A new study has found ground-breaking evidence from an ice core in the Swiss-Italian Alps that proves the 7th century switch from gold to silver currencies in western Europe actually occurred a quarter of a century earlier than previously thought.
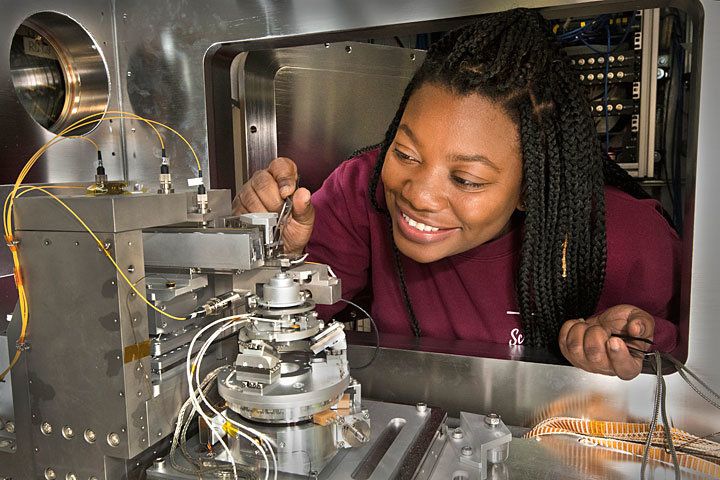
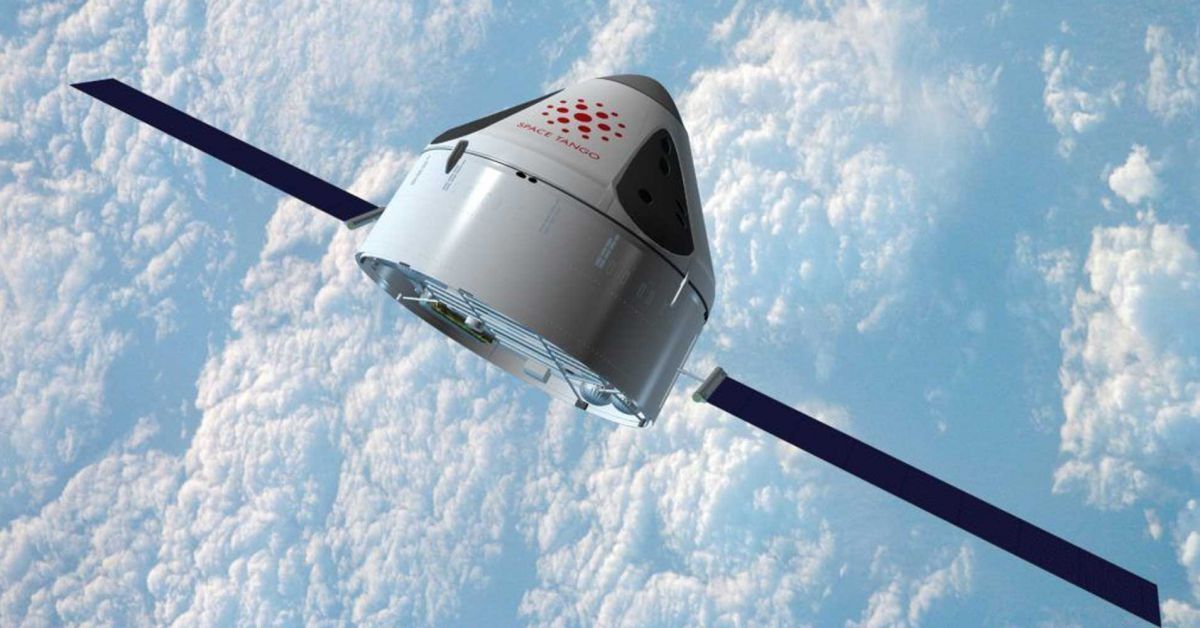
Scientists at the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II)—a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility at DOE’s Brookhaven National Laboratory—have used ultrabright x-rays to image single bacteria with higher spatial resolution than ever before. Their work, published in Scientific Reports, demonstrates an X-ray imaging technique, called X-ray fluorescence microscopy (XRF), as an effective approach to produce 3D images of small biological samples.
