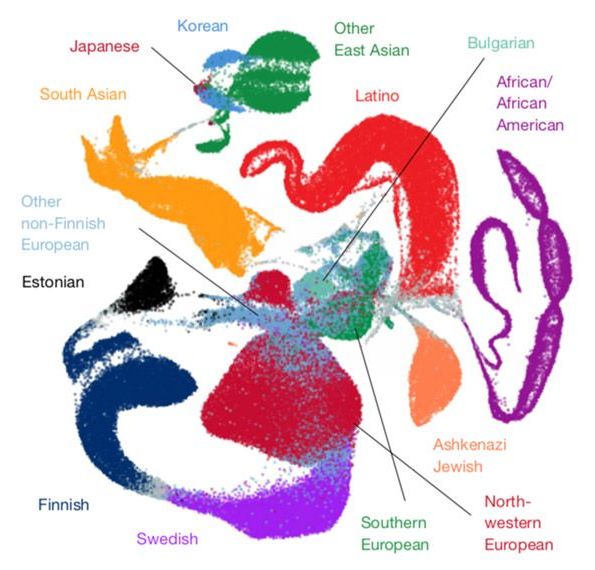
A trove of DNA sequences from 141,456 people — and counting — offers researchers an unparalleled look at genetic variation across the general population1,2. The resource has been helping researchers to identify variants that contribute to autism since it was released online about four years ago3,4.
The genomes of autistic people harbor hundreds of potentially harmful mutations. But to firmly connect a specific variant to the condition, researchers need to see if it is common among typical people — a sign that that variant may actually be benign.
In 2014, researchers debuted one of the first tools to probe the prevalence of a mutation in the general population. Known as the Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC), it contained 60,000 sequences of exomes — the protein-coding regions of the genome5.