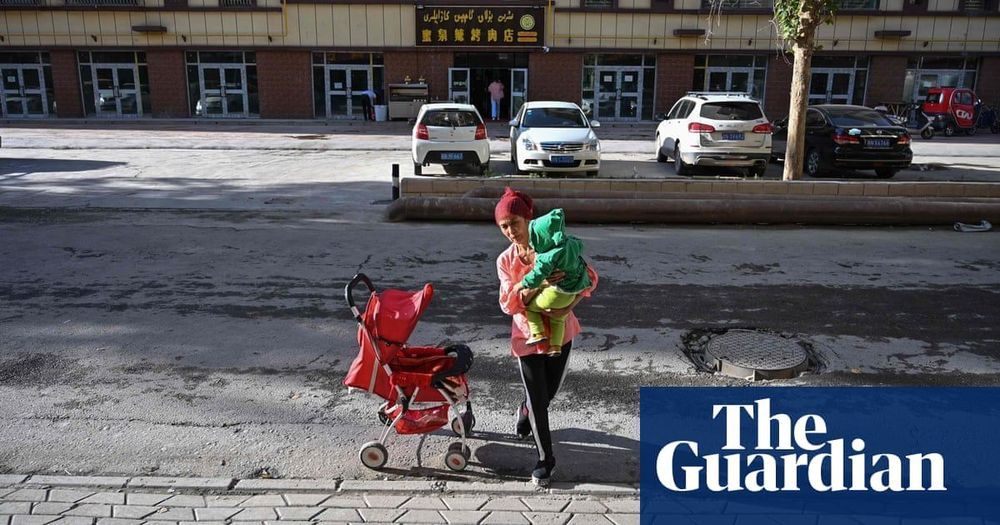
The new strain, scientists say, is carried by pigs but can infect humans and requires close monitoring.
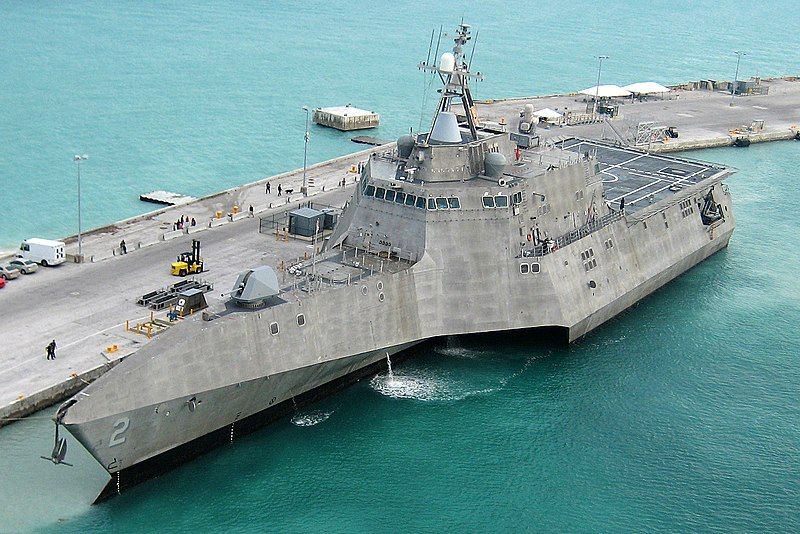




Austal USA has delivered the US Navy’s 12th Independence-class littoral combat ship (LCS), the future USS Oakland (LCS 24).
The vessel was accepted by the service during a ceremony in Mobile, Alabama. It is the 22nd LCS to join the fleet and the third LCS delivered to the US Navy this year.
LCS programme manager captain Mike Taylor said: “This is a great day for the navy and our country with the delivery of the future USS Oakland. This ship will play an essential role in in carrying out our nation’s future maritime strategy.”
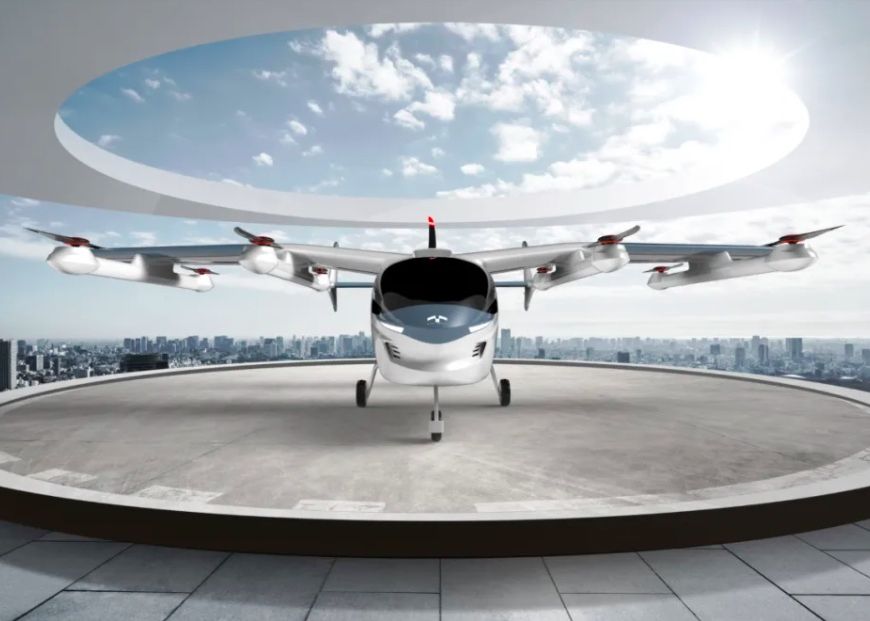

The Zhejiang Geely Holding Group recently unveiled the prototype design of the Terrafugia TF-2A eVTOL aircraft, and announced that they have already begun flight tests as well. The newer design is a clear upgrade over the previous demonstrator that was revealed in December 2019.
Based on the aesthetics of a tiger shark, the TF-2A features a large upper wing, H-shaped tail, eight lift propellers for vertical takeoff or landing (VTOL) as well as one rear propeller for horizontal flight. According to Geely, the design should make certification easier to obtain as opposed to the more common tilt-rotor designs in the industry. For example, the New Hampshire Senate recently motioned to pass a number of bills, one of which pertained to the topic of aerial mobility. HB-1517, “An Act Relative to Roadable Aircraft,” adds the words “roadable aircraft” to existing laws for vehicles concerning things like inspections and crashes, requiring the roadable aircraft to be “required to take off and land from a suitable airstrip and shall be prohibited from taking off and landing from any public roadway, unless under conditions of an emergency”. Currently, only Terrafugia’s TF-2A and PAL-V’s eVTOL meet these standards.


A replay of the gala can be seen on YouTube.