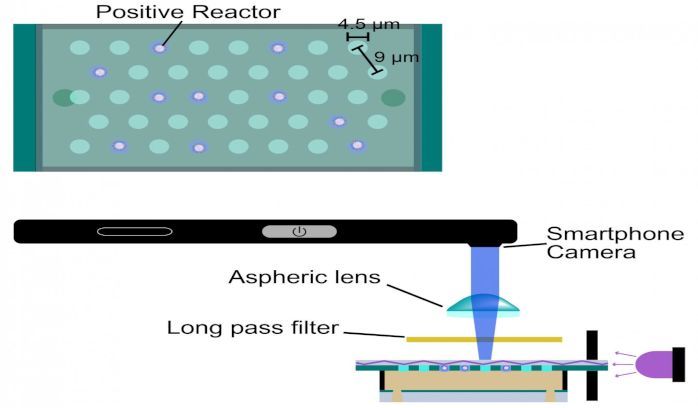
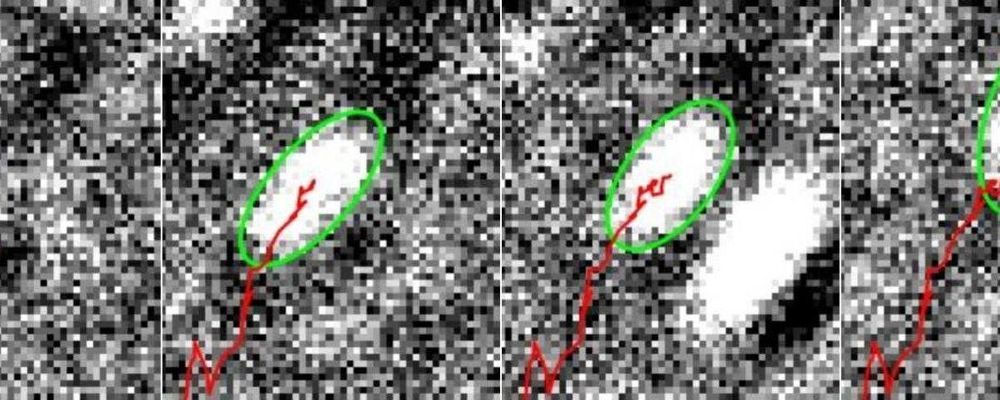
Most of us are similar with ‘viruses’ and malware relating to our computers or smartphones, but Yoshihiro Minagawa, a researcher from the University of Tokyo has taken it on literally – he has invented a portable, low-cost, battery-powered device that pairs with a smartphone, which was tested with viruses but could also detect other biological markers. His initial findings, together with other teammates were published recently in the journal, Lab on a Chip.
The current leading method to assess the presence of viruses and other biological markers of disease is effective but large and expensive. It is prohibitively difficult for use in many situations, especially due to certain economic and geographic factors. Although highly accurate at counting viruses, these tools are just too cumbersome for many situations, especially when rapid diagnosis is required.
“I wanted to produce a useful tool for inaccessible or less-affluent communities that can help in the fight against diseases such as influenza,” said Minagawa. “Diagnosis is a critical factor of disease prevention. Our device paves the way for better access to essential diagnostic tools.”