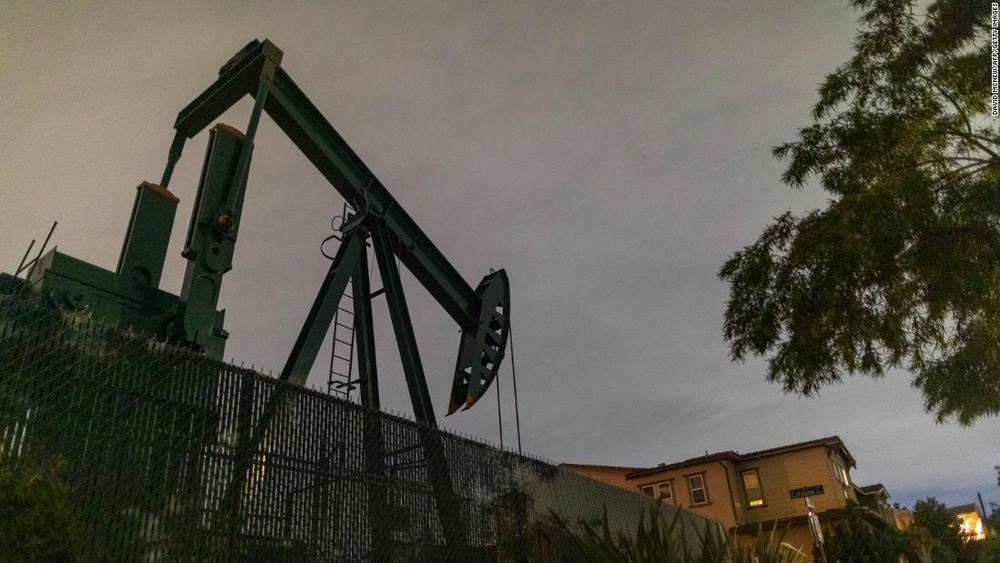
WTI, the US benchmark, finished at -$37.63 a barrel on Monday. Producers are paying stockpilers to take barrels off their hands, as the coronavirus crisis saps demand and producers run out of places to store excess crude.


👽 Stalin’s Crab is eating the Oceans biodiversity and tis gaining terrain as we are speaking now.
They’re multiplying in the Barents Sea. And they’re heading West. Meet the red king crabs. 🦀.
Salamanders and lizards can regrow limbs. Certain worms and other creatures can generate just about any lost part — including a head — and the latest genetics research on body part regeneration is encouraging.
Since they are adult stem cells that have reverted back to a less developed — more pluripotent — state, iPSCs remind scientists of the stem cells that enable lizards to regrow limbs, and zebrafish to regrow hearts. When it comes to limbs, the understanding the regrowth process could help scientists promote nerve regeneration in cases when a limb is severely damaged, but not physically lost. Nerves of the human peripheral nervous system do have the ability to regrow, but whether this actually happens depends on the extent of the injury, so understanding the stem cell physiology in zebrafish and other animals could help clinicians fill the gap. The knowledge gained also could impact development of treatments aimed at promoting nerve regrowth in the central nervous system, for instance in the spinal cord after an injury.
Caveats
Even where regeneration is natural for humans, numerous regeneration cycles can put a person at greater risk of cancer. In the liver, for instance, disease can result in liver cancer largely because the organ produces new cells to replace the damaged ones. This is what happens in cirrhosis and after certain viral conditions when there are periods when regeneration overtakes liver deterioration. Prometheus avoided this fate, but we don’t know how well the process would work in humans, if a regenerative system based on iPSCs or some other types of stem cell is used clinically on a large scale. Regenerative medicine is promising and exciting to hear about. But we are at a very early stage, and reports on limb regrowth should be taken with caution.

Your phone’s GPS, the Wi-Fi in your house and communications on aircraft are all powered by radio-frequency, or RF, waves, which carry information from a transmitter at one point to a sensor at another. The sensors interpret this information in different ways. For example, a GPS sensor uses the angle at which it receives an RF wave to determine its own relative location. The more precisely it can measure the angle, the more accurately it can determine location.
In a new paper published in Physical Review Letters, University of Arizona engineering and optical sciences researchers, in collaboration with engineers from General Dynamics Mission Systems, demonstrate how a combination of two techniques—radio frequency photonics sensing and quantum metrology—can give sensor networks a previously unheard-of level of precision. The work involves transferring information from electrons to photons, then using quantum entanglement to increase the photons’ sensing capabilities.
“This quantum sensing paradigm could create opportunities to improve GPS systems, astronomy laboratories and biomedical imaging capabilities,” said Zheshen Zhang, assistant professor of materials science and engineering and optical sciences, and principal investigator of the university’s Quantum Information and Materials Group. “It could be used to improve the performance of any application that requires a network of sensors.”