En Taro AI
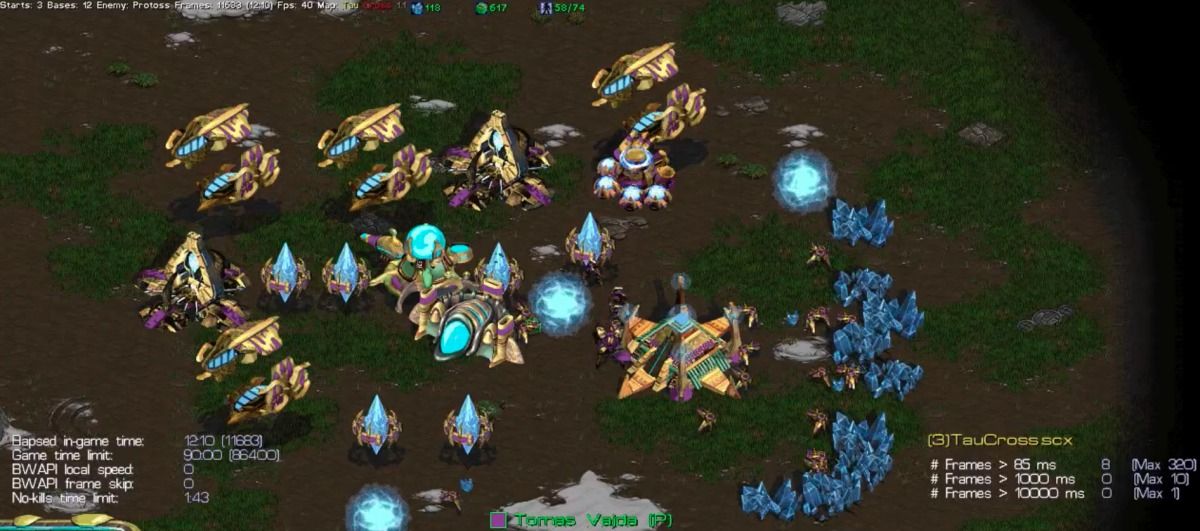
The latest results in a long-running contest of video-game-playing AIs reveal how hard it is for machines to master swarming insectoid Zergs or blitzing Protos. They also show that even old-school approaches can still sometimes win out.
The AIIDE Starcraft Contest has been running at Memorial University in Newfoundland, Canada, since 2010. Participating teams submit bots that play an original version of Starcraft, a sprawling sci-fi-themed game, in a series of one-on-one showdowns.
Starcraftiness: Video games are generally useful in AI because they offers a constrained environment and a good way to quantify progress. The popular online strategy game Starcraft has emerged as an important benchmark for AI both because it is extremely complicated and because it’s a game where it’s hard to measure progress. There are a vast number of possible states and a huge number of potential moves at every moment. And it can be hard to tell if a strategy is a good one until much later on in a battle.
The “goodnight” commands finalize the spacecraft’s transition into retirement, which began on Oct. 30 with NASA’s announcement that Kepler had run out of fuel and could no longer conduct science.
Coincidentally, Kepler’s “goodnight” falls on the same date as the 388-year anniversary of the death of its namesake, German astronomer Johannes Kepler, who discovered the laws of planetary motion and passed away on Nov. 15, 1630.
