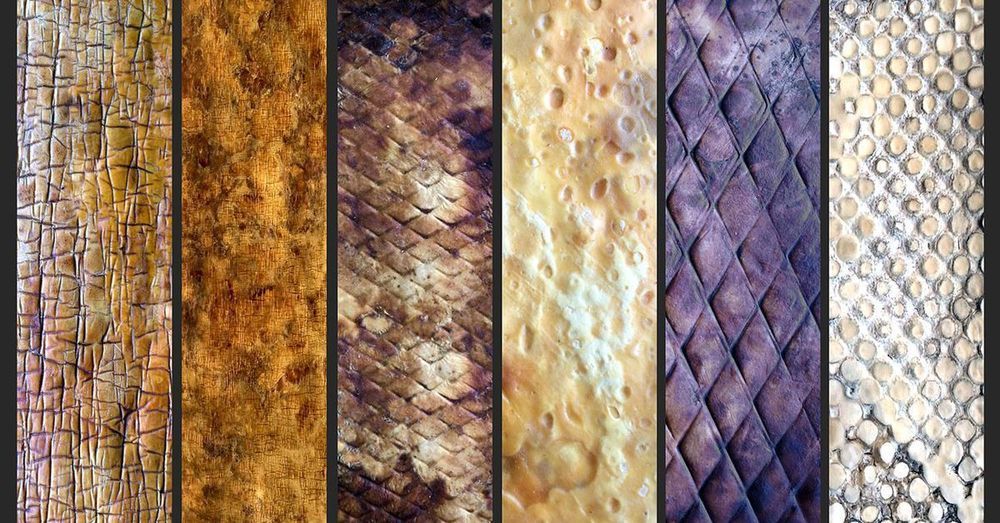
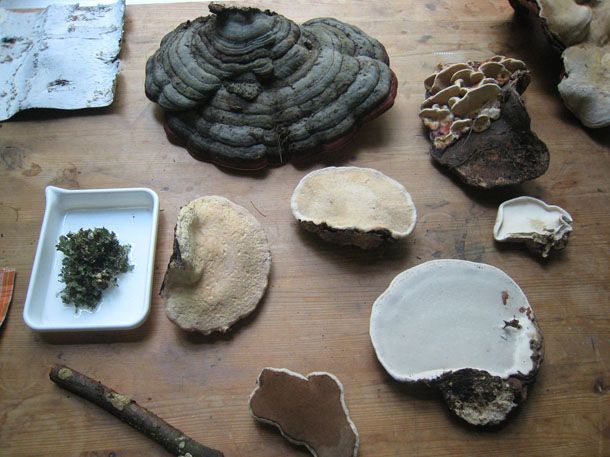
Bay Area based artist-inventor and amateur mycologist Phil Ross has an international patent pending on a method of producing fungus as a sustainable construction material. It may be surprising to hear that a biodegradable, durable, and non-toxic building material is on sale in the vegetable aisle at the supermarket. However, it’s not the tasty caps that Ross is after, but the root-like fibers of mushrooms form an enormous underground tangle called mycelium. Dried mycelium forms a lightweight mold and water resistant fire-proof material that is an effective insulator. It is also very sturdy stuff. Bob Engels of Gourmet Mushrooms notes, “Hardened steel blades on equipment at our farm need regular attention following their encounters with these massed threads of hyphae.”
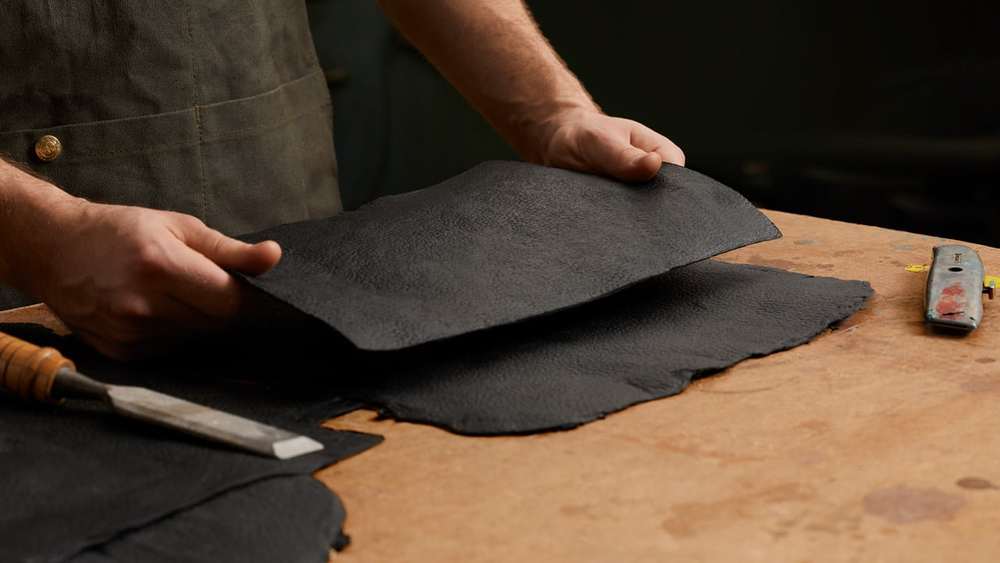
Ross reported that multiple saw blades and metal files were destroyed while shaping the five hundred mycelium bricks he grew into an archway. The archway was a 6×6 foot sculpture titled Mycotectural Alpha, and was likely the first man-made structure made entirely out of mushrooms. Others have taken notice of the potential of fungus—a new start-up called Evocative Design producing mycelium alternatives to styrofoam and insulation material has received grants from the National Science Foundation, the Environmental Protection Agency, and the Department of Agriculture.
Ross’s “biotechnical” artwork encompasses drawings, paintings, sculptures, prototypes, and extensive materials research. Over the past 15 years he has been experimenting with fungus, growing and shaping mushrooms in sterile laboratory-like environments, even learning to make his own air filters to provide the necessary clean air. He says mycelium bricks can be grown in about a week from a mixture poured into a mold, but the more organic-looking mushroom sculptures that are created by adding or subtracting gas or air from their growing environment can take years to create. the artist explains how the “myotecture” bricks are made: