Even AI likes a trip to the movies.
The scientists also used functional MRI scanners to study the participants’ brain activity, enabling them to map 78 brain regions and examine the connections between these areas.
“The major challenge in this study,” explains first study author Tomoki Tokuda, who is a statistician at OIST, “was to develop a statistical tool that could extract relevant information for clustering similar subjects together.”
Tokuda developed a new statistical method that allowed the researchers to break down more than 3,000 measurable features into five data clusters. The measurable features included the incidence of childhood trauma and the initial severity of the depressive episode.
Europe delivers Orion’s ‘powerhouse’
Posted in space
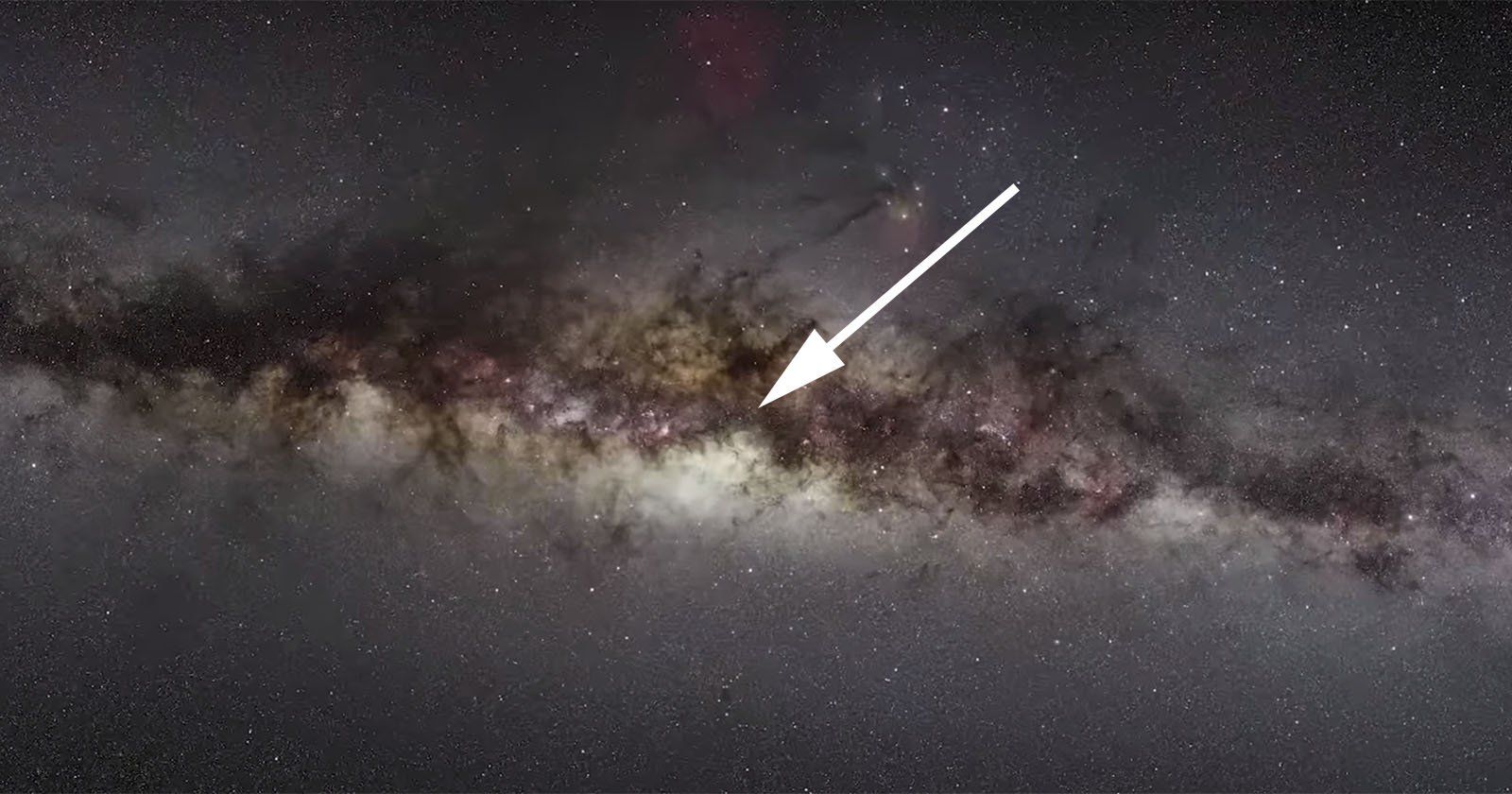
Scientists just further confirmed what has long been believed: that there’s a supermassive black hole scientists named Sagittarius A* at the center of our Milky Way galaxy. This mind-blowing 1.5-minute video zooms in from a wide view of the night sky into the tiny little area where the latest telescopic observations were just made.
In a paper published on October 31st, 2018, scientists at the European Southern Observatory (ESO) detailed how they used the GRAVITY interferometer and the four telescopes of the Very Large Telescope (VLT) to create a virtual telescope that effectively has a diameter of 427 feet (130m).
Pointing this ultra-telescope straight at Sagittarius A*, scientists detected bright spots of gas traveling in orbits around Sagittarius A* at 30% the speed of light.
An ambitious effort to sequence the genome of every complex organism on Earth was officially launched on 1 November in London.
“Variation is the fount of all genetic knowledge,” says project member and evolutionary geneticist Jenny Graves of La Trobe University in Melbourne, Australia. “The more variation you have the better — so why not sequence everything?”
The Earth BioGenome Project aims to sequence the genomes of the roughly 1.5 million known animal, plant, protozoan and fungal species — collectively known as eukaryotes — worldwide over the next decade. The initiative is estimated to cost US$4.7 billion, although only a small proportion of that money has been committed so far.