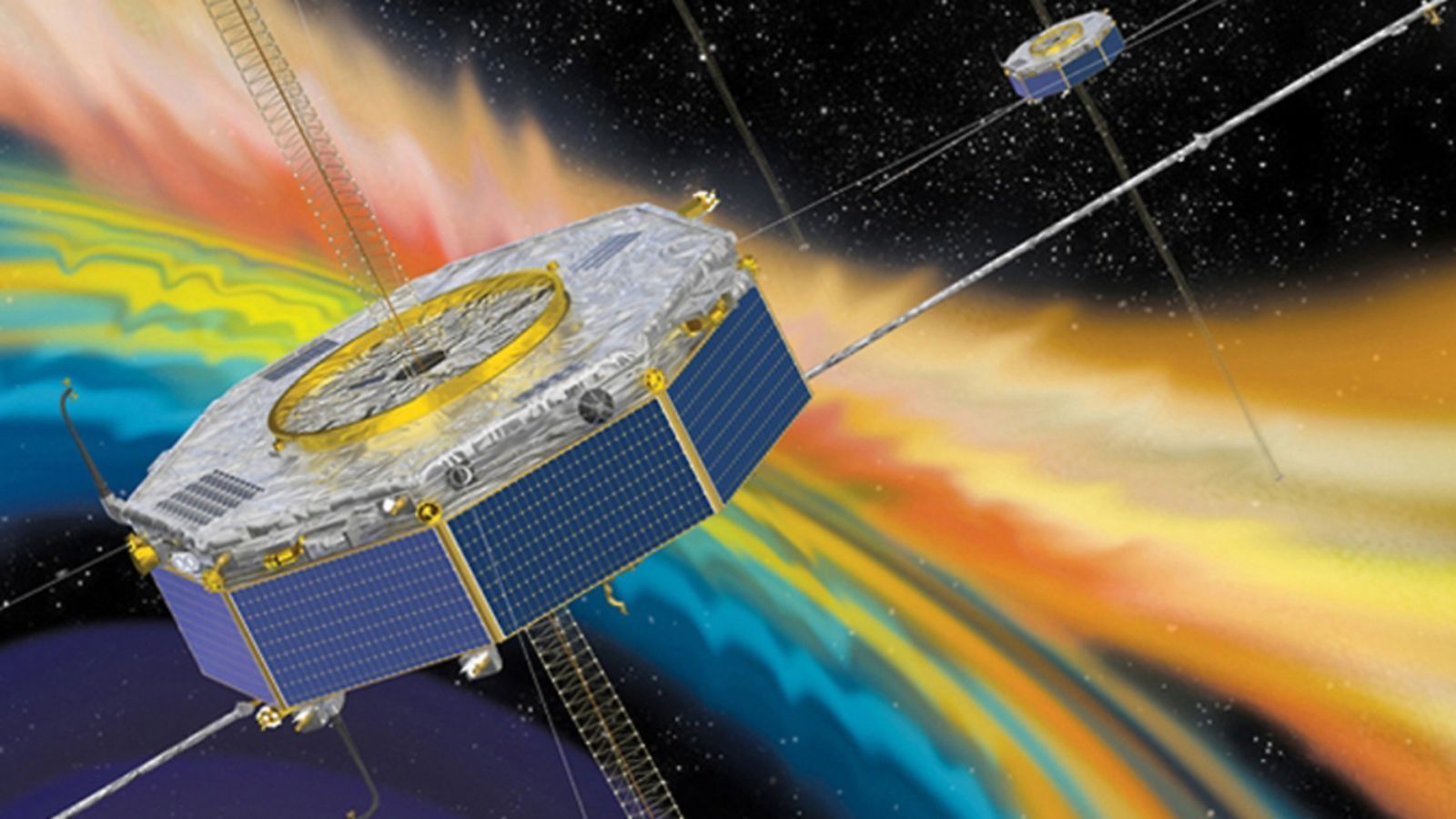
Magnetic fields around the Earth release strong bursts of energy, accelerating particles and feeding the auroras that glow in the polar skies. On July 11, 2017, four NASA spacecrafts were there to watch one of these explosions happen.
The process that produces these bursts is called magnetic reconnection, in which different plasmas and their associated magnetic fields interact, releasing energy. The Magnetospehric Multiscale Mission (MMS) satellites launched in 2015 to study the places where this reconnection process occurs. This newly released research shows for the first time that the mission encountered one of these reconnection sites in the night side of the Earth’s magnetic field, which extends behind the planet as a long “magnetotail.”
The next time you’re gazing out of the window in search of inspiration, keep in mind the material you’re looking through was forged inside the heart of an exploding ancient star.
An international team of scientists said Friday they had detected silica—the main component of glass—in the remnants of two distant supernovae billions of light years from Earth.
Researchers used NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope to analyse the light emitted by the collapsing mega-cluster and obtain silica’s “fingerprint” based on the specific wavelength of light the material is known to emit.