Many emerging technologies rely on high-quality lasers. Laser-based LiDAR sensors can provide highly accurate scans of three-dimensional spaces, and as such are crucial in applications ranging from autonomous vehicles to geological mapping technologies and emergency response systems. High-quality lasers are also a key part of the high-speed, high-volume data centers that are the backbone of the internet.
When assessing the quality of a laser, researchers look to the noise in a laser’s frequency, or the number of times the laser’s light wave toggles in each second. Low-quality, “noisy” lasers have more random variations in those toggles, making them useless for systems that are meant to return accurate measurements or convey densely packed information.
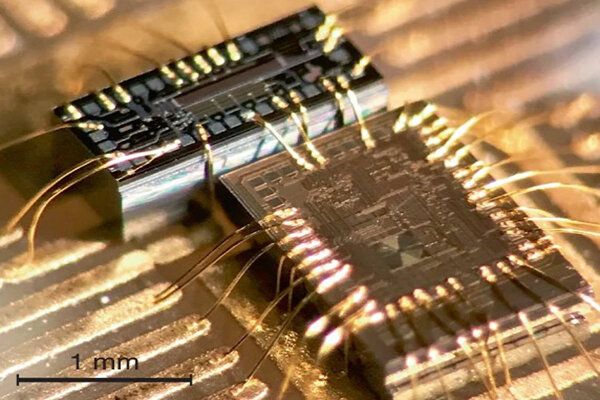
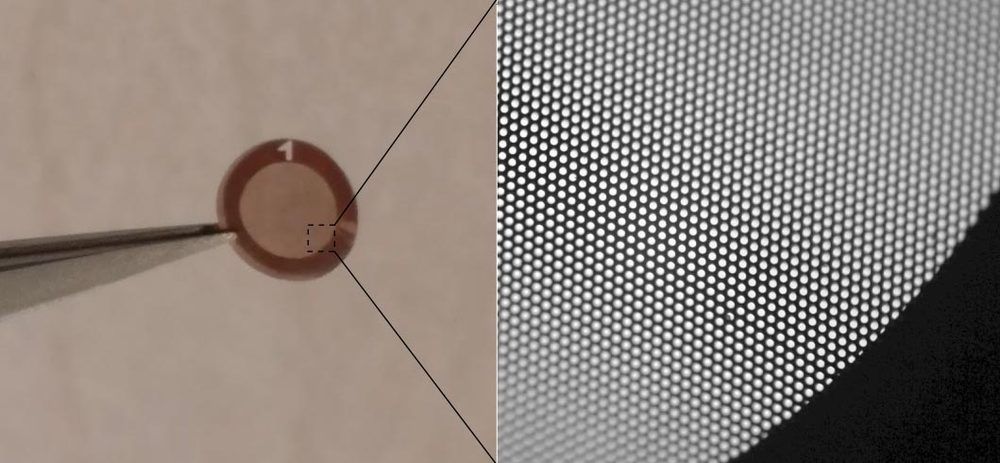
At present, lasers with adequately low frequency noise are bulky, expensive and an impractical choice for mass manufacturing. Penn Engineers have set out to solve this problem with a device called a “phase noise filter” that can turn low-cost, compact lasers into those suitable for LiDAR and more.