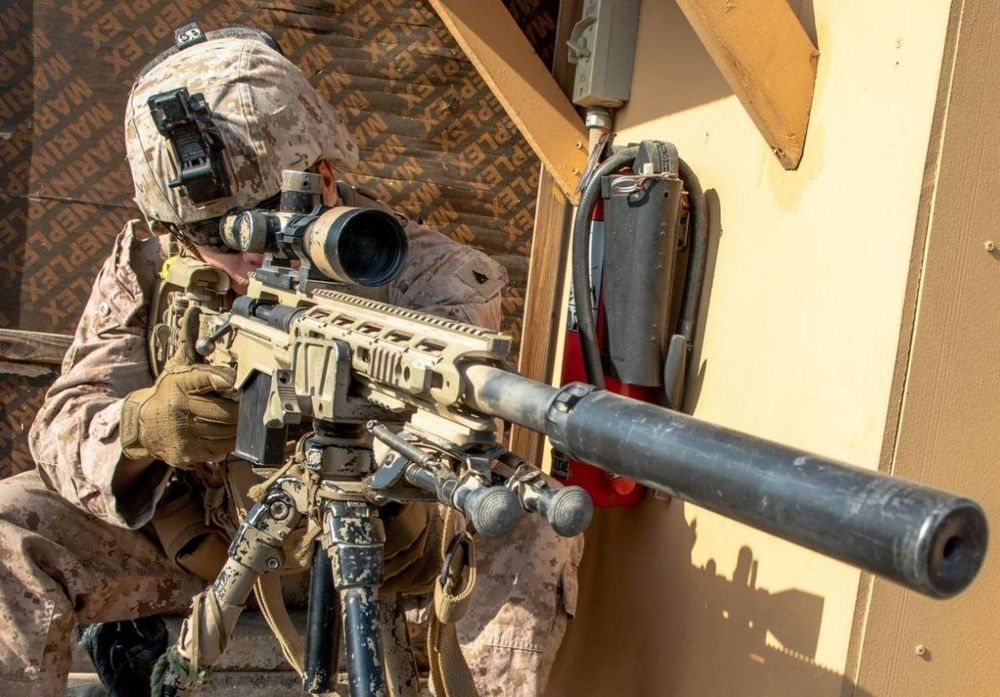
Key point: Washington knows it needs high-tech weapons and machines to win future wars. That includes robots to haul supplies and assist the Marines in winning any fight.
The U.S. Navy is moving quickly to develop robotic warships that could hunt submarines and other ships, screen aircraft carriers and convoys from air attack and sweep away enemy mines.
But there’s another mission the Navy should consider assigning to unmanned surface vessels, Neil Zerbe, a retired Navy officer, argued for the Center for International Maritime Security: shuttling supplies from ship to shore in the aftermath of an amphibious assault by U.S. Marines.