,” says the FBI document, dated more than a month after the federal court ruling. The FBI says such encounters could include traffic stops or domestic disputes, which gives law enforcement “the opportunity to acquire additional biographic identifiers, fraudulent identification documents, financial information and associates of watchlisted individuals,” which might assist in thwarting terrorist acts.
The Terrorism Screening Database, widely known as the watch list, was created in 2003 and consists of names of people suspected of being involved with terrorism. Over the years, the list has grown to include the names of 1.1 million people, raising concerns that many of those on the list have no involvement in terrorism but have little or no legal resources with which to challenge the designation.

Matter-wave interference experiments provide a direct confirmation of the quantum superposition principle, a hallmark of quantum theory, and thereby constrain possible modifications to quantum mechanics1. By increasing the mass of the interfering particles and the macroscopicity of the superposition2, more stringent bounds can be placed on modified quantum theories such as objective collapse models3. Here, we report interference of a molecular library of functionalized oligoporphyrins4 with masses beyond 25,000 Da and consisting of up to 2,000 atoms, by far the heaviest objects shown to exhibit matter-wave interference to date. We demonstrate quantum superposition of these massive particles by measuring interference fringes in a new 2-m-long Talbot–Lau interferometer that permits access to a wide range of particle masses with a large variety of internal states. The molecules in our study have de Broglie wavelengths down to 53 fm, five orders of magnitude smaller than the diameter of the molecules themselves. Our results show excellent agreement with quantum theory and cannot be explained classically. The interference fringes reach more than 90% of the expected visibility and the resulting macroscopicity value of 14.1 represents an order of magnitude increase over previous experiments2.
30 years ago, scientist Carl Sagan asked NASA’s Voyager 1 to capture an iconic portrait of our world. This humbling view of Earth from 6.4 billion km away is known as the “Pale Blue Dot.”
➡ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/NatGeoSubscribe
About National Geographic:
National Geographic is the world’s premium destination for science, exploration, and adventure. Through their world-class scientists, photographers, journalists, and filmmakers, Nat Geo gets you closer to the stories that matter and past the edge of what’s possible.
Get More National Geographic:
Official Site: http://bit.ly/NatGeoOfficialSite
Facebook: http://bit.ly/FBNatGeo
Twitter: http://bit.ly/NatGeoTwitter
Instagram: http://bit.ly/NatGeoInsta
Pale Blue Dot – 30th Anniversary | National Geographic.
National Geographic
https://www.youtube.com/natgeo