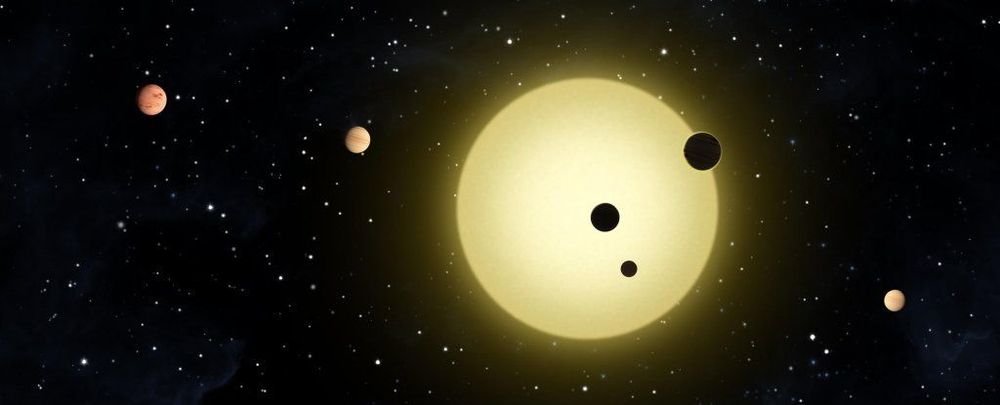


The star itself is about the same mass and a little larger than the Sun — a minority in our exoplanet hunts. It’s orbited by six planets: a super-Earth and five mini-Neptunes.
After monitoring it for seven years, astronomers have discovered that all six of those planets are orbiting HD 158259 in almost perfect orbital resonance. This discovery could help us to better understand the mechanisms of planetary system formation, and how they end up in the configurations we see.
Ladies Monday with ReallyGraceful going a bit further into Bill Gates.
Patreon: http://patreon.com/reallygraceful Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/reallygraceful Twitter: https://twitter.com/reallygraceful Instagram: http://instragam.com/reallygraceful
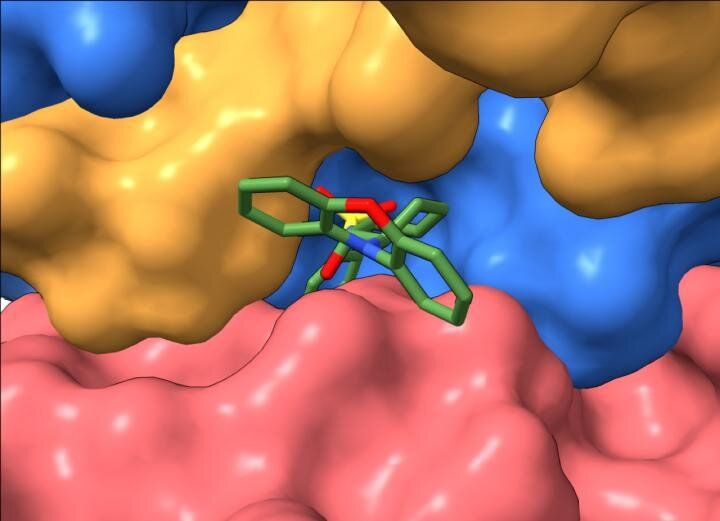
A team of scientists led by the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center and Case Comprehensive Cancer Center has identified the binding site where drug compounds could activate a key braking mechanism against the runaway growth of many types of cancer.
The discovery marks a critical step toward developing a potential new class of anti–cancer drugs that enhance the activity of a prevalent family of tumor suppressor proteins, the authors say.
The findings, which appear in the leading life sciences journal Cell, are less a story of what than how.

Multiple sclerosis (MS) is known as “the disease with a thousand faces” because symptoms and progression can vary dramatically from patient to patient. But every MS patient has one thing in common: Cells of their body’s own immune system migrate to the brain, where they destroy the myelin sheath—the protective outer layer of the nerve fibers. As a result, an electrical short circuit occurs, preventing the nerve signals from being transmitted properly.
Many MS medications impair immune memory
Researchers don’t yet know exactly which immune cells are involved in stripping away the myelin sheath. Autoreactive T and B cells, which wrongly identify the myelin sheath as a foreign body, travel to the brain and initiate the disease. “Up until now, MS drugs have essentially targeted these T and B cells, both of which are part of the acquired immune system,” says Dr. Alexander Mildner, a scientist at the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (MDC) and the senior author of the paper now published in Nature Immunology.
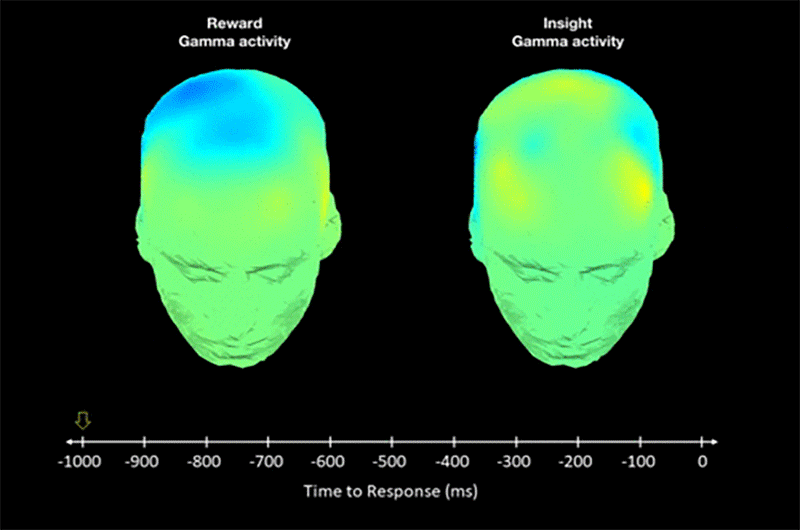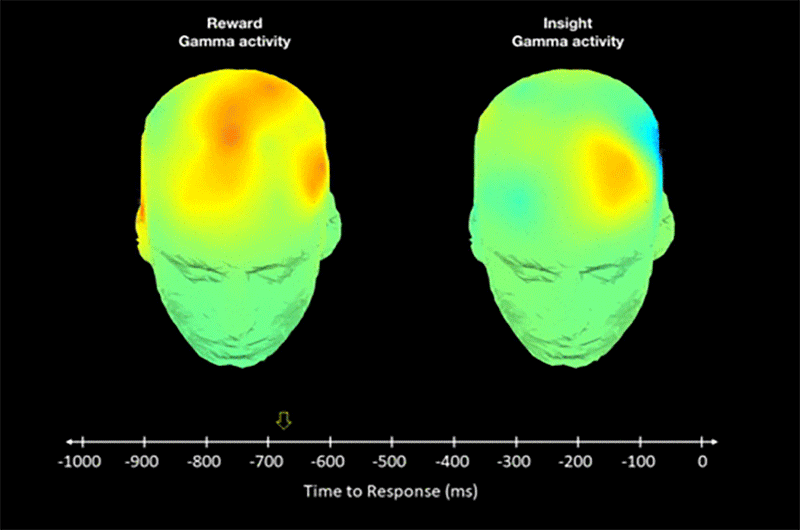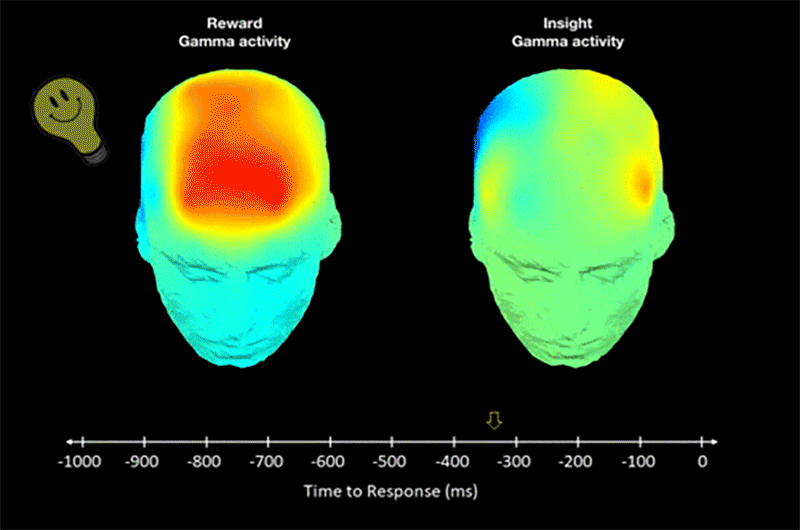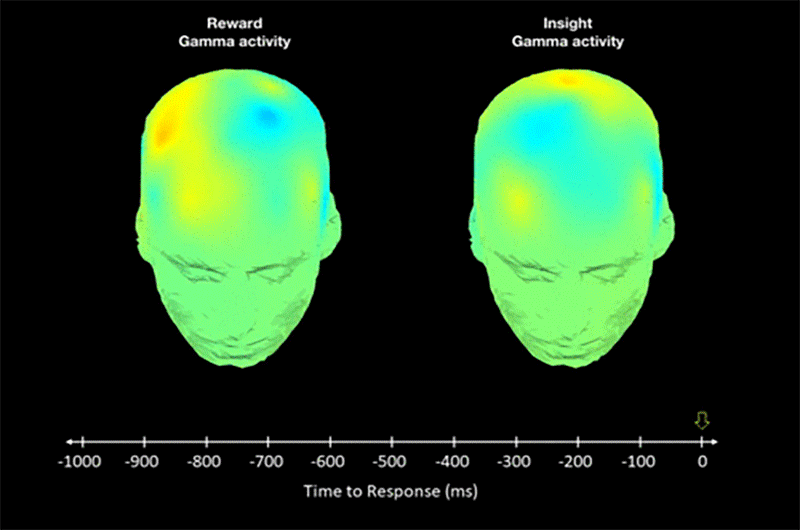
New psychology study shows that some people have increased brain sensitivity for “aha moments”.
The researchers scanned brains of participants and noticed orgasm-like signals during insights.
The scientists think this evolutionary adaptation drives creation of science and culture.
If you found this article interesting or informative and you’d like to share it you can do so from the following link: https://m.facebook.com/story.php?story_fbid=569991543629194&id=383136302314720
Research shows how “aha moments” affect the brain and cause the evolution of creativity.